Photosynthesis Work Package II
advertisement

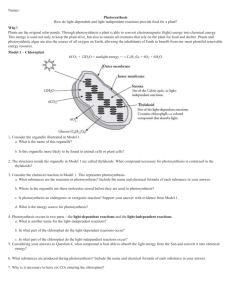
Photosynthesis Work Package II The Reactions of Photosynthesis 1. List the three major events that occur in photosynthesis. - absorption of light energy - conversion of light energy into chemical energy - storage of chemical energy in sugars 2. Draw the diagram summary of the reactions of photosynthesis. Include any labels. 3. What are the two parts of photosynthesis called? 4. Record the overall reaction of photosynthesis. 5. What is the purpose of the light reactions? 6. Where, in the chloroplast, do the light reactions take place? 7. What is a “photosystem”? How are the two photosystems related? 8. What happens to a chlorophyll molecule and accessory pigments when they are struck by light? 9. If photosystem II supplies the electrons lost by photosystem I, what supplies electrons to replace those lost by photosystem II? 10. In order for the above to happen, water molecules must be split apart. Write out the equation showing the breakdown of water. * When water is broken down due to the action of light we call this photolysis 11. Referring to the above equation, what happens to: i) the oxygen atoms ii) the electrons (e-) iii) the protons (H+) 12. In summary, what events occurred in the light reactions? 13. What are the three products that result from the light reactions? 14. Why is the Calvin Cycle sometimes called the dark reactions? 15. Where, in the chloroplast, do the dark reactions take place? 16. What, in general, occurs in the Calvin Cycle? 17. The Calvin Cycle depends on the presence of a 5-C molecule called _________________. (internet) 18. This 5-C molecule combines with a molecule of ________________ to form a 6-C molecule. 19. This 6-C molecule will then immediately split into two, 3-C molecules. These 3C molecules pick up hydrogen and phosphate groups to become a type of sugar molecule. Where do the hydrogens come from? Where do the phosphate groups come from? 20. It takes three CO2 molecules (ie: three turns of the Calvin Cycle) to make six of the 3-C sugar molecules (PGAL). What happens to five of these sugar molecules? 21. A 6 C sugar molecule leaves the Calvin Cycle and can have one of several different outcomes. What are these outcomes? 22. Summarize in one sentence, the overall result of the Calvin Cycle.