Curriculum Information Year 3 - St Helen's Catholic Junior School
advertisement

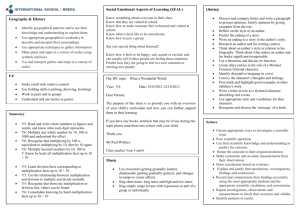
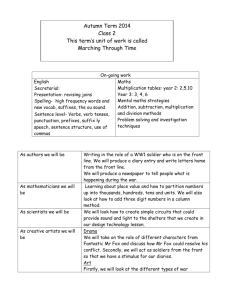
St Helen's Catholic Junior Academy Curriculum Information Year 3 At St Helen’s Catholic Junior Academy all children have access to a broad and balanced curriculum. Subjects are taught using a range of resources, including I.C.T. and cross-curricular links. Structured daily lessons are provided to teach English and Mathematics. Children are taught to understand the relevance of what they are learning and to apply their learning in different contexts. Using and applying their literacy and mathematics knowledge and skills in other subjects and contexts will help to reinforce confidence. English In English the learning objectives are grouped into the following strands: speaking, listening, discussion, drama, reading, spelling, word structure, sentence structure, punctuation, presentation and handwriting. Children will learn: To read using tone and volume To keep conversation, explain and give reasons for expressing views, agree or disagree in discussion To learn specific vocabulary To read texts in order to answer questions (comprehension) To spell high and medium frequency words To recognise a range of prefixes and suffixes To spell unfamiliar words using known conventions and spelling rules To explore different texts To create stories using beginning, middle and ending To select and use a range of descriptive vocabulary To compose sentences using verbs, nouns and adjectives To use exclamation marks and speech marks To write legibly using cursive handwriting, with correct size and proportion of letters and spacing within and between words. Mathematics The children will learn to: Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time, choosing and carrying out appropriate calculations Read, write and order whole numbers to at least 1000 and position them on a number line; count on from and back to zero in single-digit steps or multiples of 10 Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 in different ways (e.g. 125 = 100 + 20 + 5) Round two-digit or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and give estimates for their sums and differences Read and write proper fractions (e.g. 3/7, 9/10),interpreting the denominator as the parts of a whole and the numerator as the number of parts; identify and estimate fractions of shapes; use diagrams to compare fractions and establish equivalents (e.g. ½ = 2/4) Know and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 times-tables and the corresponding division facts; recognize multiples of 2, 5 or 10 up to 1000 Use knowledge of number operations and corresponding inverses, including doubling and halving, to estimate and check calculations Develop and use written methods to record, support or explain addition and subtraction of two-digit and three-digit numbers Multiply one-digit and two-digit numbers by 10 or 100, and describe the effect Use practical and informal written methods to multiply and divide two-digit numbers (e.g. 13 × 3, 50 ÷ 4); round remainders up or down, depending on the context Understand that division is the inverse of multiplication and vice versa; use this to derive and record related multiplication and division number sentences (e.g. 2 x 3 = 6, 3 x 2 = 6, 6 ÷ 2 = 3 and 6 ÷ 3 = 2) Find unit fractions of numbers and quantities (e.g. 1/2, 1/3, 1/4 and 1/6 of measurements) Relate 2-D shapes and 3-D solids to drawings of them; describe, visualise, classify, draw and make the shapes Draw and complete shapes with reflective symmetry; draw the reflection of a shape in a mirror line along one side Read and record the vocabulary of position, direction and movement, using the four compass directions to describe movement about a grid Use a protractor to draw right angles and to identify right angles in 2-D shapes; compare angles with a right angle; recognise that a straight line is equivalent to two right angles Know the relationships between kilometres and metres, metres and centimetres, kilograms and grams, litres and millilitres; choose and use appropriate units to estimate, measure and record measurements Read, to the nearest division and half-division, scales that are numbered or partially numbered; use the information to measure and draw to a suitable degree of accuracy Read the time on a 12-hour digital clock and to the nearest 5 minutes on an analogue clock; calculate time intervals and find start or end times for a given time interval Answer a question by collecting, organising and interpreting data; use tally charts, frequency tables, pictograms and bar charts to represent results and illustrate observations; use computing to create a simple bar chart Use Venn diagrams or Carroll diagrams to sort data and objects. Religious Education (R.E.) The children learn about the Catholic faith and values through the “Come and See” programme. They also participate in assemblies, masses and class-based worship, where they are encouraged to develop their individual spirituality and reflect on what they have learned. Themes for this year are: Autumn Domestic Church- Family- Homes Baptism/Confirmation- Belonging- Promises Advent/ Christmas- Loving- Visitors Spring Local Church- Community- Journeys Eucharist- Relating- Listening and Sharing Lent/Easter- Giving- Giving all Summer Pentecost- Serving- Energy Reconciliation- Inter-relating- Choices Universal Church- World- Special Places Science Science is taught through four strands. These are Scientific Enquiry, Life Processes and Living Things, Materials and their Properties and Physical Processes. Children will learn to: Identify different materials and their properties and plan investigations to test materials Identify common rock types and their uses, and recognise natural and man-made materials Compare rocks and find ways of testing them Learn how soil is formed, recognise different soil types and plan investigations to test soils Recognise different types of magnets and their properties Recognise the relationships between light sources and the formation of shadows Recognise different food groups, how to eat healthily and how to look after their teeth Learn what plants need to grow well History History is taught from a range of perspectives. Different information sources are used to investigate the past. In year three the children study: Why have people invaded and settled in Britain in the past? A Roman case study Why do people move away from where they are born? Who invaded and settled in Britain a long time ago? Who were the Celts? Who were the Romans? Who was Boudicca? What happened in AD60? What were the short-term and long-term results of Boudicca’s revolt? How did the Romans change Britain when they settled here? Why have people invaded and settled in Britain in the past? A Viking case study Why did the Vikings travel from their homelands and where did they go? How did the Vikings travel so far from their homelands? Why did the Vikings come to Britain to raid and to stay? Why were monasteries good places to raid? What evidence is there that the Vikings settled in Britain? Where did the Vikings finally settle in England? The children will also have a ‘Roman Day Workshop’ run by ‘Portals to the Past’ during the autumn term. They will act like Romans and Celts for a day finding out more about Celtic and Roman ways of life and Boudicca’s revolt. Geography Geographical skills are used to find out about different places, physical and human features within the environment, and the ways people and the environment affect each other. The children study: Identify Brentwood and London on a map of the United Kingdom, and the United Kingdom on a world map The outline of the United Kingdom and understand the United Kingdom as an island The capitals of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland Understand the United Kingdom as part of Europe and the European Community The outline of Europe Place countries studied in the year three curriculum on a map The location of Italy on a map and learn about the language spoken, food eaten and main religion The Vatican City The artist Leonardo Da Vinci Through the topics Village Settlers and Weather around the world children study: Where early settlers chose to settle and how these settlements can be identified? What villages look like today How isolated farms and houses are connected to villages How settlements develop Where hot and cold places are located on a world map Where people go on holiday and how to get there What a place is like, how it is similar to and different from Brentwood, what the weather will be like and how it will affect any activities to be carried out Children create suitcase project based on our topic ‘Weather Around the World.’ Computing The children have the opportunity to utilise computer applications to support their work in other subjects, as well as: Communicate messages by using a combination of graphics and text Explore and develop musical ideas using simple software to explore various musical and sound effects Use a database to answer simple questions Understand that computer simulations can represent real and imaginary situations Use e-mail (electronic mail) to send and receive messages Design and Technology (D.T) /Art The children will: Design and make a stable, free-standing photograph frame Investigate patterns from different times and cultures and use these to develop their own designs Investigate print-making techniques Explore ways of combining and organising shapes, colours and patterns Make a model of a sculpture for a site in the school Music The children are taught to play the recorder, perform music in groups, and evaluate their own musical contribution within the group. Autumn Term Singing skills: learn how to use the voice correctly and with confidence; accuracy of pitch, breathing, articulation; including a weekly hymn practice Recorder: Introducing/Re-introducing the descant recorder & notation: - Learn/Revise G, A, B - Developing note- reading skills Exploring rhythm, pulse, pitch, pentatonic scale, ostinato - Exploring pulse and rhythm patterns on African drums - Creating ostinato patterns (repeating patterns) - Creating melodies on tuned percussion, using the pentatonic scale (5 note scale) Christmas preparation Singing together in unison and harmony, understanding how to achieve a quality performance Spring Term Singing skills: learning how to use the voice correctly and with confidence; accuracy of pitch, breathing, articulation; including a weekly hymn practice Recorder: Revise notes G, A, B and learn low E and D - Developing note-reading skills Exploring arrangements: learning how instruments can be used to accompany songs Preparation for Stations of the Cross Singing together in worship in unison and harmony Summer Term Singing skills: learning how to use the voice correctly and with confidence; accuracy of pitch, breathing, articulation Recorder: Reinforce knowledge of notes and rhythm+ learn high C Exploring descriptive sounds: how music can be used to describe things/characters (i.e., Prokofiev’s ‘Peter & the Wolf’) - Creating our own descriptive character music using the elements of pitch (high/low), tempo (speed), dynamics (loud/soft) - Learning about the instruments of the orchestra Physical Education (P.E.) The children experience P.E. through five key areas. Dance. They will create and perform dances to express ideas and feelings through movement. Games. They play and invent games to score points or goals against others – either individually or in small teams; Gymnastic Activities. They make up and perform sequences of movements, still shapes and balanced poses, both on the floor and using apparatus; Swimming. They will learn strokes such as front crawl, back crawl and breast stroke. They will also learn safety rules so that they can be confident in or near water. Athletics. They will run, jump and throw, aiming to beat their own records, and competing against others. PSHE/Citizenship The children are taught personal skills, such as how to: Be more independent, confident and mature; Recognise their own achievements and mistakes; Share their views, and discuss what is fair/unfair, right/wrong. Set themselves goals, and try to achieve them; Keep themselves safe and healthy as they grow. The children also learn social skills: Think about how the choices they make, affect other people, and the environment; Consider the different groups within society, and how to get on with them; Think of how and why rules are made. These skills are taught through the themes of Taking Part (Developing Skills of Communication and Participation), Choices, and Animals and Us. Sometimes the skills will be taught in special times set aside for the subject (e.g. class “circle time” and R.E. reflection time). Homework Homework will consist of: Spellings and sentences A piece of longer writing on occasion which may be related to any of the core or foundation subjects Numeracy work related to the topic of study or mental arithmetic Reading Music (practise the recorder). Year 3 Homework Guidelines Homework Spellings/Sentences Day given Monday Topic Mental Arithmetic Reading Monday Wednesday Daily Hand In Wednesday Tests on Friday Following Monday Friday Daily Expectations A minimum of twenty minutes each night should be spent on homework. Homework should be completed in the homework books provided unless otherwise stated. Pencil should be used for all written work and mathematics. All homework is to be neatly presented and include a date and title underlined with a ruler. For English homework, children are often asked to write sentences using their spelling words. Sentences should be complex and correctly punctuated using capital letters and full stops, question marks or exclamation marks to correctly end each sentence. All pieces of homework are to be initialled by a parent or guardian. Children also need to read regularly to a parent or guardian, and independently for at least thirty minutes each night. Reading books will not be changed unless an adult has confirmed that the book has been finished. Additional Information Useful Websites for Mathematics Snappy Maths - http://www.snappymaths.com/ - any of the areas but particularly addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, counting, place value, number patterns and sequences and ordering and comparing numbers. Can print off various worksheets to complete for each of these areas. Woodlands Maths - http://resources.woodlands-junior.kent.sch.uk/maths/ - has various sections which will provide practice, especially on times tables and mental maths. Has lots of games which reinforce learning by promoting enjoyment and interaction through mathematical activities. BBC Bitesize - http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks2/maths/ - covers all areas of the KS2 curriculum. Number sections would be most appropriate at the moment, mainly the four operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division), mental maths, place value and number patterns. Each section gives explanations, has interactive activities and finishes with a quiz to see what children have learnt. Crickweb - http://www.crickweb.co.uk/ks2numeracy.html - various sections covered. Mad for Maths - http://www.mad4maths.com/ - various activities http://www.mad4maths.com/multiplication_table_math_games/ (this link will take you directly through to multiplication games) IXL - http://uk.ixl.com/math/year-3 – breaks all the sections of the Year 3 Mathematics curriculum down with activities based upon each objective. This is generally a paid subscription website but you can complete a few questions each day for free – very useful as children complete activities and get an instant response to their answers, along with helpful advice of where they have gone wrong if they make any mistakes. A 100 number square would help with addition and subtraction, similarly, a multiplication square would help with learning multiplication facts (there is already one in the back of the blue homework book). Using a multiplication square and focusing on a particular times table and colouring all the numbers which appear within it would also support learning of the multiplication facts. Using physical models to represent multiplication and division would also help, for example, using Lego bricks or suchlike to share out numbers into equal groups. Children can then group and regroup depending on which times table they are working on. You could also test their knowledge by taking some away and asking how many are missing or how many more they need to add to make up the multiplication/division fact. This will help to reinforce the patterns and gives them a visual model to work from. In relation to learning times tables, one way which has been successful in the past with other children I have taught is to use a pack of playing cards and focus on one times table (for example, 2s) and then shuffle the cards, turn one over and then the child has to tell you what 2 x that number is. This is a great way of improving their recall of multiplication facts and they love it as they see it as a game rather than simply something they need to learn. Aces represent 1, Jack becomes 10, Queen becomes 11, King becomes 12. You can also purchase multiplication/division facts flash cards from retailers such as Toys R Us, WH Smith, Amazon etc but there are also free ones available to print online (use Google search facility to find sites such as http://www.multiplication.com/resources/flash-cards). There are so many enjoyable ways to learn times tables, Youtube has lots of popular multiplication songs, there are various apps on iPads or iPhones (for example, Multiplication for Kids, My Times Tables, Maths for Kids), tailored to times tables and the internet has countless resources. You can also buy multiplication CDs/download from Amazon and iTunes – these are really helpful because the child listens and remembers the tune along with the words – you’d be surprised how effective this is even after only a few listens! I hope this information has been useful. Kind regards Year 3