Notes from the Chemistry of Life PowerPoint
advertisement

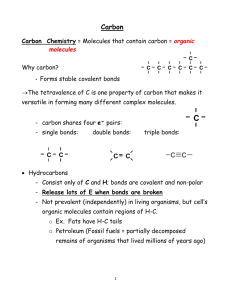
Notes from the Chemistry of Life PowerPoint The Chemistry of Life: The nature of matter Properties of water Atoms Basic unit of matter Greek (atomos) unable to be cut Subatomic particles protons, neutrons, electrons Nucleus protons and neutrons Elements and Isotopes Elements a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom Number of protons= element’s atomic# Isotopes Same element different number of neutrons (same chemical properties) Atomic mass # = weighted average mass of the isotopes Radioactive Isotopes Nuclei are unstable and break down at a constant rate Can be used as a dating tool, treatment for cancer, food sanitation, tracers to follow movement in bodies. Chemical compounds and bonds Compound – Formed by the chemical combination of 2 or more elements in definite proportions Example: C6H12O6 (glucose) Chemical bonds: Ionic bonds Electrons are transferred from one atom to another Covalent bonds (strongest bond) Electrons are shared between atoms Forms molecules Van der Waals Forces Intermolecular forces – an attraction between oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules The water molecule Polarity Uneven distribution of electrons between the H and O atoms Hydrogen end slightly positive Oxygen end slightly negative Hydrogen bonds Negative to positive attractions btw molecules Strongest bond that can form btw molecules Cohesion = attraction between molecules of the same substance (ex. Water on a penny) Adhesion = attraction between molecules of different substances (ex. meniscus) Solutions and Suspensions Mixture = 2 or more elements or compounds physically mixed (not chemically) 2 types = solutions and suspensions Solutions Components are evenly distributed Solvent (dissolves the solute) ex. water Solute (substance that is dissolved) ex. salt Suspensions Mixtures of water and nondissolved material Movement keeps material suspended Blood solution and suspension! Made of mostly water with many dissolved components (solution) Also contains nondissolved material like blood cells (suspension) Acids, Bases, and pH pH scale = factor of 10 btw steps Acids (strong acid = 0/weak acid = 6) Forms H+ ions in solution The higher the concentration of H+ more acidic Bases (strong base = 14/weak base = 8) Forms OH- ions in solution and low concentrations of H+ The lower the concentration of H+ more basic Buffers Weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids and bases to prevent sharp changes in pH Helps to maintain homeostasis in the body (pH of the body = 6.5 – 7.5) Chemistry of Life Carbon compounds Chemical Reactions and Enzymes The chemistry of carbon Organic chemistry: The study of all compounds that contain carbon Can form single, double, or triple covalent bonds with other carbon molecules Macromolecules: Monomers – small organic compound units Polymers – many monomers strung together 4 groups = carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins Carbohydrates Main energy source for living things Can also be used for structural purposes (ex. cell wall in plants) Made up of C, H, and O ratio of 1:2:1 Monomer = glucose (sugar molecule) or monosaccharides Polymer = starch or polysaccharides Lipids (fats) Generally not soluble in water Used to store energy, found in membranes, waterproof coverings, and used as chemical messengers Typically = glycerol molecule combined with fatty acid molecules Saturated – maximum # of hydrogen bonds (no double bonds) in a fatty acid Unsaturated – at least one carbon-carbon double bond in a fatty acid Nucleic Acids Contains H, O, N, C, and P Stores, transmits hereditary/genetic information 2 kinds = RNA and DNA Monomer = nucleotide (a 5C sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base) Polymer = polynucleotide or nucleic acid Protein Contain N, C, H, O Some proteins control the rate of reactions (enzymes), regulate cell processes, form bone and muscle, cell transport, and fight disease Monomer = amino acids Polymer = polypeptide or protein Chemical Reactions A process that changes one set of chemicals into another Always involves the breaking and formation of bonds Reactants Enter into a reaction Bonds are broken Products Result from a reaction New bonds are formed Energy in Reactions Energy changes Release energy spontaneous Absorb energy needs energy to proceed Where does this energy come from in plants? Animals? Activation energy Energy needed to get a reaction started Activation energy: Enzymes Catalyst = substance that speeds up a chemical reaction Lowers activation energy Enzyme Action The enzyme-substrate complex Reactants = substrates Enzyme has an active site where the substrate binds and is transformed into products "Lock and Key" (each enzyme is specific to its substrate) Regulation of Enzyme Activity Human body = 37C Most enzymes work best at a specific temperature and pH (depends on enzyme) Enzymes play essential role in: Regulating chemical pathways making materials that cells need releasing energy transferring information