AP Psychology Review
advertisement

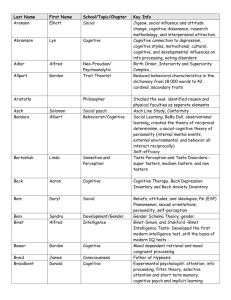
AP Psychology Review Directions: In Pairs see if you know the difference between these commonly confused pairs. The answers to almost all of them are in order in the beginning Independent Variable vs. Dependent Variable Experiment Group vs. Control Group Left Brain vs. Right Brain Corpus Collosum vs. Cerebral Cortex Sympathetic Nervous System vs. Parasympathetic Neurotransmitters vs. Hormones Lateral Hypothalamus vs. Ventromedial Hypothalamus Broca’s Area vs. Wernicke’s Area Identical Twins vs. Fraternal Twins Afferent Neurons vs. Efferent Neurons Assimilation vs. Accommodation Concrete Operations vs. Formal Operations Sensation vs. Perception Rods vs. Cones Classical Conditioning vs. Operant Conditioning Primacy Effect vs. Recency Effect Proactive Interference vs. Retroactive Interference Implicit Memory vs. Explicit Memory Recall Memory vs. Recognition Memory Algorithms vs. Heuristics Representative Heuristics vs. Availability Heuristics Phonemes vs. Morphemes Fluid Intelligence vs. Crystallized Intelligence Validity vs. Reliability Achievement Test vs. Aptitude Test Intrinsic Motivation vs. Extrinsic Motivation Theory Y vs. Theory X Internal Locus vs. External Locus of Control Type A vs. Type B Naturalistic vs. Laboratory Observations Negative Reinforcement vs. Punishment Psychotherapy vs. Psychoanalytic Schizophrenia vs. Dissociative Identity Disorder Sensory vs. Motor Neurons Positive vs. Negative Correlation Obsession vs. Compulsions James-Lange vs. Cannon-Bard Nature vs. Nurture Random Sample vs. Random Selection CNS vs. PNS Absolute vs. Difference Threshold Authoritarian vs. Authoritative Famous Contributors to Psychology and Experiments In pairs try to guess what famous study and/or contribution they made to psychology. Hawthorne Effect- humans being watched behave differently Jean Piagetstages of COGNITIVE Development Erik EriksonPsychoSOCIAL development (identity. Role confusion) Lawrence Kohlberg- stages of MORAL development Carol Gilligancritic of Kohlberg, girls/boys differ in moral development Konrad LorenzImprinting, attachment of ducks with critical period Harry HarlowAttachment, monkeys preferred cloth mother Mary AinsworthStrange Situation, Secure/Insecure Attachments Eleanor Gibson Visual Cliff, crawling infants have depth perception Hubel and Weisel Feature Detectors, specific cells for angles, lines, motion Ernest Hilgard Hidden Observer in Hypnosis, Dissociation causes loss of sensation Ivan Pavlov Classical Conditioning John B. Watson Behaviorism, Little Albert B.F. Skinner Operant Conditioning, Skinner Box, reinforcement/punishment Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory, Bo-bo Doll, Social-Cognitive, self-efficacy Wolfgang Kohler Insight Learning- Cognitive component to operant, Chimps stack boxes TolmanLatent Learning, rats run maze create cognitive maps. Binet1st intelligence test, concept of mental age Stanford-Binet Terman, most widely used intelligence test, IQ formula James and Lange Physiological arousal followed by experiencing emotion Cannon and Bard Physical Arousal/emotion same time Schachter-Singer (Lazarus Experiment) physical arousal plus cognitive label then emotion Maslow and Rogers Humanists, unconditional positive regard, client centered therapy Aaron Beck Cognitive Therapy, change thinking Albert Ellis Cognitive Rational Emotive Therapy, challenge logic of patient Eysenck and Myers-Briggs Trait Perspective- introvert/extrovert Hans-Selye Bodies response to stress (ARE)- Alarm, Resistance, Exhaustion Solomon Asch Conformity, line study Stanley Milgram Obedience- 63% go all the way Muzafer Sherif Superordinate goals to alleviate prejudice Elizabeth Loftus Constructive Memory, misinformation effect, false uncovered memories Martin Seligman Positive Psychology, Learned Helplessness Noam Chomsky Cognitive Linguist, Language Acquisition Device Benjamin Whorf (Linguistic Hypothesis)- words affect In pairs write as many terms/names/philosophies associated with the following perspectives: Humanist, Psychoanalytic, Cognitive, Behavioral. Eclectic (using all perspectives to explain behavior is most common)