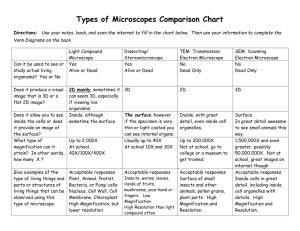
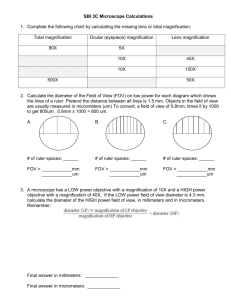
A2. Cell Diversity Acitivity
advertisement
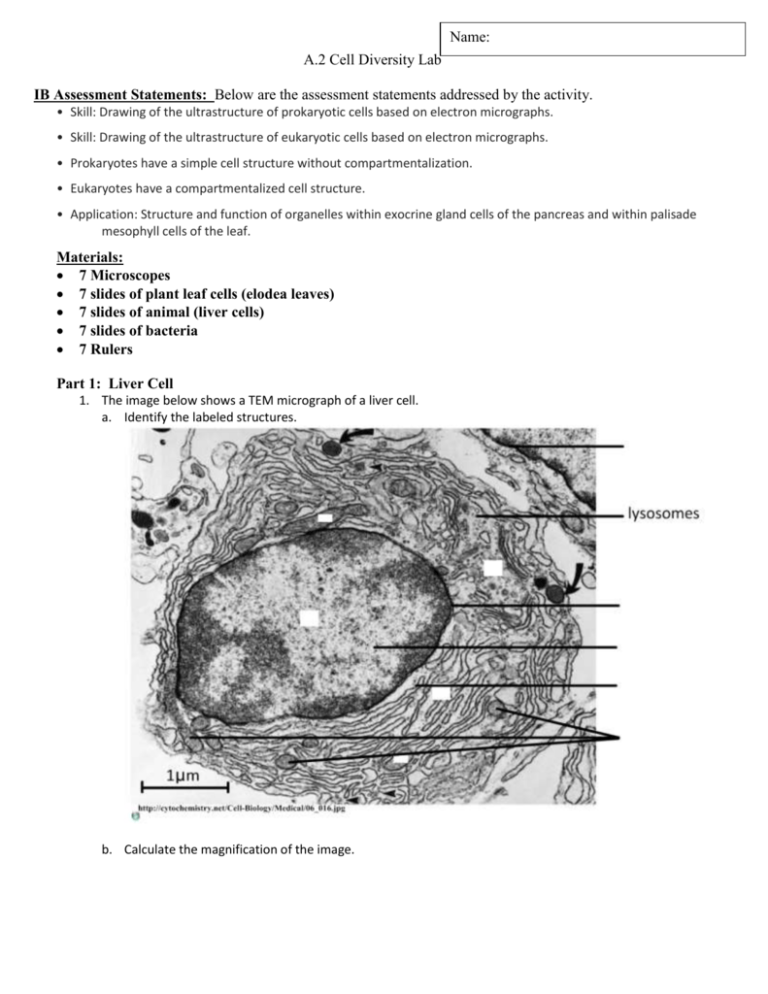
Name: A.2 Cell Diversity Lab IB Assessment Statements: Below are the assessment statements addressed by the activity. • Skill: Drawing of the ultrastructure of prokaryotic cells based on electron micrographs. • Skill: Drawing of the ultrastructure of eukaryotic cells based on electron micrographs. • Prokaryotes have a simple cell structure without compartmentalization. • Eukaryotes have a compartmentalized cell structure. • Application: Structure and function of organelles within exocrine gland cells of the pancreas and within palisade mesophyll cells of the leaf. Materials: 7 Microscopes 7 slides of plant leaf cells (elodea leaves) 7 slides of animal (liver cells) 7 slides of bacteria 7 Rulers Part 1: Liver Cell 1. The image below shows a TEM micrograph of a liver cell. a. Identify the labeled structures. b. Calculate the magnification of the image. Part 2: 1. Identify if the below cells are a prokaryotes or eukaryotes: a. Explain your why you called the below cell a prokaryote or eukaryote: b. Label and annotate the cellsbelow. Be sure to include: cytoplasm, pili, flagella, ribosomes, Nucleoid c. Calculate magnification of the image on the right (be sure to show your work). d. Calculate Actual length of the cell on the right (show you work). . 2. Identify if the below cell is a plant or animal: a. Explain your why you called the below cell a plant or animal: . b. Label the organelles and annotate the organelles function in the cell below.Be sure to include: cytoplasm, nucleus, Smooth ER, rough ER, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosome , lysosomes c. Calculate magnification of the image on the right (be sure to show your work). d. Calculate Actual length of the cell on the right (show you work). 3. Identify if the below cell is a plant or animal: a. Explain your why you called the below cell a plant or animal: . b. Use a ruler and annotate the cells below. Be sure to include: cytoplasm, nucleus, Smooth ER, rough ER, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosome, cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole Part 3: Making Microscope Drawings: Instructions for Microscope drawings: 1) Draw what you actually see. 2) Center your drawing/ diagram on the page and leave room of labels. 3) Make your drawing big enough so you can see all the important details. 4) Drawings should be accurate representation of what you observe 5) Proportions should be accurate. 6) Labels: all parts of your diagram must be labeled accurately using vertical or horizontal label lines and simple clear descriptions. 7) Drawing should have a title, magnification (or scale bar), names of structures. Plant Cell. Instructions: Look at plant cell under low magnification(5x) and then under a higher magnification (either high (40X) or medium (10X)) Draw your plant cell in the boxes below. Be sure to label all the visible organelles, and follow the above instructions about “Making Microscope Drawings” Plant Cell – Low Power (5X) Plant Cell – med (10X) or high power (40X) Animal Cell. Instructions: Look at animal cell under low magnification(5x) and then under a higher magnification (either high (40X) or medium (10X)) Draw your animal cell in the boxes below. Be sure to label all the visible organelles, and follow the above instructions about “Making Microscope Drawings” Animal Cell – Low Power (5X) Animal Cell – med (10X) or high power (40X) Bacteria/ prokaryote Cell. Instructions: Look at Bacteria cell under low magnification(5x) and then under a higher magnification (either high (40X) or medium (10X)) Draw your bacteria cell in the boxes below. Be sure to label all the visible organelles, and follow the above instructions about “Making Microscope Drawings” Bacteria Cell – Low Power (5X) Bacteria Cell – med (10X) or high power (40X)