PS250 PHYSICS III FOR ENGINEERS – Exam 2 Material Summary
advertisement

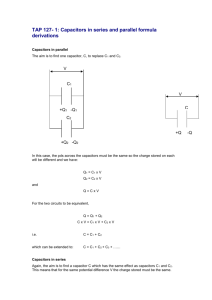
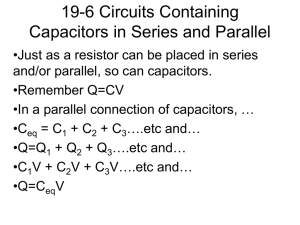
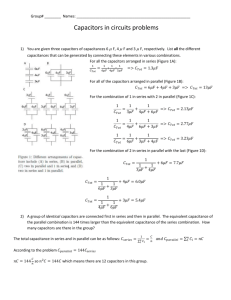
PS250 PHYSICS III FOR ENGINEERS – Exam 2 Material Summary Chapter 24 Learning Objectives: Understand concept of capacitance, and mathematical relation between charge, potential difference, and capacitance. Calculate capacitance for parallel plate, cylindrical, and spherical capacitors. Calculate equivalent capacitances for parallel and series capacitors. Calculate and understand energy storage in capacitors. Understand dielectric constant and dielectric strength. Lecture 10-11. Mastering Physics Assignment #4; Problems: 24.9, 12, 13, 17, 21, 30, 53, 66, 67, 69. 24.1 – Capacitors and Capacitance Board examples: Calculation of capacitance for coaxial, spherical, and parallel-plate capacitors. 24.2 – Capacitors in Series and Parallel Board examples: Multiple parallel plate capacitors, combining series/parallel capacitors. 24.3 – Energy Storage in Capacitors and Electric Field Energy Understand physical meaning + Board Examples: derivation of stored energy in field. 24.4 – Dielectrics Board Examples: Effects of dielectric materials, change in capacitance, energy storage, potential. Chapter 25 Learning Objectives: Understand concept of current (I) and current density (J). Understand physical basis for resistivity and resistance, and how they are related. Understand Ohm’s law in terms of potential difference and electric field in the conductor). Understand concept of electromotive force for ideal (r=0) and realistic (r≠0) sources (i.e., batteries, etc.). Understand simple circuits involving resistors and emf sources. Understand power and energy in circuits (i.e., P=IV) Lecture 12-14. Mastering Physics Assignment #5; Problems: 25.3, 13, 18, 29, 41, 62, 69. 25.1 – Current Understand definitions of current, drift velocity, current density. 25.2 – Resistivity Board Examples: Ohm’s Law in vector and scalar forms, definitions of resistivity. 25.3 – Resistance Board Examples: Copper wire examples (choosing required dimensions). 25.4 – Electromotive Force and Circuits Board Examples: Wire examples, ideal/non-ideal source examples, pencil lead example. 25.5 – Power and Energy Board Examples: Max power transfer example, general examples with resistors, short circuit examples. Chapter 26 Learning Objectives: Understand parallel and series combinations of resistors, and be able to calculate equivalent combinations. Understand Kirchhoff’s Rules, and be able to apply them to determine potential differences across and currents through devices in a simple circuit. Understand R-C circuits, and be able to obtain time-dependent expressions for i(t), q(t), and v(t) during capacitor charging and discharging. Lecture 14-15. Mastering Physics Assignment #6-7; Problems: 26.7, 10, 18, 19, 25, 27, 41, 45, 48, 66. 26.1 – Resistors in Series and Parallel Board Examples: Pencil Lead example, circuit combination example, please also understand the homework! 26.2 – Kirchhoff’s Rules Board Examples: Simple 2-Loop analysis problem (also understand the homework problems!) 26.4 – R-C Circuits Board Examples: Detailed On-Board Derivations, examples 26.12, 26.13, also a Quiz. Chapter 27 Learning Objectives: Understand the geometry of magnetic fields and the concept of poles. Calculate force on moving charged particles due to magnetic fields. Understand magnetic flux, and Gauss’s laws. Calculate particle motions (cyclotron frequency and radii) in magnetic fields. Understand how a velocity selector works. Calculate magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor. Lecture 16-17. Mastering Physics Assignment #7; Problems: 27.4, 6, 15, 23, 25. PS-250-07DB: Fall, 2015. Exam #2 Material Summary. 1/2 PS250 PHYSICS III FOR ENGINEERS – Exam 2 Material Summary 27.1 – Magnetism Understand “dipole” model of Earth’s field (i.e., what is really “North” and “South”). 27.2 – Magnetic Field and Force Board Examples: Initial Force on Proton. 27.3 – Magnetic Flux Board Examples: Quick Conceptual Discussion (i.e., that it is zero for a closed surface!!!) 27.4 – Motion of Charged Particles Board Examples: Proton launched from origin, radius of orbit, period of orbit, helical trajectories. 27.5 – Applications of Motion of Charged Particles Board Examples: Velocity Selector / Mass Spectrometer (Conceptually). PS-250-07DB: Fall, 2015. Exam #2 Material Summary. 2/2