Menstrual Health Worksheet
advertisement

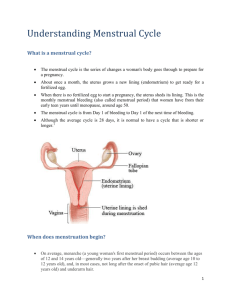
Name_________________________ Date__________________________ Instructor______________________ Health/Female Reproductive Health Menstrual Health/Female Reproductive Health Menarche First ____________ _____________ Average age in the United States ______ Normal age range _______ Factors: Length of normal cycle ______ In the first year or two menstrual periods are usually _______ ______ Amenorrhea ___________ of menstruation Primary amenorrhea –absence of menarche for more than _____ years Secondary amenorrhea – prolonged _________(about __ months or more) of menstrual bleeding after menarche has been established Oligomenorrhea ___________, __________ bleeding and/or a condition in which a female who is __ years past menarche has ___ to ___ cycles a year. An excess of _______ from the ovaries is often the cause. Dysmenorrhea Very _____________ menstruation There might be cramping, __________, and ___________ in the pelvic region as well as ___________, ______________, and __________. Primary dysmenorrheal is caused by _______ __________ and usually starts within three years of menarche and lasts _____ to ____ days each month. Secondary dysmenorrheal is associated with _______________________________, ________________, or ___________ ______________ later in life. Menorrhagia An abnormally ______ _________ flow. Affects about _______% of females of reproductive age worldwide Excessive bleeding should be _____________________________ Premenstrual Syndrome A combination of severe ________________ and _____________ symptoms during the four premenstrual and first four menstrual days of the menstrual cycle. Affects ___ to __% in the United States The physical and psychological symptoms include: Treatment includes_________ therapy, ________, exercise, _________ supplements, ________________________ and _______support and counseling. Toxic Shock Syndrome A ______, serious _________caused by certain ______________strains of Staphyloccus aureus __________________. Early symptoms include ____fever of more than _____,________,______,____________and a ______ that appears like a sunburn. Might progress to a dangerous drop in _________ __________ ____________ output is decreased and patients might be ___________ or _____________. Adult ________________ ___________ __________ or cardiac dysfunction might also occur. 96% of cases of TSS occurred in those who were ________________ The Staphylococcus aureus was localized in the ____________ The use of certain barrier contraceptive devices, such as the __________, have the _________ ______, and the __________ _______________ __________, have all been associated with nonmenstrual-related TSS cases. May 1980 CDC examined risk factors for TSS and found a significant relationship between TSS and __________use. Under the age of _______ with females between ________at greatest risk The Menstrual Cycle – a _________ cycle of approximately _____ month in which hormonal levels fluctuate to prepare a female’s body for the possibility of ____________. Three phases: 1. The Proliferative Phase, or ____________phase, is the first phase when _________ causes ____to ___ primary follicles to grow in the ovaries and when ____________ occurs. Graafian follicle- an immature primary follicle that balloons into full maturity in the middle of the menstrual cycle. The stigma – a small dot or nipplelike protrusion that develops on the surface of the Graafian follicle. Pituitary secretes LH causes stigma to disintegrate which causes Graafian follicle to rupture and release ovum. Ovulation – release of mature ovum by an ovary;occurs on or about 14th day before beginning of next menstrual period. 2. The Secretory Phase or _______________ phase. During this phase the __________ __________ secretes ________________ and _____________ to prepare a female’s body for the ______________ of a fertilized __________. Corpus luteum – yellow glandular body that is formed in the ovary from the follicular remains. 3. The Menstrual Phase - the _________ __________ degenerates, the secretion of ______ and _____________ sharply ________, and the menstrual flow occurs. Like the other two are under ___________ influence. It is related to the function of the __________ __________. The corpus luteum remains active for about _____ to ______ days. What happens during this time? Secretes estrogen and progesterone to prepare lining of uterus/Blocks FSH AND LH so that no new primary follicles begin to grow What happens when fertilization does not occur? What happens two days before the beginning of the menstrual flow? The secretion of estrogen and progesterone decreases sharply as corpus luteum degenerates. Cells shrink/blood vessels to lining of uterus closed/Lining of uterus dies. Menstruation is the process by which the ___________ of the _________ is ______________ each month that an ovum is not ____________. Approximately______ fluid ounce of blood, _____ounce of ________, and the ______of the ______are expelled. Bleeding lasts approximately _____ to ____ days, with the average being ____________. The menstrual flow marks the ____ of the three-phase female cycle. Menopause- the ____________of the monthly menstrual cycle as part of the natural process accompanying aging. This occurs on the average at age ___. What other factors can affect this process? What happens with the ovaries? Common symptoms- ____ ______ and decrease in the _________ and ______________ of the ___________. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) use of supplemental estrogen and progesterone to supplement or replace the decreasing amounts of hormones produced during menopause. --