Laryngeal Tremor
advertisement

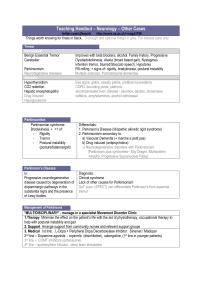
Laryngeal Tremor 92-9-24 R3 郭彥君 1. Definition Tremor :An involuntary , approximately rhythmic, roughly sinusoidal movement. 1983 Mardsden et al: 4 types of human action tremor a. Enhanced physiologic tremor: fast(8-12 hz), fine, postural b. Classical essential tremor: lower frequency, greater amplitude c. Classical essential tremor with disabling in degree d. Symptomatic essential tremor: associated with other neurologic disorders Vocal tremor tremor: tremulous voice,wavy voice,quavering speech Rapid decrease and increase in loudness and pitch or incomplete phonation stoppages 2.Long-term phonatory instability accompanying vocal tremor A.Essential tremor: ◆Prevalence: 4-60 per 1000 people, elderly persons, upper limbs and head most involved, 4-20 % with vocal tremor ◆Family history (+),AD ,cause unknown (suggest olivocerecellar tract abnormal by PET*) ◆ Absent at rest, maximal during maintenance of posture, attenuated during movement, accentuated at the termination of movement ◆ Pitch beaks and voice arrest(similar to SD) ; vertical oscillations in the larynx , predominant involvement in TA muscles ◆ Greater with emotional stress and fatigue ◆ Treatment: propranolol, clonazepam+propranolal+diszepam, thalamotomies, chronic electrical stimulation of the thalamic nucleus , speech therapy ,injection of botulism toxin (reduce laryngeal airway) B.Parkinson’s disease ◆Cell death in substantia nigra ◆ Resting tremor (5-7 Hz),muscle rigidity,bradykinesia,loss of postual reflex , “pill-rolling” tremor ◆ Sluggish articulation, monotone voice,decreased loudness(vocal fold: adynemic and bowed ◆ Treatment: Levodopa Fundamental frequency↑, jitter, soft phonation(noise) index↓ Speed quotient, shimmer↓, SPL↑ C.Spasmodic dysphonia ◆Action-induced laryngeal motion disorder(focal dystonia ,not a spasmodic disorder) , irregular tremor, imply psychologic etioligy ◆ Increasing vocal fatigue, spasmodic constriction of throat muscles, pain around the larynx ,crescendo onset prior and during phonation,drcrascendo with offset of voicing ◆ 1985 Aroson: Adductor involved(spastic dysphonia) ,abductor involved (whispering dysphonia) <pseudo-abductor spasmodic dysphonia> ◆ Treatment: Botulism toxin injection D. Palatophryngeal myoclonus ◆slow form of tremor(1-4 hz) nonsinosoidal periotic tremor ◆ Involve pharynx,larynx,diaphragm,eye muscles ,rhythmic movement occur in both phonation and rest ◆ Tremulous voicemvoice arrest,clicking or popping sound in the ear ◆ Disorder interrupt the central tegmental tract, usually due to brainstem infarct or idiopathic degeneration ◆ Treatment :serotonin precursors,carbamazepine,clonazepam but usually resist to treatment E.Cebeller lesion ◆vocal strain (like SD), dysarthria, scaning speech ◆ Combined with intention tremor, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, ataxia, nystagmus 3. Acoustic characters of vocal tremor ☆Higher pitch phonation rapid rate for both amplitude and frequency modulation ☆Louder phonation amplitude modulation is faster ☆Low-pitched phonation decreased the extent of amplitude tremor 4. Hypotheses of tremor : (1) Central oscillator hypothesis : similar EMG activity across muscles affected by tremor , stable frequency of tremor ( vocal tremor is not consistency to EMG activity in pairs of laryngeal muscles)4 (2) Peripheral oscillator hypothesis: change in frequency of tremor increase muscle load , entrainment of tremor frequency to the frequency of imposed muscle ,reflex response to stretch (3) Originate from multiple regions of brain : not a single frequency (4) Abnormal enhancement of normal physiologic tremor: essential limb tremor is produced by central oscillator but enhanced by the connected reflex Reference: 1. Diagnosis and treatment of voice disorder /John S Rubin 1995 [et al.] 2. Neurologic disorder of the larynx/Andrew Blitzer[et al.] 3. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery/Charles W.Cummings 4. Synchrony of laryngeal muscle activity in persons with vocal tremor. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003 Mar;129(3):313-8. Finnegan EM [et al.] 5. The influence of pitch and loudness changes on the acoustics of vocal tremor. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2002 Oct;45(5):879-90 Dromey C [et al.] 6. The treatment of essential voice tremor with botulinum toxin A: a longitudinal case report.J Voice. 2000 Sep;14(3):410-21. Warrick P [et al.] 7. Botulinum toxin for essential tremor of the voice with multiple anatomical sites of tremor: a crossover design study of unilateral versus bilateral injection. Laryngoscope. 2000 Aug;110(8):1366-74. Warrick P [et al.] 8. The effect of levodopa on vocal function in Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2001 Mar-Apr;24(2):99-102. Sanabria J [et al.]