Flash Cards - My Gigantic Jump Drive!
advertisement

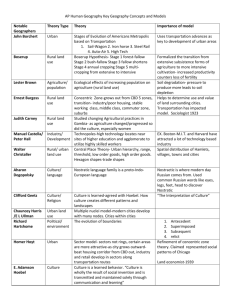
"Demographic Transition" Warren Thompson 1929 England Explains population growth using CBR and CDR 4 Stages – 5th is Hypothetical o None in 1 o LDC 2-3, MDC 3-poss.5 Assumptions: o fall in the death rate in Stage 2 due to industrialization o Stage 3 has been less rapid than the model suggests Applications: Works on global scale; still valid today Malthus’s Theory Malthus – 1798 Population will out grow carrying capacity of food source Assumptions: Food grows linearly; Population grows exponentially Issues: predictions were inaccurate; new technology makes food production easier Strengths: Some still believe, spawned Neo-Malthusianism Heartland Theory Halford Mackinder 1904 Who rules East Europe commands the Heartland Who rules the Heartland commands the World-Island Who rules the World-Island commands the world Weaknesses: No water access; disconnected by rimland Strengths/proofs: Air travel makes more possible; Eurasia had its imperialistic periods Rimland Theory Nicholas Spykman 1942 If one controls the Rimland of Eurasia, one controls the world Opposed heartland theory Weaknesses: Not as much starting land; between two areas as opposed to being “in a corner” like heartland Strengths: Access to water allows trade and navy; more access to resources 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Von Thunen’s Rural Land Use Model Von Thunen Uses 4 concentric rings to explain the location of agricultural activities in a commercial, profit making, economy; based on transportation to market Assumptions: Uniform Terrain; Isolated area; Self Sufficient Society Strength: Based on transport weight; would make for a self sufficient society Core-Periphery Model/World System’s Theory Walt Wallerstein Core Countries = MDC Semi-Periphery = Newly Industrialized Countries Periphery = LDC Periphery depends on core Strengths: applies on a global scale; incorporates the dependency theory Rostow’s Model W. W. Rostow 1960’s Based on Successful MDCs Model of Economic Development Traditional society Preconditions for take-off Take-off Drive to maturity Age of High mass consumption Assumptions: Equal Resource Distribution; No stages can be skipped or altered Criticisms: Not realistic; Not all countries have same opportunities Strengths: maps out path of certain current MDC’s; provides a base for some countries to model after Weber’s Least Cost Theory Alfred Weber 1909 Showed placement of production plants based on transport costs Assumptions: Uniform Topography; labor indefinite; industrial point within triangle; homogeny Strength: Accommodates for many weight scenarios; Agglomeration Weakness: Doesn’t consider employment costs and SEZ Central Place Theory Walter Christaller 1933 Germany Urban Hierarchy based on functions available in city Shows hierarchy of settlements with hexagons Assumptions: Flat Land; Uni. Soil Fertility; PP evenly distributed; Uni. Transport Network; Constant max range and threshold Strengths: Applicable to China and Midwest Concentric Zone Model Burgess 1923 Anglo-America (Chicago) 5 rings show urban development: CBD, Zone Transition, Working class homes, zone of better housing, commuter zone Criticisms: Upperclass would cluster not ring, areas would not form in rings Sector Model Homer Hoyt 1939 Anglo-America (Chicago) Response to CZM, but sectors used instead of rings Poor near CBD, middle class buffer, High class sector Strengths: allowed for geographical intrusions, more realistic Multiple Nuclei Model Harris & Ullman 1945 Anglo-America Independent of CBD, nodes dictate businesses, more activity centers Strengths: Most realistic, conforms to different nodes Urban Realms Model San Francisco Most people live in edge cities Contains retail and industry outside of the CBD Latin American Model Griffin & Ford Mexico City Spine with elite shops and residences meets a market Periterico – squatter settlements on outside Industry at top African City Model South Africa Fastest Growing Cities 3 CBDs: Colonial, Informal Market Zone, Transitional Buisness Mixed ethnic neighborhoods Surrounded by squatter cities (10% South Africa live in shanty towns)

![Model_and_Theory_Chart[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008565077_1-f7a3d3b1b3bb86c6e31ff39e95c26da5-300x300.png)