BRYOPHYTA
advertisement

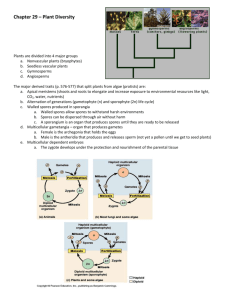
BRYOPHYTA Mosses Bryophyta Seedless nonvascular Clumps of grass, tiny trees, and small pieces of green yarn Use free standing water to allow that sperm to fertilize eggs EX: Peat moss/ Sphagnum Can withstand harsh conditions HEPTOPHYTA Liverworts Heptophyta Seedless nonvascular Thallus- moss look-alike that is flat and leafless Wet rocks, flower pots, and other areas with plenty of moisture Produce eggs on umbrella-like structure EX: Jungermanniales (Leafy) and Lunularia cruciata (Thallus) ANTHOCEROPHYTA Hornworts Anthocerophyta Seedless nonvascular Green horn-like structures Tropics Green horns produce spores EX: Dendroceros and Megoceros LYCOPHYTA Club mosses Lycophyta Seedless vascular Stand upright like little trees Moist shaded woodlands Produce spores EX: Alaskan club moss, Alpine club moss, and Chinese club moss Oldest living vascular plants PTEROPHYTA Ferns Pterophyta Seedless vascular Have Trophyll- leaves that do not produce spores but produce sugar for photosynthesis Shady woodlands Produce spores EX: Staghorn Fern, Boston Fern, and Maidenhair Fern CYCADOPHYTA Cycads Cycadophyta Seeded vascular Look like Palm trees with large cones Tropical Seeds are fertilized by pollination EX: Balansa’s Sago and Mountain Sago GINKGOPHYTA Seed Ferns Ginkgophyta Seeded vascular Two loped leaves of the plant China Drop seeds to be scattered Oldest species of seeded plants CONIFEROPHYTA Conifers Coniferophyta Seeded vascular Needle-like leaves Mountainous regions Drop cones bearing their seeds EX: Pine Tree, Douglas Fir, and Mountain Hemlock Two conifers living in California are 4,700 years old ANTHOPHYTA Flowering plants Anthophyta Flowering vascular Have flowers and fruits Basically live anywhere where there is a steady supply of water and sunlight Use pollination to reproduce EX: Apple Trees, Sunflowers, and Magnolias