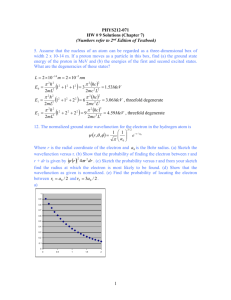
Rules for building an atom Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two e
advertisement

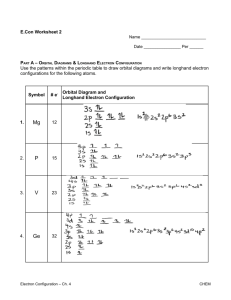
Rules for building an atom • Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two e- can have the same 4 quantum numbers Aufbau Principle: e- go into the lowest available orbital Hund’s Rule: e- try to stay unpaired if possible Note on magnetism: If an atom has unpaired e-, it has a weak, but measurable, magnet field paramagnetic. only paired electrons diamagnetic. To determine electron configuration 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f 5s 5p 5d 5f 5g 6s 6p 6d 6f 6g… 7s 7p 7d 7f 7g… Homework Pg 191 #1, Pg 194#6,7,8,10,11 Pg 197 #2, 4, 11 Read Pg 196 – Anomalous Electron Configurations Lab Exercise Quantitative Paramagnetism Pg 215 Prereading Pg 224-230, Pg 251-253 Building an atom Part 2 Determine electron configuration Determine the electron configuration of: a) Manganese b) Yttrium c) Iodide ion d) Zinc ion Short Form Electron Configuration Find the element on the periodic table. Look for the inert gas just previous to it. Use this as the core of you configuration. (i.e. [Xe]) Continue the pattern from there. Use what you know about the periodic table to help you. Short form configuration for silver. Special Electron Configurations Some elements, such as silver, have electron configuration different from what we would expect. Predicted: Actual: This is due to the fact that completely filled subshells, empty subshells, and half filled subshells are lower in energy. Orbital Diagrams A visual way of showing electron configuration. Figure out electron configuration Represent each orbital with a circle or a square. Put electrons in using lines or arrows For example:Strontium Homework Short form electron configuration for: a) zirconium b) arsenic c) iron 2+,3+ and 6+ Orbital diagram: a)bromine b) chromium Pg 197#6,7,9, 13