AHD Keezer Feb 4 Midbrain
advertisement

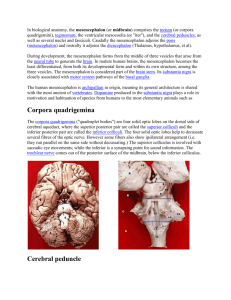
A Mesencephalon Decathlon Jim Thorpe Gold medal in the 1912 Olympic decathlon Questions • What are the 3 primary brain vesicles? • What are the corpora quadrigemina? • Which anatomic structures comprise the basis pedunculi? • What is Claude syndrome? – What is a rubral tremor? Outline 1. Embryology 2. External anatomy 3. Internal anatomy 4. Vascular supply 5. Stroke syndromes 6. Herniation syndromes Embryology • 1 of 3 primary brain vesicles – Prosencephalon – Mesencephalon – Rhombencephalon • Intermediate zone gives rise to alar and basal plates – Alar = colliculi, red nucleus and substantia nigra – Basal = general somatic efferent (CN III & IV) and general visceral efferent (E-W nucleus) • Crus cerebri arise from cells outside the mesencephalon External Anatomy • Crus cerebri – Bordered anteriorly by optic tract • CN III exit medial edge of crus cerebri and pass through interpeduncular fossa • Corpora quadrigemina = 4 colliculi • CN IV marks midbrain/pons junction • SC brachium leads to pulvinar nucleus • IC brachium leads to MGB • Anterior subarachnoid space = interpeduncular cistern • Posterior subarachnoid space = quadrigeminal cistern Internal Anatomy • 3 divisions – Tectum (roof) – Tegmentum (floor) – Basis pedunculi (crus cerebri + substantia nigra) • Cerebral peduncle = crus +basis pedunculi • Ascending and descending pathways • Caudal Midbrain – Inf Colliculi receive auditory input from lateral lemniscus – PAG involved in pain modulation (connections to thalamus, hypothalamus and somatosensory input) – Fronto-, parieto-, occipito- & temporopontine fibres project to pons and enter MCP • Caudal Midbrain – CN IV axons pass postero-lateral, crossing midline • Somatotopographic organization of the medial lemniscus • Rostral Midbrain – SN • Pars compacta = output to corpus striatum • Pars reticulata = output to thalamus • Rostral Midbrain – RN • Input from contra cerebellum & ipsi cortex • Rubrospinal and rubro-olivary tracts • Diencephalon-mesencephalon junction – Edinger-Westphal nucleus • Output to ciliary ganglion • Input from pretectal neuclei • Diencephalon-mesencephalon junction • Reticular nuclei – Part of ascending reticular activating system – Responsible for alert, wakeful state • Raphe nuclei – Modulate activity in sleep/dream cycles Vascular Supply Stroke Syndromes Herniation Syndromes • Vascular supply – Branches of SCA and PCA – Lateral midbrain also supplied by anterior choroidal artery (branch of ICA) • Weber – Ipsi CN III, contra bulbar motor • Claude – Ipsi CN III, contra tremor, ataxia and incoordination • Benedikt – Weber + Claude • Central/transtentorial herniation • Upward cerebellar herniation – May lead to • Cerebellar stroke from SCA occlusion • Hydrocephalus from aqueduct compression • Uncal herniation – Lesion most often in temporal lobe – Ipsi CN III is often earliest sign Questions • What are the 3 primary brain vesicles? • What are the corpora quadrigemina? • What anatomic structures comprise the basis pedunculi? • What is Claude syndrome? – What is a rubral tremor? • Rubral tremor (aka Holme’s tremor) – A coarse, slow (4Hz) tremor, especially present in the upper extremities, that is found at rest, postural and intention. The End