Chapter 4 notes
advertisement

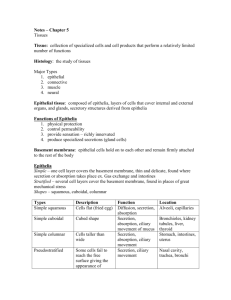
Chapter 4: Tissues Tissues are groups of I. Epithelial Epithelial and Glands formed of closely joined cells Regenerate well always underlain with avascular: Functions: 1. Provide physical protection 2. Control permeability 3. Provide Sensation 4. Produce specialized secretions Microvilli and cilia (fig 4-1) Intercellular Connections: cell adhesion molecules (CAM) intercellular cement: glycosaminoglycans – hyaluronan Cell Junctions tight junctions desmosomes (CAMS) gap junctions Connective tissue attaches by Basement Membrane: basal lamina: 1. Lamina lucida 2. lamina densa Classified by the number of layers and the shape of cells A. Layers: 1. simple: 2. stratified: B. Shape of Cells: 1. squamous: 2. cuboidal: 3. columnar: Types of epithelial tissues: 1. Simple Squamous: -good for -found in the linings of 2. Stratified Squamous: -most widespread -functions: -found in areas subject to friction: 3. Simple Cuboidal: -have large spherical central -found in glands: 4. Simple Columnar: -oval nucleus -may contain goblet cells: -some have cilia -ciliated found in 5. Pseudostratified Columnar -single layer of cells of -nuclei vary in shape & -function in -found in Glandular Epithelium -Most glands composed - secretion -2 types of glands: A. Endocrine Glands: B. Exocrine Glands: -Modes of secretion 1.) merocrine: exocytosis of secretions (mucin) 2.) apocrine: loss of cytoplasm with secretion 3.) Holocrine: destroys the cell – ruptures with secretion sebaceous glands -Types of secretions: 1.) serous glands 2.) mucous glands 3.) mixed Unicellular vs. Multicellular -Glands can be simple or compound in structure II. Connective •Functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Defends the body against Support and structure for __ cells and tissues Protects Storage sites for Forms rigid skeletal framework for body Limits ROM Transports and fights Cells associated with connective tissue 1. fibroblast: 2. macrophages: (free and fixed) 3. adipocytes: 4. mesenchymal: 5. melanocytes: 6. mast cells 7. lymphocytes 8. microphages: (neutrophils and eosinophils) Connective tissue consists of few cells with a lot of intercellular matrix - intercellular material: ground substance and fibers 1. Ground substance: 2. Fibers: 3 types A. collagenous: most abundant B. elastic: C. reticular: short, thin: Types of Connective Tissue: Loose Connective Tissues - large spaces between cells; unorganized fiber arrangement 1. Areolar: • consists mostly of collagenous fibers • fibroblasts, WBC • ”loose” arrangement of its fibers • good site for injecting medications 2. Adipose Tissue: (adipocytes) surround and protect adipocytes dominate tissue mass 3. Reticular Connective Tissue: •similar to loose connective tissue, but the only fibers in its matrix are reticular •forms a strom or internal framework that can support many free blood cells Dense connective Tissue (2) 1. Dense Regular Connective Tissue: •tightly packed bundles of collagenous fibers •referred to as white fibrous connective tissue •only has fibroblasts for cells •resists tension in •found: 1. tendons 2. ligaments 3. fascia 4. aponeuroses 2. Dense Irregular Connective Tissue: •contains more collagenous fibers than above •fibers oriented randomly: •found in: 1. dermis 2. fibrous coverings: (perichondrium), (periosteum), & (perineurium) 3. joint capsule Fluid connective Tissue Blood Lymph Supporting Connective Tissue (2) 1. Cartilage •numerous collagen fibers in a firm matrix •fibers/matrix formed by cells: -chondroblast: -chondrocytes: -lacunae •avascular: 3 types of cartilage A. Hyaline: most abundant -provides support with some pliability -articular cartilage -also found in: -precursor to bone B. Fibrocartilage (fibrous) -collagen fibers in thick bundles -slightly compressible -found in regions where -intervertebral discs, meniscal discs, and pubic symphysis C. Elastic -nearly identical to hyaline but -found in 2. Bone: • support and protects; provides cavities for fat storage and synthesis for blood cells • mineralized matrix constructed from • osteoblasts • bone well supplied by • single bone may be classified as an organ Membranes: 1.) mucous membranes -found in areas with opening -secrete mucin: -function 2.) serous membranes -found in -form parietal and visceral portions of pleura, pericardium, peritoneum -cells secrete clear watery fluid: 3.) cutaneous membrane: skin 4.) synovial membranes Fasciae (–a, singular) Superficial fascia Deep fascia Subserous fascia III. Muscular •highly cellular, well vascularized especially adapted for movement •3 types of muscle tissue: 1. skeletal: 2. cardiac: 3. smooth (visceral): IV. Nervous •brain, spinal cord, nerves •Two types of cells: neurons & supporting cells -neurons: generate and conduct nerve impulses -supporting cells: nonconductive cells; support, protect, insulate the neurons Tissue Response to Injury and Tissue Repair: First phase - Inflammation: short term (acute) inflammation has 4 symptoms: 1. 2. 3. 4. what causes this? 1. initial insult causes release of chemicals from neutrophils, macrophages, mast cells these chemicals cause • why is this good? a. helps dilute toxins b. brings c. brings 2. stasis: "standing" -slowdown of blood flow Second phase - Repair: 2 major ways: 1. regeneration: 2. fibrosis: scar tissue Aging, Tissue Structure and Cancer Review Selected Clinical Terminology pg.138