Biology 1 – Study Guide for Test # 1
advertisement

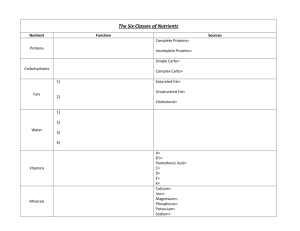
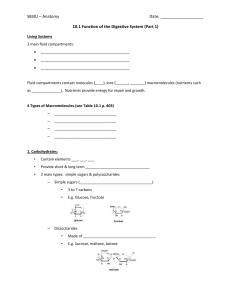
Biology 1 – Study Guide for Test # 1 Chapter 1 – Introduction: Biology Why Study Science? What are the 5 reasons Jared Diamond says everyone should study science? What is Biophilia? What is science? What is the scientific method? What is the difference between a hypothesis, theory and a law? Science does what to possibilities? What is evolution? Why is Intelligent Design or Creationism not usually taught in science classes? What is life? What are the seven properties of life? What is the smallest unit of life? Are Viruses alive? What are the two types of cells discussed in class? Know the two different hierarchies in biology. Chapter 2 – Chemistry, Water and pH Know the following terms: matter, element, molecule, and compound. Know the parts of an atom. Where are they each located? What charge do they have? What is their mass? Know how to read a periodic table. How many elements are there? How many are needed by life? What is CHNOPS? What is an atomic number mean? Mass number? What are isotopes? How are radioactive isotopes used? How do you make an atom “happy”? Know how many electrons can go into each orbital? What is an ion? (cation, anion) What are the different types of bonding? Know the examples from class. What are the seven properties of water given in class? What causes water to have all these properties? What is heat? Temperature? What is a solute? Solvent? Solution? What is hydrophobic? Hydrophilic? What is an acid? Base? Buffer? What is acid precipitation? What causes it? What types of damage does it do? Chapter 3 - Macromolecules What does organic mean to a biologist? What is a hydrocarbon? Know the different isomers discussed in class and why their shape is important. What is a monomer? Polymer? What is dehydration synthesis? Hydrolysis? Know why the different functional groups are important? Know the four macromolecules discussed in class. What is a simple sugar (monosaccharide? Disaccharide?) and complex sugars (Polysaccharide?) Know the examples given in class. What do all lipids have in common? What are the functions of lipids? What is a saturated fat? Unsaturated fat? Partially hydrogenated fat (trans?) Phospholipids? Steroids? What are anabolic steroids? What do they mimic? What damage can be caused by long term abuse? What is a protein made of? What types of bonds are formed? Know the 4 levels of structure seen in proteins? What are their shapes and what bonds are involved? What are the functions of proteins? What are nucleic acids? What are they made of? What are their functions? Chapter 31 – Animal Digestion and Nutrition Know the following terms: undernourished, overnourished, and malnourished. What is the nutritional requirement for you? Know the different essential nutrients discussed in class. (amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins and minerals). How many amino acids are essential? Why? What is the difference between fat soluble and water soluble vitamins? Know which type or which? Know the examples for the essential minerals given in class. Know the food pyramid. Know the difference between the sources for simple and complex carbohydrates. What is the difference between glycemic load and glycemic index? What are the ideal numbers for each? How do you read a nutrition label? Know the parts of the digestion system and their functions. Know the accessory glands and what they do? What is peristalsis? Sphincters? What is bolus? Acid chime? Feces? Where is the initial and main site for macromolecule digestion? What is the difference between carnivore and herbivore digestive tracts? Chapter 4 – The Cell What is the cell theory? What limits cell size? What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? What are the two theories on how eukaryotic cells evolved? Know the following organelles and their functions: nucleus, nucleolus, cytoplasm, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles/vesicles, mitochondrion, chloroplast, cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrosomes, gap junctions and plasmodesmata. What is the endomembrane system? What organelles make this up? What is its function? Chapter 5 – Membrane Structure and Function Know the Fluid Mosaic Model. What are the four main components of a membrane and what are their functions? What are integral proteins? Peripheral proteins? What are glycoproteins? Glycolipids? Know the following definitions: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport, concentration gradient, solution, solvent, solute, osmolality (hyperosmotic, isosmotic, hypoosmotic). Know what happens to plant and animal cells when they gain and lose water (crenate, turgid, etc). What is endocytosis (phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated)? Exocytosis? Chapter 8 – An Introduction to Metabolism What is energy? What does the word metabolism mean? What are catabolic and anabolic pathways? What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy? What are the laws of thermodynamics? What are endergonic and exergonic reactions? What is energy coupling? What is ATP? What is actually happening when we move energy around by ATP? What is equilibrium? What is an enzyme? What do they actually do? What is activation energy? What is an active site? Substrate? What are coenzymes? Cofactors? What is an induced fit? What is enzyme inhibition? What are the two types of inhibitors? Know the examples given. What are allosteric sites?