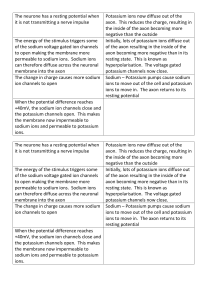
Name: _______________________________ Date: _____________________ Cell Transport Study Questions 1. Phospholipid bilayers are differentially permeable to different types of molecules. Which types of molecules can readily cross such bilayers without the help of transport proteins? Name some of the physical properties of molecules that prevent them from freely diffusing across lipid bilayers. 2. What are the two kinds of transport that can happen in the cell? 3. What is the difference between the two kinds of transport? 4. Which type of transport needs energy? Why do they need that energy (talk about the concentration gradient)? 5. Which type of transport does not need energy? Why don’t they need that energy (talk about the concentration gradient)? 6. What are the three types of passive transport the cell can go through? 7. What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? (mention concentrations) 8. Give ONE real world example of diffusion. 9. Why is it important for molecules to able to travel into and out off your body’s cells? Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided. 1. The energy needed for active transport is usually supplied by _________. 2. The sodium–potassium pump is a(n) ________ protein. 3. The concentration of sodium ions inside the cell is usually __________ than the concentration of sodium ions outside the cell. 4. The concentration of potassium ions inside the cell is usually _________ than the concentration of potassium ions outside the cell. 5. The sodium–potassium pump picks up ___________ ions outside the cell. 6. The sodium–potassium pump releases ___________ ions inside the cell. Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 7. Explain why proteins and polysaccharides cannot diffuse through the membrane like water does. 8. How do sodium–potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells? 9. Illustrate endocytosis and exocytosis and explain the steps for each process.