Chapter 19 Notes 19C
advertisement
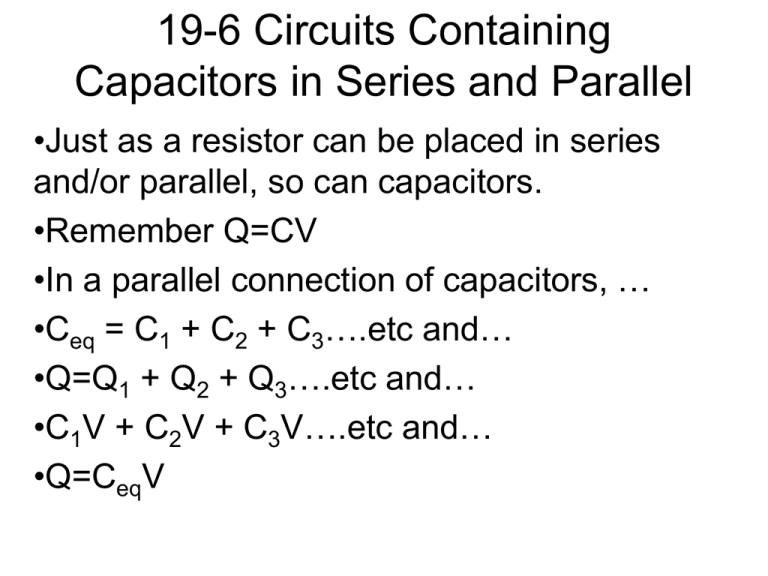
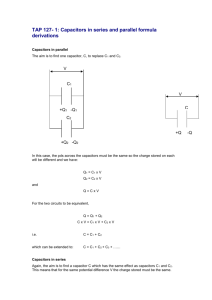
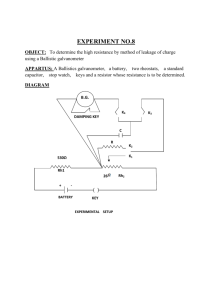
19-6 Circuits Containing Capacitors in Series and Parallel •Just as a resistor can be placed in series and/or parallel, so can capacitors. •Remember Q=CV •In a parallel connection of capacitors, … •Ceq = C1 + C2 + C3….etc and… •Q=Q1 + Q2 + Q3….etc and… •C1V + C2V + C3V….etc and… •Q=CeqV 19-6 Circuits Containing Capacitors in Series and Parallel (cont’d) • In a series connection of capacitors, 1/Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2 +1/C3 ……and…. Q/Ceq = Q/C1 + Q/C2 +Q/C3 ……and…. V= V1+ V2 + V3 …… See Page 569 diagrams See Example 19-9 p570 19-8 Circuits Containing a Resistor and Capacitor • • • • RC circuits have resistors and capacitors. See diagram p570. V= e(1-e-t/RC) The product of the resistance and capacitance is called the time constant t of a circuit. t=RC When a circuit does not have a EMF, but is charged and the charge is released across a resistor, use V=V0et/RC See p571 diagram 19-18a See Example 19-10 p 572 19-8 Heart Pacemakers • One use of RC circuits is a pacemaker. • A pacemaker can make a stopped heart start again…our heart has a natural pacemaker 19-9 Electric Hazards; Leakage Currents • Most people can feel 1mA of current. • Currents above 10mA cause severe contraction of the muscles, and a person may not be able to release the device and death from paralysis of the respiratory system may occur. • If 70mA or more passes through the torso or heart region for more than a second, ventricular fibrulation may occur and cause death. • Dry skin has a resistance of 104 to 106W ... Wet skin has 103 W . I=V/R means 120 V could be lethal. • See p 574 19-10 DC Ammeters and Voltmeters • An ammeter measures current and a voltmeter measures potential difference. • The crucial part of either is the galvanometer…. • A galvanometer works on the principal of the force between a magnetic field and a current-carrying coil of wire. • Some of the meters on your car’s dash are connected as galvanometers. • The full-scale sensitivity Im, is the current needed to move the needle to the full-scale reading. • An ammeter, represented by the symbol -A- consists of a galvanometer –G- in parallel with a resistor called a shunt resistor…with resistance R, while the galvanometer has resistance r. (See p 575) See Example 19-12 and 19-13. HOMEWORK • P 582 36-43,55-57, 60 Due Wednesday • Test Thursday