KHALLIKOTE UNIVERSITY, BRAHMAPUR M.Sc . BOTANY
advertisement
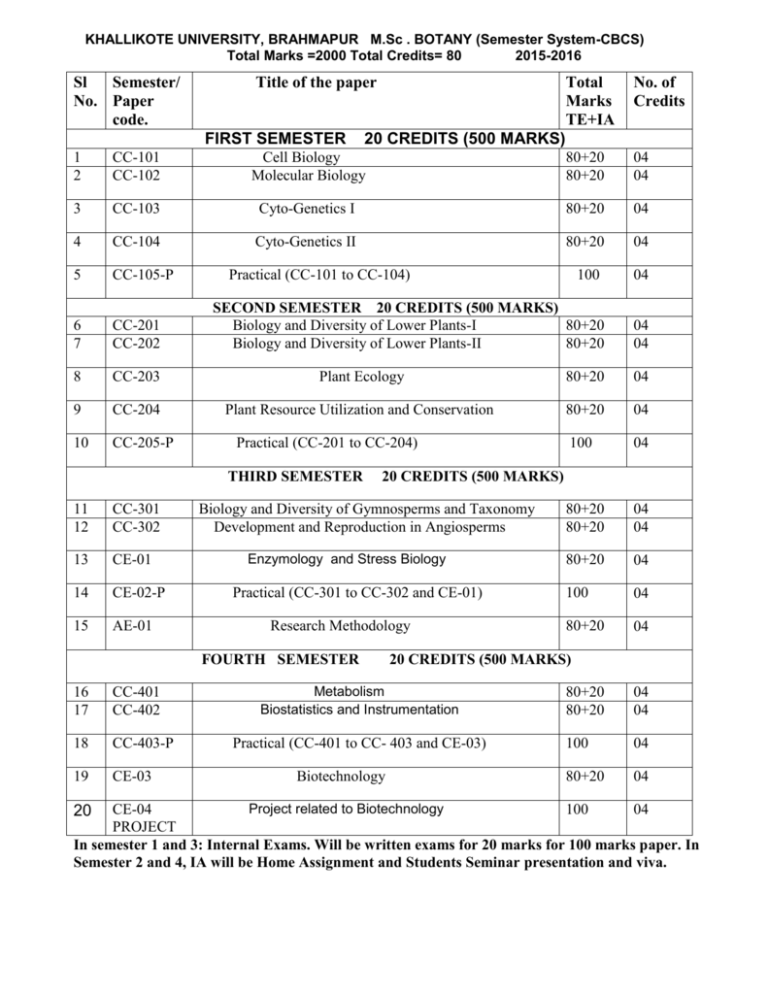
KHALLIKOTE UNIVERSITY, BRAHMAPUR M.Sc . BOTANY (Semester System-CBCS) Total Marks =2000 Total Credits= 80 2015-2016 Sl Semester/ No. Paper code. Title of the paper FIRST SEMESTER Total Marks TE+IA No. of Credits 20 CREDITS (500 MARKS) 1 2 CC-101 CC-102 Cell Biology Molecular Biology 80+20 80+20 04 04 3 CC-103 Cyto-Genetics I 80+20 04 4 CC-104 Cyto-Genetics II 80+20 04 5 CC-105-P 100 04 6 7 CC-201 CC-202 8 CC-203 Plant Ecology 80+20 04 9 CC-204 Plant Resource Utilization and Conservation 80+20 04 10 CC-205-P 100 04 80+20 80+20 04 04 80+20 04 100 04 80+20 04 Practical (CC-101 to CC-104) SECOND SEMESTER 20 CREDITS (500 MARKS) Biology and Diversity of Lower Plants-I 80+20 Biology and Diversity of Lower Plants-II 80+20 Practical (CC-201 to CC-204) THIRD SEMESTER 11 12 CC-301 CC-302 13 CE-01 14 CE-02-P 15 AE-01 20 CREDITS (500 MARKS) Biology and Diversity of Gymnosperms and Taxonomy Development and Reproduction in Angiosperms Enzymology and Stress Biology Practical (CC-301 to CC-302 and CE-01) Research Methodology FOURTH SEMESTER 16 17 CC-401 CC-402 18 CC-403-P 19 CE-03 04 04 20 CREDITS (500 MARKS) Metabolism Biostatistics and Instrumentation Practical (CC-401 to CC- 403 and CE-03) Biotechnology 80+20 80+20 04 04 100 04 80+20 04 Project related to Biotechnology CE-04 100 04 PROJECT In semester 1 and 3: Internal Exams. Will be written exams for 20 marks for 100 marks paper. In Semester 2 and 4, IA will be Home Assignment and Students Seminar presentation and viva. 20 M.Sc.(Botany) FIRST SEMESTER PAPER – CC-101 CELL BIOLOGY (04 credits) Unit I - The dynamic cell : Marks: 100 (80+20) 20 Marks Structural organization of the plant cell; Specialized plant cell types; Chemical foundation; Biochemical energetics; Cell wall: Structure and function; Biogenesis; Growth; Plasma membrane: Structure, latest models and functions; sites of ATPases; Ion carriers; Channels and pumps; Receptors; Unit II - Chloroplast : 20 Marks Structure: Genome organization; Gene expression; RNA editing; Nucleochloroplastic interactions; Mitochondria: Structure; Genome organization; Biogenesis; Endoplasmic Reticulum and Dictyosomes: Structure and function. Unit III – Ribosomes:20 marks Structure and function; Ribosome: Structure; Site of protein synthesis; Structure and role of RNA; Mechanism of translation: Initiation, elongation and termination; Protein Sorting: Targeting of proteins to organelles. Unit IV- Lysosomes and Micro bodies : 20 Marks Plant Vacuole: Tonoplast membrane, micro bodies and Lysosomes Transporters; Vacuole as a storage organelle Plasmodesmata: Structure; role in movement of molecules; Comparison with gap junctions; Cytoskeleton: Organization and role of microtubules and microfilaments; Motor movements PAPER-CC-102 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (04 credits) 100 marks (80+20) . Unit I - Nucleus: 20 Marks Structure; Nuclear pores; Nucleosome organization: DNA: Structures A, B and Z forms; Replication, damage and repair; Transcription: Promoters and transcription factors; RNA: RNA splicing, mRNA transport; Nucleolus: Structure and r RNA biosynthesis. Unit II- Cell cycle :20 Marks Mitosos and Meiosis: stages and molecular events Details of cell cycle; Control mechanisms : Role of cyclins and cyclin dependant kinases; Cytokinesis: General mechanism and cell plate formation Unit-III Techniques in Cell Biology: 20marks Microscopy; Electron microscopy, SEM and TEM, FTIR Immuno techniques; in situ hybridization to locate transcripts in cell type., measurement of cell death, Comet Assay, Unit-IV : Molecular Pathogenesis: 20marks Apoptosis: Mechanism of programmed cell death, Measurement of Cell death Biology of cancer: A generalized account of biology of cancer, Brief introduction to the life cycle and molecular biology of important pathogens like AIDS, Malaria, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis and Filsria CC 103 CYTO- GENETICS-I (04 credits) Marks: 100(80+20) Unit I -: Chromosomes 20 Marks Chromosome structure and packaging of DNA: Molecular organization of centromere and telomere; Euchromatin and heterochromatin: Karyo type analysis; Banding patterns; Karyotype evolution Polytene, lamp brush, B and sex chromosomes;Structural alterations in chromosomes: Origin, meiosis and breeding behaviour of deficiency, duplication, inversion and translocation heterozygote; Unit-II: Chromatin Organization-I : 20 marks Breeding behaviour and genetics of structural heterozygote; complex translocation heterozygotes; Translocation tester tests; Robertsonian translocations; B-A translocations; Haploid and euploids: Characteristics, origin and production of autopolyploids; Chromosome and chromatid segregation in autopolyploids; Types, genome constitution and analysis of allopolyploids. Unit III Chromatin organization-II: 20marks Transfer of individual chromosomes and chromosome segments; Methods of detecting alien chromatin; Production, characterization and utility of alien addition and substitution lines.Genetic basis of inbreeding, Exploitation of Hybrid Vigor ,Heterosis Unit-IV - Aneuploids : 20 Marks Induction and characterization of trisomics and monosomics; Effect of aneuploidy on phenotype of plants; Transmission of monosomics and trisomics and their use in chromosome mapping in diploid and polyploid species; Alien gene transfer through chromosome manipulation: Transfer of whole genome(Examples from Zea, Arachis and Brassica); PAPER-CC-104 CYTO-GENEITCS-II (04 credits) Marks: 100(80+20) Unit I - Genetics of prokaryotes and eukaryotic organelles : 20Marks Mapping the bacteriophage genome; Geneticrecombination in phage; Genetic transformation, conjugation and transduction in bacteria; Genetics ofmitochondria and chloroplasts; Cytoplasmic male sterility: Gene structure and expression: Genetic finestructure; cis-trans test; fine structure analysis of eukaryotes; introns and their significance; Regulationof gene expression in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Unit II - Genetic recombination : 20 Marks Recombination: Independent assortment and crossing over; Molecular mechanism of recombination; Role of Rec A.B,C,D enzymes: site specific recombination; Genetic, physical and restriction mapping :Chromosome mapping; Linkage groups; Physical mapping of genes on chromosomes; Genetic markers; Construction of molecular maps; Correlation of genetic and physical maps; Somatic cell genetics , an alternative approach to gene mapping; Restriction mapping: General idea. Unit III : Mutations : 20 Marks Spontaneous and induced mutations: Physical and chemical mutagens; Molecular basis of gene mutations: Transposable elements in prokaryotes and eukaryotes; Mutations induced by transposons; Site-directed mutagenesis; Cancer: Initiation of cancer at\cellular level; protooncogenes and oncogene Unit-IV MOLECULAR CYTOGENETICS:20 marks Molecular cytogenetics: Nuclear DNA content: C value paradox: Multigene families and their evolution Chromosome microdissection and micro cloning ,flow cytometry, Application of confocal microscopy in karyotype analysis PAPER CC- 105 PRACTICALS Marks : 100 Practical of Paper CC-101 to-104. M.Sc.(Botany) SECOND SEMESTER PAPER CC-201 BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF LOWER PLANTS: I Marks: 100 (80+20) Unit I – Bacteria and Virus : 20 Marks General account Eubacteria: Ultrastructure; Nutritionand reproduction; Biology and economic importance;Cyanobacteria: Salient feature and biologicalimportance; Viruses: Characteristics, ultrastruture,chemical nature, replication and transmission;economic importance; Phytoplasma: Generalcharacteristics and role in causing plant diseases. Unit II – Phycology-I : 20 Marks Algae in diversified habitats (terrestrial, freshwater andmarine); Thallus organization; Cell ultrastructure;Reproduction (Vegetative, Asexual and Sexual);Criteria for classification of algae; Pigments; Reservefood; Flagella; Unit-III Phycology-II 20 marks Salient features of Protochlorophyta, Chlorophyta, Charophyta, Xanthophyta, Bacillariophyta, Phaeophyta and Rhodophyta ; Algal blooms; Algal biofertilizers; Algae as food, feed and its uses in industry. Unit IV– Mycology-I : 20 Marks General characters of fungi; Substrate relationship infungi; Cell ultrastructure; Unicellular and multicellularorganisation; Cell wall composition; Nutrition;Reproduction (Vegetative, Asexual and sexual);Heterothallism; Heterokaryosis: Parasexuality; Recenttrends in classification agents. PAPER CC-202 (04 Credits) BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF LOWER PLANTS: II Marks :100 (80+20) Unit-I : Mycology-II 20 marks General account of Mastigomycotina, Zygomycotina, Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina; Fungi in industry, medicine and as food; Fungal disease in plants and humans; Mycorryzae; Fungi as bio control agent Unit II - Bryophyta : 20 Marks General classification, morphology. structure, reproduction and life history; Distribution and general account of Marchantiales. Jungermaniales ,Anthocerotales, Sphagnales, Funariales and PoIytricales: Economic and ecological importance. Unit III - Pteridophyta -I: 20 Marks General classification: Morphology, anatomy and reproduction; Evolution of stele; Heterospory and origin of seed habit; Unit IV- Pteridophyta – II: 20 Marks General account of fossil pteridophyta; Introduction to Psilopsida, Lycopsida, Sphenopsida and Pteropsida . General Classification ,Morphology ,anatomy and reproduction of genera related to Psilopsida, Lycopsida, Sphenopsida and Pteropsida . PAPER CC- 203 PLANT ECOLOGY (04 credits) Marks : 100 (80+20) Unit I - Ecosystem organization : 20 Marks Structure and functions; Primary Production: Methods of measurement. Controlling factors: Energy dynamics :trophic organization, energy flow pathways. Ecological efficiencies: mechanism of litter decomposition: Global biogeochemical cycles carbon. Nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur: Unit II - Vegetation organization: 20 Marks Concepts of community and continuum; Analytical and synthetic characters of a community; Community coefficients; Inter specific associations; Ordination; Concept of ecological niche Vegetation development; Cyclic and non-cyclic temporal changes;; floristic composition; Facilitation, tolerance and inhibition models, Changes in ecosystem properties during succession: Major biomes and vegetations of the world Unit III - Pollution: 20 Marks Kinds, sources and quality parameters of air water and soil pollution; Effects of pollutants on plants and ecosystems; Climatic changes: Greenhouse gases; Ozone layer and ozone hole; Consequences of climatic change (CO2 utilization, global warming, sea level rise, UV radiation) Unit-IV : Conservation of Biodiversity: 20 marks Biological Diversity : Concept; IUCN categories of threat; Distribution and global patterns; Terrestrial biodiversity hot spots; Inventory; World centres of primary diversity of domesticated plants: The IndoBurmese Plant Introductions and Secondary centres. Paper CC-204; PLANT RESOURCEUTILIZATION AND CONSERVATION Marks100 (80+20) Unit I - Economic Botany : 20 Marks Origin, evolution, botany, cultivation and uses of important food, forage, fodder, fibre, vegetable, fruit. oil yielding and medicinal plants; Important fire wood and timber yielding plants like bamboos, rattans; Plants used for paper making, gums, tannins, dyes and resins; Plants used as avenue trees for shade, pollution control and aesthetics Unit- II Ecosystem Development : 20marks Mechanism of ecological succession: Initial and relay Ecosystem stability: concept: Resistance and resilience: Natural and anthropogenic ecological perturbations and their impact on ecosystem; Environmental impact assessment; Ecosystem restoration: Unit III - Principles of conservation : 20 Marks Extinctions; Environmental status of plants based on International Union for Conservation of Nature: in situconservation: Concept; International efforts and Indianinitiative: Protected areas in India: Sanctuaries.National Parks, Biosphere reserves, wetlands.Mangroves, and Coral reefs for conservation of wild biodiversity; ex situ conservation: Principles and practices; Botanical gardens; Unit-IV : Conservation Strategies :20 marks Field gene banks: Seedbanks; in vitro repositories; Cryobanks; Generalaccount of the activities of Botanical Survey of India(BSI); National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources(NBPGR): Indian Council of Agricultural Research(ICAR); Council of Scientific and Industrial Research(CSIR); Department of Biotechnology (DBT) for conservation, Non-formal conservation efforts. PAPER –CC- 205 PRACTICAL Marks : 100 Practical of Paper 201 to 204 M.Sc.(Botany) THIRD SEMESTER PAPER 301 BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF GYMNOSPERMS and TAXONOMY, (04Credits) Marks: 100(80+20) Unit I - Gymnosperms I : 20 Marks Classification of gymnosperms and their distributionin India; General account of Gymnosperm orders Pteridospermales (Lyginopteridaceae, Medullosaceae,Caytoniaceae and Glossopteridaceae), Cycadeoideales, Cordaitales Unit II - Gymnosperms II :20 Marks Structure and reproduction in Cycadales, Ginkgoales,Coniferales, Ephedrales, Welwitschiales and Gnetales Unit III - Taxonomy -I: 20 Marks The species concept : Taxonomic hierarchy; species, genus, family and other categories; principles used in assessing relationship; delimitation of taxa and attribution of rank; Salient features of International Code of Botanical Nomenclature Unit-IV: Taxonomy-II : 20marks Taxonomic evidence and tools: Anatomical, palynological, histological,cytological, phytochemical, molecular and genomic techniques as evidences and tools for solving taxonomic problems; phenetic vs phylogenetic system of classifications with special emphasis on Taktajan and Cronquist systems of classification PAPER-302 DEVELOPMENT AND REPRODUCTION IN ANGIOSPERMS (04 credits) Marks 100(80+20) Unit I – Development-I: 20 Marks Shoot development : Organization of the shoot apical meristem (SAM); Cytological and molecular analysis of SAM; Control of cell division and cell to cell communication; Control of tissue differentiation; Leaf growth and differentiation: Determination; phyllotaxy; control of leaf form; differentiation of epidermis and mesophyll; Root development: Organization of root apical meristem (RAM), cell fates and lineages; vascular tissue differentiation; lateral-roots; root hairs; root-microbe interactions Unit II – Reproduction: 20 Marks Floral organ differentiation in Arabidipsis,Microsporegensis, Male gametophyte, Megasporegensis, Female Gametophyte, Ovule development, Megasporegensis,Embryo Sac, Double Fertilization, Endosperm and embryo development Flower development and genetics : Floral organ differentiation in Arabidopsis; Male gametophyte: Microsporogenesis; pollen development and gene expression; Male sterility; Sperm dimorphism; Female gametophyte: Ovule development, megasporogenesis, organization of embryo sac; Pollination, Unit-III Seed Dormancy 20 marks Dormancy :Importance and types of dormancy; seed dormancy; overcoming seed dormancy; bud dormancy; Plant growth regulators and elicitors: Physiological effects and mechanism of action of auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, abscisic acid, brassino steroid polyamines, jasmonic acid and salicylic acid Unit-IV : Pollen –Pistil Interaction: 20 marks Pollen-pistil interaction; and Fertilization: Structure of pistil; Pollen-stigma interactions; Cytological, biochemical and molecular aspects of sporophytic and gametophytic incompatibility; Double fetrtilization ;Endosperm and embryo development: General features; Ultra-structure, nuclear cytology and cell lineage during embryo development PAPER CE-01 Enzymology and Stress Biology (04Credits) Marks : 100 (80+20) Unit I - Energy Flow and Enzymology 20 Marks Energy flow : Principles of thermodynamics; free energy and chemical potential; redox reactions; structure and function of ATP; Enzymology: General aspects; allosteric mechanism; regulatory and active sites; mechanism of enzyme action ( chymotrypsinas an example); isozymes; kinetics of enzymatic catalysis; Michaelis -Menten equation and its significance; Lineweaver-Burk equation; Enzyme inhibition and kinetics; Unit-II Signal Transduction 20 marks Signal transduction: Overview; receptors and G proteins; phospholipid signaling; roleof cyclic nucleotides; calcium-calmodulin cascade; diversity in protein kinases and phosphatases ;specific signaling mechanisms (two component sensory regulatory system in bacteria and plants; sucrosesensing mechanism) Physiology of stress: Plant response to biotic and abiotic stress mechanism of biotic and abiotic stress tolerance; HR and SAR; water deficit and drought resistance; salinity stress; metal toxicity; freezing and heat stress; oxidative stress Unit III – Water Relation and physiology of Growth: 20 Marks Mechanism of water absorption; Ascent of sap: Mechanism of water transport through xylem; Transpiration: Stomatal mechanism Phloem loading and unloading; mechanism of transport of photosynthate Seed germination and seedling growth : Metabolism of nucleic acids and proteins and mobilization of food reserves during germination; hormonal control of seedling growth; gene expression; use of mutants in understanding seedling development Unit- IV : Sensory Photobiology- 20 marks History of discovery of phytochromes and cryptochromes and their photochemical and biochemical properties; photo physiology of light-induced responses; molecular mechanism of action of photomorphogenic receptors, signaling and gene expressionPhotoperiodism and its significance; endogenousclock and its regulation; floral induction and development -genetic and molecular analysis; role ofvernalization: Physiology of senescence: Types of senescence; metabolic changes associated withsenescence and its regulation; influence of hormones and environmental factors on senescence PAPER CE-2 PRACTICAL Marks : 100 Practical of Paper CC-301 to CC-302 and CE-1 PAPER AE-01 RESEARCH METHODO LOGY (04 CREDITS) Marks: 100 (80+20) Unit-I Ecological Methods:20 marks Bomb Calorimetry, Determination of Energy Content of Plant Materials General Methods for Physical and chemical Analysis of Soil. Chlorophyll and Leaf area determination of Plant Communities Dose Response and determination of threshold Values: EC 50, EC100 and TLC Unit-II Microbial Methods 20 marks: Preparation of Solid and Liquid Media for Algae, Fungi and bacteria, Mass Culture Techniques and application Data Analysis: ANOVA, Chi-square Test, Simple Correlation and Regression Analysis Unit-III Biochemical Methods: 20 marks Purification and identification of biomolecules by Chromatography Spectrometric analysis of Biomolecules : Plant pigments, Carbohydrates, proteins, Nucleic Acids and Enzymes Unit-IV Research paper writing and presentation: 20 marks Structuring and writing a research paper (Review of literature, title, introduction, materials and methods, results and discussions and Citing References) Choice of Journals and publishers in plant sciences, Journal Impact factor, Searching Literature M.Sc.(Botany) FOURTH SEMESTER PAPER CC- 401 METABOLISM 04 credits Marks : 100 (80+20) Unit I - Photosynthesis : 20 Marks Photosynthesis : General aspects and historical background; evolution of photosynthetic apparatus; photosynthetic pigments and light harvesting complexes; photo oxidation of water; mechanism of electron and proton transport; carbon assimilation; Calvin cycle; photorespiration and its significance; theC4 cycle; the CAM pathway; biosynthesis of starch and sucrose; Unit-II Respiration 20 marks Respiration : Overview of plant respiration; glycolysis; TCA cycle; electron transport, cytochrome system and ATP synthesis, Redox potential ; pentose phosphate pathway; glyoxalate cycle. Energy budget of Respiration Unit III - Lipid, and Sulphur Metabolism : 20 Marks Lipid metabolism : Structure and function of lipids; fatty acid biosynthesis; synthesis of membrane lipids ,structural lipids and storage lipids; catabolism of lipids;; Sulphur metabolism: Sulfate uptake, transport and assimilation. Unit- IV Nitrogen Metabolism 20 marks Nitrogen of metabolism: Types of Nitrogen fixation, Biological nitrogen fixation; nodule formation and nod factors; mechanism of nitrate uptake and reduction; ammonium uptake, Nitrogen fixation by BGA and other plants Paper CC- 402 Biostatistics and Instrumentation 04 credits 100(80+20 marks) Unit I - Biostatistics I : 20 Marks General concepts; Frequency distribution : Bargraphs, histograms, polygons, curves; Central tendency: Mean, mode and median; Dispersion: Mean deviation, variance; standard deviation, Concept of probability: Addition and multiplicative theorems of probability; conditional probability; Theoretical distributions: Normal, Binomial and Poisson distribution Unit II - Biostatistics II : 20 Marks Estimation : Types of estimation; confidence interval land level of confidence Hypothesis testing : Test of significance; standard error of mean; t-Test: t distribution, student t-test and paired t-test; Chi square test: Chi square distribution and Chi square test for Goodness of fit; F -test: F -statistic and analysis of variance; Non-parametric test: General idea. Unit III - Instrumentation : 20 Marks Centrifugation: Principles of .centrifugation; normal,ultra, refrigerated, differential, density gradient methods of centrifugation;; Chromatography: General principles; paper, thin layer,adsorption, ion exchange, affinity, gel filtration techniques; GLC and HPLC; Electrophoresis :General principles; paper, starch gel, cellulose acetate, polyacrylamide, SDS polyacrylamide andagarose electrophoresis; isoelectric focusing; electroblotting; elctroelution; idea on tube gel, slab gel,gradient gel, 2D and immuno electrophoresis. Unit-IV Physical techniques :20 marks Spectrophotometry : Beer-Lambert law; colorimetry; principle and applications,, Microscopy, SEM and TEM. Mass Spectroscopy, X-Ray Crystallography PAPER CE-03 BIOTECHNOLOGY 04 credits Marks : 100 ( 80+20) Unit I - Basic Biotechnology: 20 Marks Restriction enzymes : Types and their role in genetic engineering and cloning; Vectors: plasmids, phages, cosmids, YAC and BAC vectors and their role in gene cloning; Cloning in bacteria and eukaryotes; Molecular probes: Types and uses; Blotting methods: Southern ,Northern, Western blotting; Dot and Slot blots; PCR technology: Normal, inverse and anchored PCR techniques; Gene isolation: Mechanism of isolation of gene; Gene sequencing: Maxim-Gilbert and Sanger's methods of sequencing Unit II - Plant Biotechnology : 20 Marks Tissue culture techniques : Culture room, culture media and aseptic conditions; Cell, tissue and organ culture: General and individual protocols and applications; Protoplast culture: Isolation and purification of protoplast; protoplast fusion and somatic hybridization; cybrids; production and importance of haploids; somaclonal and gametoclonal variations; Transgenic plants: Methods of gene transfer; use of plasmids with special reference to Ti and Ri plasmids; use of agrobacteria; transgenic plants Unit –III Environmental Biotechnology 20 marks Pollution Control, Treatment schemes for industrial waste, Solid waste management, Bioremediation and phytoremediation, use of GM microbes and natural microorganisms, Green Energy, Biofules, Bio sensor and their role in biomonitoring ,Environmental Impact assessment Unit IV - Medical Biotechnology and Ethics of Biotechnology : 20 Marks Use of genetically engineered Vaccines, MABs, Diagnosis of diseases using PCR, RFLP and VNTR principles, Targeted gene modification, skin grafting, Role of Biotechnology in fertility control Intellectual property rights: Copy rights, trade mark, patents etc; international conventions relating to patents, patents for microbes, plants and transgenic organisms; patenting of genes and DNA sequences; Rights of farmers: General idea with examples. PAPER CC-403 PAPER CE-04 PRACTICAL Marks : 100 PROJECTS 04 credits Practical of Paper CC-401 to CC-402 and CE-3 100 marks









