Hormone and Enzyme Sources and Targets
advertisement

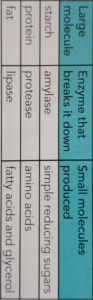
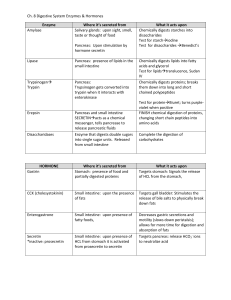
Name _______________________________ Hour____ Study the chart below and fill in the missing information about the following hormones that are activated during digestion. Hormone Triggered by Released from Actions Gastrin Vagus nerve; food in stomach, esp. undigested proteins G-cells within Gastric glands and also the duodenum Stimulates the stomach (prod. of acids and enzymes and also increase motility) Secretin chyme entering duodenum duodenum Stimulates pancreas to secrete buffers; slows down digestion in stomach; increases production of bile Cholecystokinin (CCK) chyme entering the duodenum containing lipids and partially digested proteins duodenum Stimulates pancreas to digestive enzymes; slows down digestion in stomach; causes gall bladder and liver to release contents; reduces feeling of hunger Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) chyme entering the duodenum containing many lipids and/or glucose duodenum Stimulates the release of insulin from pancreas, inhibits stomach Study the chart below and fill in the missing information about the following enzymes that are released during digestion. Enzyme Released by Optimal pH Breaks down Products amylase Salivary glands and pancreas 6.7 – 7.5 complex carbs disaccharides trisaccharides maltase, sucrase, lactase Small intestine 7-8 maltose, sucrose, lactose (disaccharides) monosaccharides pepsin chief cells in stomach 1.5 – 2.0 proteins; polypeptides short polypeptides trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase pancreas 7-8 proteins; polypeptides dipeptides, tripeptides peptidases small intestine 7-8 dipeptides, tripeptides amino acids pancreas 7-8 triglycerides (fats & oils) fatty acids and monoglyderides pancreas 7-8 nucleic acids nitrogenous bases and simple sugars CARBOHYDRASES PROTEASES LIPASES pancreatic lipase NUCLEASES nucleases