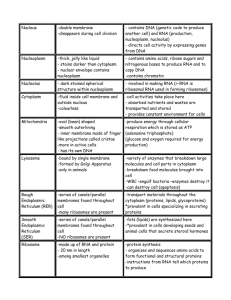
structure location function prokaryote eukaryote
advertisement

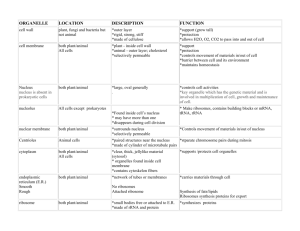
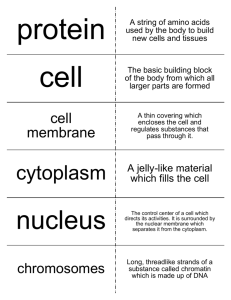
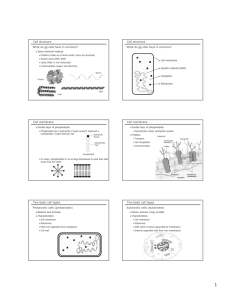
STRUCTURE LOCATION FUNCTION PROKARYOTE EUKARYOTE CELL WALL Around the cell membrane Support and Protect the cell Yes Plants: Yes Animals: No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes NUCLEUS About mid-cell Controls most of the cell’s processes and contains the DNA No * Chromatin Located within the nucleus Consists of DNA bound to Protein No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes Assembly of ribosomes begins No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes Has thousands of pores which allow material to move into and out of the nucleus Helps the cell maintain its shape and also involved in many forms of movement No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes Some Plants: Some Animals: Some Some Plants: Some Animals: Some Some Plants: Some Animals: Some No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes No Plants: Yes About mid-nucleus *Nucleolus * Nuclear Envelope Double-Membrane Layer around the nucleus CYTOSKELETON Found within the Cell Membrane *Microtubule In the cytoskeleton, within the Cell Membrane *Microfilament RIBOSOME ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM In the cytoskeleton, within the Cell Membrane Either attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum or “Free” in the Cytoplasm In the cytoplasm GOLGI APPARATUS In the cytoplasm LYSOSOME In the cytoplasm Hollow tubes of protein that maintain cell shape and serve as “tracks” along which organelles move Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell Where proteins are assembled following coded instructions that come from the nucleus Components of the cell membrane are assembled and some proteins are modified; rough ER (ribosomes) or smooth ER (no ribosomes) Proteins made by the rough ER move into the Golgi Apparatus where enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to them Break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from food into particles that can be used by the rest of the VACUOLE In the cytoplasm CHLOROPLAST In the cytoplasm MITOCHONDRIA In the cytoplasm cell. They also break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness. They remove debris from the cell. To store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. Use energy from the sun to make energy-rich food molecules during photosynthesis. Contains own DNA. Use energy from food to make high-energy compounds that the cell can use for growth, development and movement. Contains own DNA. Animals: Yes No Plants: Yes Animals: Yes No Plants: Yes Animals: No No Plants: Yes Animals: yes