Neuro - review 1

Neurobiology and Behavior
More vocabulary to add to your list stimulus response instinct lateral inhibition mechanoreceptors chemoreceptors thermoreceptors retina rods/cones
Review questions blind spot fovea reflex optic nerve sensory/motor/relay neurons visual fields dorsal root ganglion receptive fields edge enhancement photoreceptors semicircular canal cochlea
Eustachian tube innate/learned behavior
1.
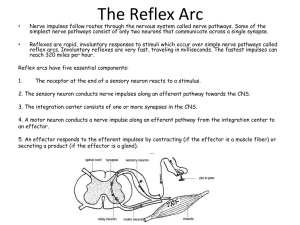
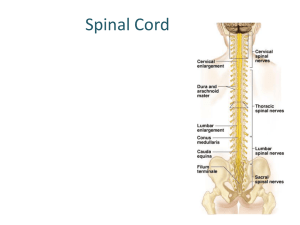
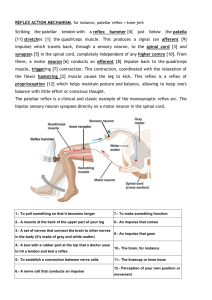
Below is a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex.
2.
3.
a) Label the parts indicated by the letters I–IV. b) Explain the role of parts I and II in a pain withdrawal reflex.
Discuss the use of the pupil reflex in testing for brain death
What is the role of the sensory receptor, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron, effector, and the synapses?
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
How can animal responses be affected by natural selection? Discuss the European blackcaps as an example.
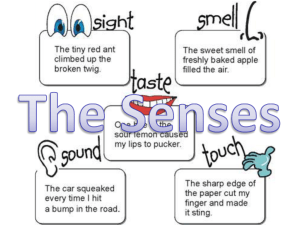
Name the major sensory receptors, examples of each, and their functions.
Know how to label a diagram of the human eye, including the sclera, cornea, conjunctiva, eyelid, choroid, aqueous humor, pupil, lens, iris, vitreous humor, retina, fovea, optic nerve, and blind spot.
What are three differences between rods and cones?
Outline how visual stimuli are processed in the retina and the visual cortex.
9.
What is the difference between edge enhancement and contralateral processing?
10.
Know how to label the ear, including the pinna, eardrum, bones of the middle ear, oval window, round window, semicircular canals, auditory nerve and cochlea.
11.
How is sound perceived by the ear, including the roles of the eardrum, bones of the middle ear, oval and round windows, and the hair cells of the cochlea?
12.
Label the diagram of the retina below.
13.
Explain how pre-synaptic neurons can either encourage or inhibit post-synaptic transmission by depolarization or hyperpolarizaton of the post-synaptic membrane.
14.
Define the term - action potential and explain its significance in nerve transmission.
15.
What are the general effects of psychoactive drugs on synaptic transmission, the brain, and behavior?
16.
What are three examples of excitatory and three examples of inhibitory drugs?
17.
Explain the role of dopamine in the reward pathway.
18.
Describe the effects of THC on synaptic transmission and behavior.
19.
Describe the effects of cocaine on synaptic transmission and behavior.
20.
How do genetic factors affect drug addiction? How might dopamine secretion relate to addiction?
21.
What are the social components of drug addiction?
22.
What is being detected in fMRI and how is it used?
23.
Compare a) somatic and autonomic control, b) sympathetic and parasympathetic control.
24.
Explain the effects of sympathetic control on heart rate, blood flow to the gut, and movement of the iris.
25.
How can pupil reflex determine brain death?