Unit 5 Exam Day

Week 14 – Tuesday – Unit 5 Exam Day
AIM: How can we demonstrate our understanding of Unit 5?
DO NOW: Final questions or comments before the exam.
MINI-LESSON: Exam overview
Introduce students to the format of the exam o Matching o Multiple Choice questions o Short Answer o Essay
Review pacing and time limits o Students will have 2 periods to take the exam
Allow students final questions or comments
ACTIVITY: 1. Cover Letter Writing
Students will begin work on the writing of their cover letters
2. Unit 5 Exam
Students will complete the Unit 5 exam
Students will have 2 periods
When students finish they may move on to completing their sculpture critique sheet
SHARE: Prediction
what will we talk about next? Why do you think that?
HOMEWORK: See homework sheet
US History – Krugman name:
Unit 5 Exam
I.
WWI, Great Depression & New Deal, WWII and the Cold War
Matching (2 points for each correct match)
New Deal
Lusitania
Red Scare a. Term used to describe periods when
American fear of communism was high b. Policy of the U.S. giving aid to people
Resisting communism around the world c. U.S. plan to stop the spread of
communism around the world
Containment d. Japanese-American who challenged
Japanese Internment
Treaty of Versailles e. movement of African-Americans from southern rural areas, to northern urban areas
Korematsu f. New Deal program that gave jobs to out of
work artists, writers, etc.
WPA g. American ship sunk by the Germans,
leading the U.S. into WWI
Great Migration
Iron Curtain
McCarthyism h. The line between Soviet-dominated
Eastern Europe and the “West” i. ended World War I j. The “hunting” of suspected communists
II.
Multiple Choice (3 points each)
1. The "clear and present danger" ruling of the Supreme Court in Schenck v. United States illustrates the continuing conflict between
1. free speech and governmental authority
2. the use of search warrants and the rights of the accused
3. state powers and Federal powers
4. religious freedom and separation of church and state
2. Which of these was neither a push factor nor a pull factor in the Great Migration?
1. Increased job opportunities in the North
2. Growing racial tension in the cities in the North
3. Widespread poverty among sharecroppers on the South
4. Fear of lynching and violence against Blacks in the South
3. In the United States, the Red Scare of 1919 and the McCarthy Era of the early 1950’s were periods of
1. severe economic depression
2. widespread support for groups promoting international anarchy
3. great growth in art, literature, and music
4. persecution of people suspected of holding anti-American political views
4. The outpouring of creativity among African-American poet, writers and artists in the 1920s is known as
1. Jazz Age
2. Roaring Twenties.
3. Harlem Renaissance
4. Back-to-Africa Movement
5. A significant cause of the Great Depression of the 1930’s was that
1. some banking policies were unsound and had led to the overexpansion of credit
2. a decrease in protective tariffs had opened American business to competition from abroad
3. a wave of violent strikes had paralyzed the major industries
4. consumer goods were relatively inexpensive
6. What was one objective of the Social Security Act?
1. To ban child labor
2. To protect workers’ rights
3. To supervise union elections
4. To lessen poverty in retirement
7. The domestic legislation of the New Deal period was based on the idea that the federal government should
1. favor big business over labor and farming
2. assume some responsibility for the welfare of people
3. own and operate the major industries of the country
4. require local communities to be responsible for social welfare programs
8. On December 7 th , 1941, President Roosevelt asked Congress for a declaration of war. Which of these events led to his request?
1. Churchill’s desperate need for help in the Battle of Britain
2. Germany’s lightning war that ended with the fall of France
3. Stalin’s agreement to sign a nonaggression pact with Hitler
4. Japan’s surprise attack on a U.S. naval base in Pearl Harbor
9. Which of these statements best describes the experience of African-Americans during WWII?
1. An end to social segregation in the United States
2. Segregation and racism in the military
3. A rise in lynching in the south
4. Economic benefits from military service
10. How did the United States respond to the Berlin Blockade in 1948?
1. By airlifting food and supplies into Berlin
2. By surrendering control of Berlin to the Soviets
3. By bombing Berlin until the Soviets surrendered
4. By sending troops to Berlin to break the blockade
11. Which is a valid conclusion based on United States involvement in the Korean War?
1. The policy of containment was applied in Asia as well as in Europe
2. United Nations economic sanctions are more effective than military action.
3. The American people will support United States participation in any war, whether declared or undeclared.
4. United States cooperation with a wartime ally ends when the war ends.
12. What was a cause for the investigations of the House Un-American Activities Committee in the late 1940s and the investigations of a Senate committee headed by Joseph McCarthy in the early 1950s?
1. the belief that there were Communist agents in the federal government
2. excessive spending by the United States military
3. the corruption and bribery of members of Congress
4. actions of President Harry Truman that might have led to his impeachment
13. The 1920’s are sometimes called the "Roaring Twenties" because
1. foreign trade prospered after World War I
2. the United States assumed a leadership role in world affairs
3. political reforms made government more democratic
4. widespread social and economic change occurred
14. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the
1. money borrowed from foreign governments
2. sale of war bonds
3. sale of United States manufactured goods to neutral nations
4. printing of additional paper money
III. Document Analysis (5 points each)
Aim for 3 – 5 sentences for each document
1.
What two sides is the wall separating AND why is there a need for separation?
2. Who is the president shown in this political cartoon? AND What do the letters stand for?
3.
Who is the woman in the cartoon AND how does she represent women’s experiences during World War II?
4.
What does it appear this cartoon is saying of the connection between the sinking of the
Lusitania and the U.S decision to declare war?
( Which war is this about ?)
III.
Short Answer (8 points total)
Choose one conflict from around the world that occurred as a result of the Cold War. Explain why the conflict started, who was involved in the conflict, where the conflict took place and how, if at all, was the conflict resolved.
IV.
Essay Question (20 points total)
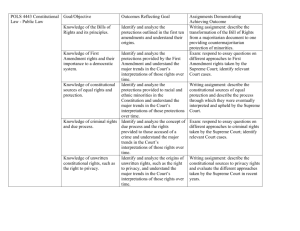
Theme: Supreme Court Cases Concerning Constitutional Civil Liberties
The United States Supreme Court has played a major role in either expanding or limiting constitutional civil liberties in the United States.
Task:
Identify two Supreme Court cases that have had an impact on civil liberties in the
United States. For each case identified:
• Discuss the facts of the case
• Identify a specific constitutional civil liberty issue addressed by the
Supreme Court
• Discuss how the decision of the Supreme Court either expanded or limited a specific constitutional civil liberty in the United States
You may use any appropriate Supreme Court case from your study of United States history. Some suggestions you might wish to consider include Plessy v. Ferguson (1896),
Schenck v. United States (1919), Korematsu v. United States (1944)
You are not limited to these suggestions.
Start your essay on the following page