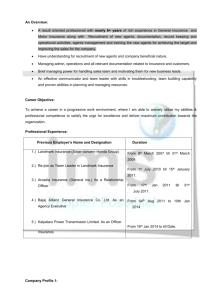
File - The Most Popular site
advertisement

IMT-56 Assignment-A Q1. “In a successful organization strategic planning works as the path finder to various business opportunities; simultaneously, it also serves as a corporate defense mechanism, helping the firm avoid costly mistakes in product market choices or investments.” Discuss this statement with reference to the nature & scope of strategic planning. A. Strategic planning provides the frame work for all the major business decisions of an enterprise, decisions in business, products & markets, manufacturing facilities, investments & organizational structure. Strategic Planning has the ultimate burden of providing a corporation with certain core competencies & competitive advantages in its fight for survival & growth. It is not just created for projecting the future but also for shaping the future in its favour. It is environmental uncertainty that make strategy & strategic conduct essential in a business. The more intense the environment uncertainty, more critical is the need for strategic planning. No business firm can afford to travel in a hap hazard crowd. It has to travel with a perfect plan or guide map. It provides discretion to the company & an competitive edge among the rivals. As a management tool it utilizes both logic & infilation to work out the prefect plan. From the above we can conclude the following: a) Strategic planning is concerned with the future or the long run term dynamics of the firm rather than day-to-day tasks. b) It is concerned with environment, the life between the business & its environment. c) Strategic Planning is concerned with growth direction, extent, pace, pattern & timing of growth. d) It is concerned with the basket of business the firm should have. More specifically it is concerned with the changes/ additions/ deletions to the finished product-market postures. e) Strategy is its concern, not the nuts & bolts of routine activities, growth priorities & choice of corporate strategies. f) Strategic planning is meant to equip the organization with capability needed to face in uncertainty. In other words the creation of competitiveness. g) Integration is its concern, a particular function is has its concern. It involves the top management tasks of taking the business forward. Hence the nature & scope of strategic planning can be defined as follows:1) It serves as a route map for the organization. 2) It lays down growth objectives of the firm. 3) It serves as a hedge against the inactivates of situations. 4) It helps to avoid the hap hazard response to the environment. 5) Provides the best possible fit between the firm & the external environment. 6) It helps to built competitive advantage & core competencies. 7) It seeks to influence the firm’s huge environs in its favour working into environment & sloping it. 8) It leads a frame work for systematic handling of corporate decisions. Q2. Distinguish between strategic decisions, administrative decisions & operational decisions. Explain how strategic planning accomplishes its purpose by providing a firm with an objective-strategy design. A. The strategic planning decisions totally differ from administrative & operational functions of management. The distinction arises because strategic planning deals with the strategic decisions in business. Strategic decisions are a class apart from administrative & operational decisions in their nature & implications. Strategic decisions are also the most difficult to handle. The major differences between strategic decisions & other types of decisions are as follows:1) Strategic decisions do not surface on their own, strategic planners/ top managers have to discuss what strategic decisions are needed, other decisions normally surface on their own. 2) Strategic decisions deal with the growth of the corporation. Accordingly they have a long range focus. Other decisions do not handle corporate growth as much. Operational decisions are routine ones. Administrative decisions, though not routine, by and large are occupied after existing practices in the company. 1 3) Administrative & operational decisions are concerned with issues that are essentially internal, matters which are purely internal issues related to structure, systems & staffing.Strategic decisions pertain to the relation between the firm & its environment, & therefore are concerned more with external issues. 4) Administrative & operational decisions do not touch the basic characteristics of the business of the firm. The decisions at these levels accept the business, the products, the markets, production facilities etc. as they are. The endeavor is to use them as efficiently as possible in tackling problem. Strategic decisions, on the other hand seek to alter, as found necessary, the basic characteristics of the business. 5) Strategic decisions involve intricate processes, external studies & analysis as they tackle long term issues. Strategic decisions always the support of external data/original information. Administrative & operational decisions generally need only internal information. 6) Operational & administrative decisions can be decided when necessary at minimized cost & without carrying any damage to the corporation. But in the case of strategic decision, they have a far reading & wide impact as the firm & its credibility. 7) The impacts of operational & administrative decisions are measurable & to some extent known in advance to those who take these decisions. But the consequences of the strategic in advance. 8) Strategic decision making is the responsibility of the top management. By their very nature, these decisions are centralized, where as the others are decentralized decisions. Strategic planning accomplishes its purpose by providing the firm an objective-strategy design. Strategic planning provides the firm with an early discernible, clear cut, objective strategy design which gives the firm the required directions. The objective strategy design actually amounts to a blue print for management activities. The objective-strategy design would contain the following elements:1) Growth objectives of the firm which essentially clarify the performance level & profitability targets the firm seeks to achieve. 2) Product market slope of the firm which specifies the business/market the firm will enter/stay with. 3) Growth vector which will indicate the direction in which the firm is moving in its products-market postures, whether its market penetration, market development, product development or diversification. 4) Competition strategy is the advantage of the firm, the attributes which will be support base for the strategy employed by the firm. 5) Synergy, the strength that emerges from linkages/joint experts between the firm & its new product market-selections. In the objective strategy design, provided by strategic planning, these five elements would be spelt out operationally, i.e. in a manner readily usable for management decisions & actions, intact these five elements:1) Growth Objective 2) Product market scope 3) Growth vector 4) Competitive advantage 5) Synergy Q3. The process of economic reforms & liberalization in India initiated in the early 1990s has made strategic planning a vital function for corporate managements. Discuss with reference to the elements of the new trade policy & its impact on established Indian businesses. A. Environmental changes which forced the firms to adopt a strategic perspective are as follows:1) Changes in Technology 2) Profilerations of new Products 3) The changing taste & preferences of the customer 4) Emergence of global brands 5) The new affluence of consumer 6) Social political changes 7) Faster commercialization of new product ideas & patents. 8) Emergence of global firms 9) Emergence of global markets 2 The new industrial policy brought major changes in the industrial environment of the country, liberalization has been the crux of N/P. A number of industries have been liberated from the clutches of licensing & control substantive have been introduced in matters like foreign investment & technology import, Monopolies & Restrictive Trade Practices (MRTP) & foreign exchange regulation Act (FERA) have been relaxed significantly & the role of the public sector has been curtailed. Details of New Industrial Policy:1. Liberalisation of Industrial Policy:a) Delicensing b) Decontrol c) Deregulations d) Broad Bonding e) Abolition of Registration 2) FERA Liberalisation: a) liberalisation of Direct Foreign Investment b) liberalisation of Technology import. 3. MRTP Liberalization: a) Abolition of threshold assets limits b) No MRTP clearance needed 4. Curtailment of Public Sector:a) Several industries wither to reserved for public sector opened up to private sector b) Only eight core industries remained reserved for the public sector c) Perview of Bcfd extended to new public sector The New Trade Policy:Liberalisation has been the crux of the new Trade Policy (NTP) too. The NTP has drastically changed the country’s foreign trade scene, releasing export import trade from the shackles of controls. At one strophe money of use age-old concepts. The main components of NTP are:1) Imports liberalized, deconlised license abolished 2) Lowering of import tariffs 3) Liberal exim regime 4) New exchange rate system & convertibility of rupees 5) Encouragement to exports 6) Encouragement to foreign investment 7) Integrating India’s economy with the global economy The sea change in the environment:1) Entrepreneurial freedom releases the growth impulse & alters industrial scene. a) Rush of entrepreneurs b) Spate of mergers & acquisitions/takeovers c) Diversification rush 2) Multi nationals consolidate their position a) MNC’s acquire in their Indian enterprises & jus’. b) Many MNC’s enter India a fresh through new job. c) MNC entry & investment alters core sectors like power, oil & telecom. 3) Imports go out of government domain & become entrepreneurial activity. a) Companies import materials free from licenses & by passing intermediaries agencies. b) Import trade emerges as a separate business opportunity. 3 4) Capital market undergo rational change. a) Capital market gain a new boundary b) FIT enter Indian Capital markets in a big way c) Foreign brokers follow the FITs d) Indian capital market getting integrated with global capital markets. 5) Banking sector comes under competitive environment a) Deregulation of interest rates land to competition in deposits. b) Disinvestment of government equity in rationalized banks c) New private banks with new technology, new products. 6) Financial services emerges as a major new business. a) Funding options multiply as capital can be raised in many ways. b) Emergence of many new financial services. c) A large basket of new financial services. 7) Ascendancy of the private sector a) Private sector enter all core industries. b) Oil, mining, telecom c) Road building, railway, ports, civil aviation. d) EPT Assignment-B Q1. (a) What do you understand by the term industry?(b) Explain with examples what is meant by fragmented industry, maturing industry, sunrise industry & declining industry? A. (a) Every organization is a part of industry. The industry is an environment concerned from the strategic planning point of view industry analysis & competitions helps the firm identity & build its competitive advantage. Industry analysis is done based on the following aspects:1) Several features/basic conditions of the industry 2) Industry environment 3) Industry Structure 4) Industry Performance 5) Industry Practices 6) Industry Attractives 7) Emerging trends in the industry/ the future of the industry. General features/basic conditions of the industry:- under general features/basic conditions of the industry, usually factors such as current size of the industry, product categories/ job categories their relative volumes, the preferences of the industry in recent years. Etc. Industry environment/ Industry setting:- Industries can be meaningfully classified based on their settings/ environment such as: Fragmented industries Emerging Industries undergoing a transition to maturity Declining industries Standard Industries Maturing Industry: Features of manufacturing industry can be listed as following: - Slowing demand generates head to head competition for market share 4 - Buyers are more sophisticated, driving harder bargain Greater emphasis on cost & service. Lower rates of market growth cause competitive pressure after producing a 1) Stock out of market competitors & 2) Skimmer profit margins industry-wide. Example- Auto Industry, Software Industry Sunrise Industry: Features of a sunrise industry may be listed as follows: - Market is new & empower - Companies grow & build mode - Buyers are first time users - Technological know how emerging - First generation products improve rapidly. Example- Insurance Industry Structure: Industry structure essentially means the underlying fundamentals economic & technical forces of an industry. Each industry will have its key structural features such as number of players, nature of competition etc. Hence the key elements are as follows:1) Number of players 2) Total market size 3) Relative shares of the players 4) Nature of competition. (monopoly, oligopoly etc.) 5) Differentiation practiced by the various players in the industry. 6) Barriers in the industry:a) Entry Barrier b) Mobility barrier c) Shrinkage Barrier d) Exit Barrier Industry Attractiveness:- The main determinants of industry attractiveness are:1) Industry potential 2) Industry Growth 3) Industry Profitability 4) Likely future pattern of Industry 5) Industry Barriers 6) Forces shaping competition in the industry. Declining Industry:- Following are the features:1) Demand grows slower as an economy-wide average or begins declining 2) Competitive pressure intensities, resulting in heated battle for market share 3) To grow & propose, firm must take market share away from rivals 4) Industry consolidates to smaller numbers of key players. Example- Steel industry, Court industry. Fragmented Industry:- Consumer market & industrial market are the areas where industries play their role. So far as the nature of fragmented industry is concerned the same is very much fragmented in nature. There are always some entrants & some players are leaving. This does not require huge investment hence entry & exit are easier. Examples - Book Publishing, Auto Repair. Q2. a) What do you mean by the term strategy? b) What are the constituents of a strategy statement? c) Explain in what way a business policy is different from strategy? A. a) The concept of strategy is central to understand the process of strategic management. The term ‘Strategy’ is derived from a Greek word ‘Strateyos’ which means generalship. The actual direction of military force, as distinct from the policy, governing its deployment. Literally therefore the word, ‘strategy’ means the art of the general. In business perform, there is no definite meaning assigned to strategy. It is often used coarsely to mean 5 a number of things. As per Alfred D.Chamdler (1962) strategy is the determination of the basic long term goals & objectives of an enterprise & the adoption of the course of action & the allocation of resources necessary for carrying out these goals. As per William F Ghicek (1972) Strategy is a unified, comprehensive & integrated plan, designed to assure that the basic objectives of the enterprise are achieved. As per Arthur Shabplin (1985) Strategy is a plan or course of action which is of vital pervasive or confirming importance to the organization as a whole. Deriving from all the above definitions:1) A plan or course of action or a set of decisions rules marking a pattern or creating a common thread. 2) The pattern of or common thread related the organization activities which are derived from the policies, objectives & goals. 3) Concerned with pursuing those activities which move an org. from its current position to a desired future state & 4) Concerned with the resources for implementing A. b) Each phase of strategic management process consists of a number of elements which are discrete & arbitiable activities performed in logical & sequential steps. As many as twelve different elements could be identified in the models provided by various authors which are following:1) Defining Business 2) Setting mission & vision 3) Determining purpose 4) Establishing objectives 5) Performing environmental appraisal 6) Doing corporate appraisal 7) Evolving strategic alternatives 8) Formulating strategies 9) Exercising strategic choice 10) Preparing strategic plan 11) Implementing strategies & 12) Evaluating strategies. A. c) Business policy is the study of the functions & responsibility of senior management, the crucial problem that affects success in the total enterprise, & the decisions that determine the direction of the organization & shape its future. The problems of policy in business, like those of policy in public affairs, have to do with the choice of purposes, the moulding of organization identity & character, the continuous definition of what needs to be done, & the mobilization of resources for the attainment of goals in the face of competition or adverse circumstances. The purpose of business policy is three-fold:1) To integrate the knowledge gained in various functional areas of management. 2) To adopt a general list approach to problem solving & 3) To understand the complex inter link operating within the organization through the arc of systems approach to decision making & evolving them to changes taking place in the external environment. Q3. Explain how the core ideology & vision of a company is interrelated with the business, a company is engaged in? Explain how in a company, mission is different than its vision? A. Vision of a company help in the following ways:1) Lends decision to corporate planning. In particular it directs the formation of the growth plan & guides the nature & pace of growth. 2) Helps the firm to clarify what its aspirations are, when exactly it would like to reach & what it would like itself to be. 3) Brings into clear focus the corporate purpose & long term objectives of the corporation. 4) Serves as the reference point in evolving the objectives as well as the strategies of the firm. 5) Helps the people at various level in the corporation understand in what decision they should move. 6 6) Helps the firm to make sense out of the changes in the environment & to decide which opportunities to tap. 7) Provides useful insights into its functioning & helps test its closed assumptions, brings to the fire the weakness in the conceptualization of business & styrategy. 8) Helps prevent people falling into an activity trap 9) Inspires the employees. It may be noted that the constituents of mission & vision are core ideology of the company as follows:Ambition & visionary Zeal: - are the main constituents of mission & vision. Values:- organizational values are the ext major constituent of mission & vision. It is values that hold the mission intact. Even while a firm’s different business operate with different strategies, the stored values of all the businesses keep the corporation together. Industry Performance: - Industry performance entails looking at production, sales, profitability & technological advancement. Industry Practices: - Industry Practices refer to what a majority of the players in the industry do with respect to essential aspects of the business such as distribution, pricing, promotion, methods of selling, service/field support, R&D and legal tactics. Emerging trend & likely future:- The emerging trends/likely future pattern of an industry can be discerned by analyzing issues such as the product life cycle stage of the industry, rate of growth, changes in buyers needs, innovations in products etc. Beliefs:- The mission & vision expresses the beliefs of the firm, Thomas Watson of IBM emphasizes the importance of beliefs in company mission as follows “ I firmly believe that any organization, in order to achieve success, must have a sound set of beliefs on which it premises all its policies & action. Specification of the business:- A specification of the business, too would form a part of mission & vision. Mission would indicate the areas of interest to the firm & the arena in which it seeks to play. Some experts are in the view that even specification of the firm’s products & markets would form part of mission & vision. It may be noted that mission & vision come alive & become relevant; it needs to be spelt out. It is through the mission that the firm spells out its vision. The corporate mission is an expression of the growth ambition of the firm. In other words the mission & vision are grand design of the firm’s future. Mission amplifies what brings the firm to this business or why it is there, amplifies what purpose it seeks to achieve as business firm. In other words, the mission serves as a justification for all firm’s very presence & existence, it legitimizes the firm’s presence. Difference between Vision & Mission:Vision 1) It expresses the growth ambition of the firm 2) It visualizes the firm’s future 3) It sets long term strategy of the firm 4) It defines the purpose of the business 5) It helps to evolve strategy of a firm. 6) It is amended with due permission of the CEO 7) Grand design of the firm’s future 8) It is a time bound approach Mission It explains firm’s existence & the role in the society. It shapes firms values & beliefs what it stands for, qualities it will cherish, what it will give & expect from the society. It explains role it will play in the society. It refers the point of guiding spirit for the growth plan of a firm. It lends direction to corporate planning It is amended according to the business environment. It is abstract It requires a zealous & ambitious approach. 7 ` Assignment-C Q1. How should a company define its business? Give the attributes of a good business definition. A. A business definition is a pity, clear cut statement of the business/businesses the firm is engaged in or is planning to pursue. It is an elaboration of the business areas it will play in. It prescribes the boundaries of the firm’s business, business definition clarities for the firm opportunities it can pursue & the area in which these opportunities are to be bored for. It also clarifies to the firm the various sources from which threats & competition can emanate. The firm understands its industry & its contours better. Business definition provides the blue print for the choice of product market and changes thereof. By delineating the boundaries of the business/businesses, the business definition serves as the reference point for the productmarket choices & corporate strategy of the firm. Defining Business:- Traditionally firms had the view for their businesses as one of the producing some goods or the other & had set their future plans around production of more of these goods & increasing profits. Such a view often shattered the future of the firm, it resulted in concentrating on what was happening in a very limited circle & planning all activities of businesses. Hence the concept of SBU’s may be indicated as following:1) A scientific method of grouping the businesses of a multibusiness corporation which helps the firm in strategic planning. 2) An improvement over the territorial grouping of businesses & strategic planning based on territorial units. 3) An SBU is a grouping of related businesses that can be taken for strategic planning based on territorial unit. 4) Products/business within an SBU receives same strategic planning treatment & priorities. 5) The tasks consist of analyzing & segregating the assortment of businesses/portfolios & regrouping them into a few, well defined, distinct, scientifically demarcated business units. 6) Product/businesses that were related to the stand point of function are assembled together as a distinct SBU. 7) Unrelated products/businesses in any group were separated. If they could be assigned to anyone. 8) Grouping the businesses in SBU lines help the firm in strategic planning. 9) Each SBU is a separate business form the strategic planning standpoint. 10) Each SBU will have its own distinct set of competitors & its own distinct strategy. With limited vision, the narrower the view prevented the firm from seeing the latest sources of competition. Evidently the corporation has to define its business as broadly as possible; it has to go beyond its immediate product, immediate competitors & immediate market boundaries. It must relate the definition to the basic needs the product seeks to satisfy, the main functions it performs will the benefit it provides. The definition must even encompass related functions & benefits. It must be wide enough to embrace new opportunities & provide a vision of latest sources of competition. Attributes of a good business definition: - A good business definition should meet the following requirements1) It must be wide enough to give a vision of latest sources of competition from substitute rpodicts. 2) It must be wide enough to embrace new opportunities 3) It must go beyond the immediate product. 4) It must be related to basic benefits the product offers. 5) It must be related to the basic benefits & functions performed by the product & not limited just to the product. Q2. Explain the difference between the competence & the capability of a firm? In what way benchmarking helps to establish the strengths & weaknesses of an organization? 8 A. Competence is the enduring strength of an company which cannot be easily imitated by the competitors & from which fevers & strong competitive advantages can keep emerging for the firm. On the basis of its resources & behaviors, an organization develops certain strengths & weaknesses which when combined lead to synergistic effects. Such effects manifest themselves in firms of organizational competencies. In other words the net result of the strategic advantages & disadvantages that exists for an organization determines its ability to compete with its competitors. Examples1) Superior product quality on a particular attribute, say a two wheeler which is more fuel efficient from its competitor’s product like Hero Honda. 2) Creation of a marketing niche by supplying highly specialized product to a particular market segment like Siemens precision instruments. Capability:- defined as the enhancing skill & technologies necessary to do something. Organizational capability is the inherent capacity or potential of the organization to use its strength & overcome its weakness in order to exploit opportunities & face threats in its external environments. Since organizational capability is the capacity or potential of the organization, it means that is measurable. Different types of an organization out of which following five are main:1) Financial capability 2) Marketing capability 3) Operations capability 4) Personnel capability 5) General management capability Benchmarking Is the process of finding the best available product features, processes & services and using them as a standard for improving a company’s own products, processes & services. It is based on the concept that it makes no sense to reinvent something that someone else is already using. It involves openly learning how others do something better than one’s own company so that one not only can imitate, but perhaps even improve on their current techniques. The benchmarking process usually involves the following steps:- Identify the area or process to be examined –an activity that has the potential to determine a business unit’s competitive advantage. - Find behavioral & output measures of the area or process & obtain measurements. - Select an accessible set of competitor’s & best-in-class companies against which to benchmark. - Calculate the differences among the company’s performance measurements & those of the best-in-class & determine why the differences exist. - Develop tactical programs for closing performance gaps. - Implement with those of the best-in-class companies. Benchmarking helps in appraising the firms position. The firm identifies & qualifies the performance gap-the gap between its own performance & benchmark & bridges the gap. Firm’s resort to take different types of benchmarking:Internal Benchmarking:- means comparison within an organization typically between related division, similar products, similar plants, similar operation. Functional Benchmarking:- refers to comparison of the firm’s performance against functional areas with other firms Competitive Benchmarking:- is the comparison of a company performance against the best in the same industry. Example:- “Xerox Corporation” in the united states pioneered this concept when it is found that foreign competition could sell its equivalent copier at a price equal to Xerox’s manufacturing cost. To find a benchmark, Xerox used its Japanese affiliate. Fuji Xerox, as a window into the competition. Xerox was able to streamline its own operations without compromising service or quality. Xerox ahs also looked internally for benchmarks, identifying the locations or units within its own organization that the best processes, then bringing the other locations or units upto the same performance level. 9 Benchmarking has reduced service labor cost of Xerox & substantially raised the productivity role of its distribution organization. Q3. What is meant by the core competence of an organization? Should it be treated as a constraint to enter into new business areas? A. A core competence in an organization is an enduring strength of an organization which cannot be easily imitated by the competitors & from which newer & stronger competitive advantages can keep emerging for the firm. Only firm’s who enjoy such strength, which is very fundamental & unique to the firm, keep winning in an enduring manner. Attributes of Core Competence: 1) Core competence is a fundamental, unique & inimitable strength of the firm that a) provides the firm the access to a variety of products/markets b) is an exclusive presence of the firm & cannot be imitated easily by competitors. 2) A core competence is largely technological competence, a competence in the root technology in particular 3) This is so because, new business/new products are largely the result of technology 4) This is especially free in today’s driven world, where technology is fast altering existing boundaries of business. 5) Corporations who enjoy a core competence in the root technology/process expertise keep gaining lasting advantages through new & proprietary products & fresh value enhancements. 6) For firms who are to play the business game through the product roots, core competence is particularly essential. Acquiring of core competence: Acquiring of core competence is much more difficult than acquiring a competitive advantage technological excellence, especially competence as the root of technologies, capacity to integrate multiple streams of technologies & the expertise to harness diverse production skills are some of the requirement for acquiring core competence. Obviously building core competence, it is necessary for firms to develop the human expertise that would use the technologies as building blocks & work in them. And only through expertise over several technologies & a command over their infinite variety of uses & applications can a firm aspire to develop a core competence. It is through this route that firm’s bring out proprietary products which confer on them an advantage of a lasting kind. This become particularly relevant in an era where technology is fast altering existing boundaries of the business. The core competencies concept does not restrict number of business a firm can be in. The core competencies concept sometimes misunderstood as a perspective that restricts the number of business a company can be in. Firms wrongly assume that when they adopt the concept of core competence, it compels them to remain with a single business which would be their core business. This is far from true. The core competency concept does not restrict the number of businesses. And with two or three core skills, a firm can have a large basket of businesses. The business will of course be having a linkage with the core ship. Assignment-D Q1.Explain the need for a business firm to survey the environment on a continuous basis. How does a SWOT analysis help a firm in strategic planning? A. Environment literally means the surroundings, external objects, influences under which or something exists. Business environment exhibits many characteristics. Some of the important & obvious characteristics are as follows: 10 1) Environment in complex 2) Environment in dynamic 3) Environment is multifaceted 4) Environment has a far reaching impact. The main purpose of environmental survey is to spot the opportunities & threats emerging in the environment. After providing a general indication of opportunities the pursuit of which will help the firm fill the gap between its currently achievable performance & the growth objectives of the firm has set for itself. To be more specific, the survey will highlight the opportunities of growth within & outside the existing business of the firm. It will also check the attractiveness & probability position of these opportunities. In other words environmental survey places before the firm list of carefully picked business opportunities out of which the firm can make its final choice. It also provides the firm the backup knowledge required for making the choice. It also highlights the merits of the various opportunities & routes them appropriately. Hence purpose of the environmental survey may be listed as following: 1) To learn about events & trends in the environment & project the future position in each factor of the environment 1from the stand point of the firm. 2) To identify the favorable & unfavorable factors in the environment of the firm. 3) To figure out the opportunities & threats hidden in environmental events & trends. 4) To assess the scope of various opportunities & short list ones which have the potential of becoming promising businesses. 5) To draw up the probability-attract position of the opportunities. Importance of environmental survey: Since a business firm functions as a part of the environment, study of environment becomes central to strategic planning. The firm has to adopt itself to the realities of the environment. It is the environment that the firm searches for & find its opportunities. And it is by tapping the opportunities present in the environment. That is why experts in strategy invariable consider study of the environment as the central task of strategic planning. Nature & scope of Environmental Survey:Basically, in its attempt ar environmental survey, a firm gathers all relevant information relating to the environment & studies them in details. It takes note of the changes currently taking place in each of the component factors of the environment & tried to forecast the future position in each of them. Component factors of environment to be covered under environmental survey External Factors:1) Demographic 2)Political/Legal 3) socio-cultural 4) Economic 5) Technological Internal Factors:1) Threat to new entrants 2) power of buyers 3) Power of suppliers 4) Intensity of Rivalry 5) Product Substitutes. SWOT Analysis:- As understandings of the external environment in terms of the opportunities & threats & the internal environment, in term of the strength & weakness is essential for existence, growth & profitability of any organization. A systematic approach to understanding the environment is the SWOT analysis. An opportunity is an favorable condition in the organization environment which enables it to consolidate & strengthen its position. A threat is an unfavorable condition in the organization which creates a risk or causes damage to the organization. Strength is a inherent. Capacity which an organization can use to gain strategic advantage over its competitors. A weakness is an inherent limitation or constraint which creates a strategic disadvantage. Through SWOT analysis, the strengths & weakness existing within an organization can be matched with opportunities & threats operating in the environment so that an effective strategy can be formulated. An 11 effective organization therefore, is one which capitalizes on the opportunities through the use of strength & neutralizes the threats by minimizing the impact of weakness. Q2. Explain how the concept of grouping business into strategic business units (SBUs) is useful in multiproduct, multi-business enterprises. Discuss how the BCG growth matrix helps a firm to analyse its product portfolio. A. Strategic Business Units (SBUs) are divisions or groups of division composed of independent productmarket segments that are given primary responsibility & authority for the management of their own functional areas. An SBU may be of any size or level, but it must have (1) a unique mission, (2) identifiable competitor’s. (3) an external market focus, & (4) control of its business functions. The idea is to decentralize on the basis of strategic elements rather than on the basis of size, product characteristics, or span of control & to create horizontal linkages among units. For Ex- rather than organize products on the basis of packaging technology like frozen foods, canned foods, & bagged foods, General foods organized its products into SBUs on the basis of consumer oriented menu segemtns: breakfast food, beverage, main meal, desert, & pet foods. An SBU is a grouping of related products businesses which is amenable to composite planning treatment. As per this concept, a multi business enterprise groups to multitude of businesses into a few distinct business units into a scientific way. The purpose is to provide effective strategic planning treatment each one of its product/businesses. The principle underlying the grouping is that all related products-related from the stand point of ‘function’ should fall under one SBU. In other words, the SBU concept helps a multi-business corporation carry out its strategic management endeavors better. The concept provides the right direction to strategies planning by removing the vagueness & confusion often experienced in such multi-businesses. PRESIDENT Corporate R&D Corporate Finance Strategic Business Unit A Strategic Business Unit B Division Strategic Planning Corporate Marketing Strategic Business Unit C Unit D Division Division Division Corporate HR Strategic Business Division Fig: SBU STRUCTURE BCGA Growth-Share matrix The BCG ( Boston Consulting Group) Growth share Matrix is the simplest way to portray corporation’s portfolio of investments. Each of the corporation’s product lines or business units is plotted on the matrix according to both the growth rate of the industry in which it competes & its relative market share. A unit’s relative competitive position is defined as its market share in the industry divided by that of the largest other competitor. By this calculation, a relative market share above 1.0 belongs to the market leader. The business growth rate is the percentage of market growth, i.e. the percentage by which sales of a particular business unit classification of products have increased. The matrix assumes that, other things being equal, a growing market is attractive. The lines separating BCG Growth Share Matrix 22 20 Business growth Rate (%) Stars Question marks 18 16 12 14 8 12 10 Cash Cows 6 4 2 Dogs 4x 2x 1.5x 1x .5x .4x .3x .1x Relative competitive position (Market share) areas of high & low relative competition position is set at 1.5 times. A product line or business unit must have relative strength of this magnitude to ensure that it will have the dominant position needed to be a “Star” or “Cash Cow”. On the other hand product line or unit having a relative competitive position less than 1.0 has “dog” Status”. Each product or unit is represented by a circle. (in fig.). The area of circle represents the relative significance of each business unit or product line to the corporation in terms of assets used or sales generated. The BCG Growth Share matrix has a lot in common with the product life cycle. As a product moves through its life cycle, it is categorized into one of four types for the purpose of finding decisions: Stars: - stars are net market leaders typically at the peak of their product life cycle & are usually able to generate enough cash to maintain their high share of the market. When their market growth rates slows, stars becomes cash cows. Question Marks: - Sometimes called “problem Children or “wild cats” are new products with the potential for success, but they need a lot of cash for development. Cash Cows: - typically bring in far more money than is needed to maintain their market share. In this declining stage of their life cycle, these products are “milked” for cash that will be invested in new Question marks. Dogs: have low market share & do not have the potential because they are in an unattractive industry, to bring in much cash. According to the BCG growth share matrix, dogs should be either sold off or managed carefully for the small amount of cash they can generate. Underlying the BCG Growth-Share Matrix is the concept of the experience curve-suggests that unit production costs decline by some fixed percentage (commonly 20-30%) each time the total accumulated volume of production in unit doubles. If a company is able to use the expensive curve to its advantage, it should be able to manufacture & sell new products at a price low enough to garner early market share leadership. Once the product becomes a star, it is destined to be very profitable, considering its inevitable future as a cash cow. BCG enables a company to project their future positions, assuming no change in strategy. Present & projected matrixes can thus be used to help identify major strategic issues facing the organization. It also helps a company to maintain a balanced portfolio, so it can be self-sufficient in cash & always working to harvest mature products in declining industries to support new ones in growing industries. Q3. “A business organization cannot remain in business with out being socially relevant & responsible. Discuss & comment upon the above mentioned statement? A. The issue of social responsibility evokes varying & often extreme responses from academicians & businessman. At one end, the body of opinion clearly does not favors including social responsibility of business is to perform its economic functions efficiently & provide goods & services for society & even maximum people profits, by doing so it is felt, its economic functions & leaves the social functions to other institutions of society such as the government. At the other extreme, there is an opposite view which favors the position that it is imperative for business to be socially responsible. This is based on the argument that business organizations are a part of society & have to serve primarily societal interest. In between the two extreme views note is a considerable support for the opinion that all business organization should not attempt to solve all, or any type of social problems. Rather, social responsible ness should be exercised on a selective basis & responsibility is limited to those areas where 13 the business organization can achieve its self enlightened interests. In other words, the economic goals & social responsibility objectives needs not be contradictory to each other & should be achieved simultaneously. Short Answers Q1. What do you understand by the term Synergy? A. Synergy is an idea that whole is greater or lesser than the sum of its parts. It is also expressed as the two plus two is equal to five or there effects. Within an organization synergistic effects may occur when the product, pricing, distribution & promotion aspects supports each other resulting in a high level of marketing synergy. Q2. How can synergy give competitive advantage to a firm? A. Synergistic effects are the coherent nature of organization that strength & weakness like resources & behavior, do not exist individual but combine in a variety of ways. For instance two strong points in a particular functional area can add upto something more than double the strength. Likewise two weakness activity in a fonder result more than double the strength or the damage. In this however, synergistic effects are an important determinant of the quality & type of the internal environment existing within an organization. Q3. Differentiate between External & internal components of environment? A. The external environment includes all the factors within an organization which imports strength or cause weakness of a strategic nature. The environment in which an organization exists can, therefore, be described in terms as the opportunities & threats operating in the external environment apart from the strength & weakness existing in the internal environment. Q4. Why are strategists interested in determining organizational capability? A. Organizational capability is the inherent capacity or potential of an organization to use its strength & overcome its weakness in under to exploit opportunities & face threats in its external environments. Organizational capability factors are the strategic strengths & weakness existing in different functional area within the organization. Q5. What are the factors that affect organizational appraisal? A. The factors that affect organizational appraisal are: 1) Strategies:- the ability of the strategists to comprehend complexity determines how well the different forces & influences, operating within the internal environment are analyzed. 2) The organization:- the size of the organization effects the quality of appraisal. Coyer organizations operating within the internal environment are analyzed. 3) The internal environment:- if the internal environment of the organization is imitated owing to opposing political forces & power games, the quality of appraisal is likely to suffer. 4) Q6. What sources of information can be used for appraising an organization? A. The strategist need to tap different types of information sources may be verbal as well as written. They may also be internal as well as external sources. The assessment of organizational capability may rely in employer’s opinion, company files & documents, financial statements, the management information system & other internal sources for comparative appraisal with similar organization in the industry & across industries, it may be necessary to have access to industry association, & other documentary sources like magazine & journal. Q7. How is the strategic advantage profile of a firm prepared? A. The strategic advantage profile (SAP) clearly shows the strength & weaknesses in different functional areas. A SAP can be prepared based on the detailed information presented in the organizational capability profile. An SAP can also be prepared directly through class room learning without making a detailed organization capability profile. A SAP provides the most critical areas which can have a relationship of the strategic posture of the firm in the future. Q8. What is the purpose of doing competitor analysis? A. The purpose of doing competitor analysis is to 1) determine each competitor’s probable relation to the industry & environmental change 2) anticipate the response of each competitor to the likely strategic monies by the other firm & 3) develop apeotile of the nature & success of the possible strategic changes each competitor might undertake. 14 Q11. Distinguish between Merger, Acquisition, Takeover? A. Merger: A merger is a transaction involving two or more corporations in which stock is exchanged, but from which only one corporation survives. Mergers usually occur between firms of somewhat similar size & are usually “friendly”. The resulting firm is likely to have a name derived from its composite firms. One example is the merging of Allied corporation & signal companies to form Allied Signal. Acquisition : is the purchase of a company that is completely absorbed or an operating subsidiary or division of the acquiring corporation. Acquisitions usually occur between firms of different sizes & can be either friendly or hostile. For ex- Procter & Gamble’s acquisition of Richardson-Vicks, known for its oil of olay & vidal Sassoon brands, & Noxell corporation, known for Noxzema & cover girl. Take over: hostile acquisitions are often called takeovers. A takeover involves the acquisition of a portion or whole of the equity capital of another firm, which enables the acquires to exercise effective control over the affairs of the takeover firm. Takeover is considered as an unfriendly act & in negative parlance. Q12. How are joint ventures & strategic alliances convenient routes for expansion strategy? A. A joint venture is a “cooperative business activity, formed by two or more separate organizations for strategic purposes, that creates an independent business entity & allocates ownership, operational responsibilities, & financial risks & rewards to each member, while preserving their separate identity/ autonomy.” Along with licensing arrangements, joint ventures lay at the midpoint of the continuum & are formed to pursue an opportunity that needs a capability from two companies or business units, such as the technology of one & the distribution channels of another. Joint ventures provide a way to temporarily combine the different strengths of partners to achieve an outcome of value to both. It constitutes a fast & economic route for gaining increased competitive capabilities. For ex- Toys “R” Us & Amazon.com formed a joint venture in August 2000 called Toysrus.com to act as online toy store. Amazon was to include the joint venture on its web site, ship the products, & handle customer service. In turn, Toy “R” Us was to choose & buy the toys, using its parent’s purchasing power to get the most desirable toys at the best price. Strategic Alliance is a partnership of two or more corporations or business units to achieve strategically significant objectives that are mutually beneficial. Strategic alliances help the business for expanding its strategy for following: - To obtain technology and/ or manufacturing capabilities. Ex- Intel formed a partnership with Hewlett-Packard to use its capabilities in RISC technology in order to develop the successor to Intel’s Pentium microprocessor. - To obtain access to specific markets:- rather than buy a foreign company or build breweries of its own in other countries, Anheuser-Busch chose to license the right to brew & market Budweiser to other brewers, such as Labatt in Canada, Models in Mexico, & Kion in Japan. - To reduce financial risk:- because the cost of developing a new large jet air-plane were becoming too high for any one manufacturer, Boeing, Aerospatiale of france, British Aerospace, & Deutsche Aerospace of germany planned a joint venture to design such a plane. - To reduce political risk:- to gain access to China while ensuring a positive relationship with the often restrictive Chinese government, Maytag Corporation formed a joint venture with the Chinese appliance maker, RSD. - To achieve to ensure competitive advantage:- General Motors & Toyota formed Nummi Corporation as a joint venture to provide Toyota a manufacturing facility in the United States & GM access to Toyota’s low-cost, high quality manufacturing expertise. Q13. What are the four generic strategic routes a firm can take? A. The four generic strategic routes are: - Low cost strategy:- is the ability of a company or business unit to design, produce & market a comparable product more efficiently than its competitors. - Differentiation Strategy:- is the ability to provide unique & superior value to the buyer in terms of product quality, special features, or after sale service. 15 - Divestment strategy:- the firm retrenches some of the activities in a given business(es) or drops the business as such through sell-out or liquidation. Combination Strategy:- the firm combines the above strategic alternatives to some permutation/ combination so as to suit the specific requirement of the firm. Q14. Under what conditions is retrenchment the best decision to take? A. Conditions under which retrenchment is the best decision to take are: - Obsolescence of product process. - business becoming unprofitable. - high competition - industry over capacity - failure of strategy - stability ensured by relocating resources from unprofitable to profitable business. Q15. Stability strategy is best followed after a period of rapid expansion. Why? A. Rapid expansion help a firm gain control on the market, psyche of the customers & redefine the business definition. Once the expansion strategy makes it mark by fresh investment & new businesses/ product/ markets, it is but natural the firm has to maintain its position in the market, the firm will have to endeavour its functional efficiencies in an incremental way through better deployment & utilization of resources. A corporation may choose stability over growth by continuing its current activities without any significant change in direction. Q16. How can takeovers be used as an effective external expansion strategy? A. A takeover involves the acquisition of a position or whole of the equity capital of another firm which enables the acquirer to exercise effective control over the affairs of the taken over business. Takeover thus constitutes external expansion. When market dynamics compel a firm to go for wide reach & deep penetration of the market, the firm has to expand & reovert its business outlook. At that stage takeover routes help to expand substantially. For ex- GE gaps which in 1997 picked up 50.5% stake in SRF finance. The assets of GE caps grew from Rs 700 crore-Rs 950 crore, its marketing network of 10 branch offices grew to 20 branch offices & it got a ready customer base for SRF’s 1,36,000 strong depositors. Hence we se that takeover provide a route for instant expansion. Q17. What leads to hostile takeover in a firm by another? A. Non-transparency in takeover deal, unfair means adoption by the acquirer, clashing of mutual intents if the concerned parties & keeping the workforce in the dark lead to hostile takeover. The takeover is considered hostile when the company being acquired resists the attempt or does not give consent. This leads to hostile takeover which is generally considered as a raid over a company. Q18. Business ethics are essential for all successful business. Explain? A. Ethics is defined as the consensually accepted standards of behavior for an occupation, trade or profession. Ethical responsibilities of an organization’s management are to follow the generally hold beliefs about behavior in a society. Business ethics operated as a system of values & code of conduct that an organization needs to follow in the process pf achieving its goals. Business ethics are important because: - Ethics correspond to basic human needs. All of us want to be ethical in our personal lives & in business dealings. - Values create credibility with the public. An organization perceived by the public to be ethically & socially concerned will be honored & respected even by those who have no intimate knowledge of its actual functioning. - Values lend management credibility with employees - Values help in better decision making-decisions which are in the interest of the public, the employees & in long term the company itself. - Business which shows high concern for ethics tend to show highest growth & profits. 16 For ex- “Reebok International has developed a set of human rights production standards for the manufacturers that supply the company with its athletic shoes on a contract basis. Reebok requires that its suppliers (1) not discriminate on the grounds of race, color, national origin, gender, religion or political opinion, (2) don’t normally require more than a 60-hour work week, (3) don’t yse forced labor, (4) provide fair wages & benefits, (5) don’t employ children, (6) provide a safe & healthy workplace. Q19. How are forecast relevant to business policy? A. Forecast is essentially a technique of anticipation. It provides key information & pertinent facts relating to the future. Without forecasting planning is impossibility. It is the very basis of planning. Forecasts are predictions or estimates of the change, if any, in characteristic economic phenomena which may effect one’s business plans. It implies the act of making a detailed analysis of the past & present to gain a foresight for future, & bring exactness & accuracy in managerial decisions. It enables a manger to probe the future economic, social & political factors that might influence his decisions & his company. By forecasts various internal & external factors, a business can plan to obtain maximum benefits from periods of expanding economy, & on the other hand, to minimize & adverse effects when business activities slacken. It ensures better utilization of resources by extending the frontiers of control in several directions. It steers the whole enterprise safely for the fixed destination, as outlined by the objectives of the organization. It awakens the management about business. Q.20 Differentiate between strategy, goals & targets? A. Strategy:- A Strategy of a corporation forms a comprehensive master plan stating how the corporation will achieve its mission & objectives. It maximizes competitive advantage & minimizes competitive disadvantages. Business historian Alfred D. chandler proposed that “strategy” be defined as “the determination of the basic long-term goals & objectives of an enterprise, & the adoption of courses of action & the allocation of resources necessary for carrying out these goals. Ex- Rockwell International corporation realized that it could no longer achieve its objectives by continuing with its strategy of diversification into multiple lines of businesses, it solds its aerospace & defense units to Boeing. Rockwell instead chose to concentrate on commercial elctronics, an area that management felt had greater opportunities for growth.” Goals:- An open ended statement of what one wants to accomplish with no quantification of what is to be achieved, & no time criteria for completion. By setting goals, people & their organizations bolster their motivation & gain a source of inspiration that helps them overcome the inevitable obstacles they counter. Ex- “Top management at Samsung has set a new goal: to become one of the world’s ten largest ‘technological Powerhouses.” To make this happen Samsung, a $54billion maker of electronics & semiconductors, chemicals, machinery, & constructive equipment as well as provider of services such as insurance & credit cards, is embarking on a new strategy. Mangers are reordering Samsung investment priorities, refocusing on product development, & taking steps to radically improve quality.” Targets:- are quantifications, specified, short & medium quantitative. Q21. What are the desirable characteristics that objectives should possess to be effective? A. Objectives are the end results of the planned activity. They state what is to be accomplished by when & should be quantified if possible. The achievement of corporate objectives should result in the fulfillment of a corporation’s mission. The desirable characteristics that objectives should possess to be effective are: - Objectives should be well formulated, specific, unambiguous, quantified, attainable, controllable & time bound. - They should be challenging, yet achievable once motivated. - Objectives should have clarity so that everyone understands them. - Proper prioritization should be there. - Objectives should be simple so as even a layman can understand them. Q22. What difficulties arise if objectives are not clearly measurable & controllable? 17 If the objectives are not clearly measurable one cannot fund the performance & progress of the firm. We will not be able to tell whether it is going in the right direction or not & if it is achieving the target or not. The organization will grape in the dark & enumerate productivity, ensure better technology etc. If the objectives are not controllable then if the firm is not on the right path it cannot be brought back on the right track. For Ex- Productivity cannot be increased, employee turnover cannot be decreased etc. Hence the objectives should be clearly measurable & controllable. A. Q23. Are societal strategies & mission statements identical? A. No, Societal strategies & mission statements are not identical. Societal strategies hold that the organisation’s task is to determine the needs, wants & interest of target markets & to deliver the desired satisfactions more efficiently & effectively than competitor’s in a way that preserves or enhances the consumer’s & the society’s well being. Whereas mission statements defines the fundamental, unique purpose that sets a company apart from other firms of its type & identifies the scope of company’s operations in terms of products offered & markets served. The mission statement p0romotes a sense of shared expectations in employees & communicates a public image to important stakeholder groups in the company’s task environment. Examples- Mission Statement of Maytag Corporation:‘To improve the quality of home life by designing, building, marketing, & servicing the best appliances in the world. Mission statement of Newport News Shipbuilding:‘We shall build good ships here- at a profit if we can –at a loss if we must-but always goodships. Q24. What role does creativity play in decision making? A. Creativity means the generation of ideas. The generation of idea in an organization depends first & foremost on the flow of people & information between the firm & its environment. It relates to intution, intellectualism & logicality of human mind. Decision making is based upon lead information, facts & figures. But a manager who is visionary cannot make a decision only on the basis of facts & figures. To scan the internal & external environment crucial & pertinent to the decision he has to blend his creativity with the facts & data presented before it. All strategic decisions are supplemented with a lot of creativity. Q25. What is the entrepreneurial-opportunistic approach for strategic planning? A. This approach is characterized by a constant search for opportunities & exploiting them to the benefit of the organization. Entrepreneurial strategic decision making is based on the perceptions of opportunities, diagnosing them for the generations of alternatives, analyzing the consequences & selecting the course of action that would best meet the objectives. Such an approach is generally adopted by entrepreneurs & family business executives but may also be adopted by managers in organization. Q26. Why is the role of entrepreneur in strategic management termed as ‘ proactive’? A. According to Peter Drucker “the entrepreneur always searches for change, responds to it & exploits it as an opportunity.” Often defined as a person who organizes & manages a business undertaking & who assumes risk for the sake of profit, is the ultimate strategist. He or she makes all the strategic as well as operational decisions. Entrepreneur has been usually considered as a person which starts a new business, has a high level of achievement-motivation & is endowed with qualities of enthusiasm, idealism, independence of thought & action. By their very nature entrepreneurs are proactive. They scan the environment, find an opportunity, approach the situation & decisions to the benefit of the organization. They provide a sense of objectives to the company, set objectives & formulate strategies to achieve them. Q27. Is strategic decision making the same as the conventional decision making? Explain? A. A conventional decision making is the process of selecting a course of action from among alternatives. The steps are (a) the objectives to be achieved are identified, (b) alternative ways of achieving the objectives are identified, (c) each alternative is evaluated in terms of its objective-achieving ability, (d) the best alternative is chosen. Strategic decisions deal with the long-run future of the entire organization & have three characteristics: - Rare: Strategic decisions are unusual & typically have no precendent to follow 18 - Consequential: Strategic decisions commit substantial resources & demand a great deal of commitment froom people at all levels. - Directive: Strategic decisions set precendents for lesser decisions & future actions throughout the organization. Q28.What is Derek Abell’s three dimensions along which a business can be defined? A. Customer Functions Alternative Technologies Customer Groups Derek Abell defined business along three dimensions, Customer groups- relate to who is being satisified. Customer functions-what is being satisfied. Alternative technologies-how the need is being satisfied. Q29. What is market driven price environment? A. In a market driven price environment the prices are fixed by the demand generated. The basic feature of market driven price method is that profits can be expected independent of the costs involved, but are dependent on the demand. As the demand increases the price increases & vice-versa. The following are the methods of pricing in a market driven price environment: - “What the tariff can bear” pricing - skimming pricing - penetration pricing Hence in a market driven price environment prices are dependent on the market demand. Q30. Under what circumstances should a firm go for diversification spree? A. Firms go for diversification spree for the following reasons: - when the growth ambition of the firm are high & cannot be met by existing business/ product market scope - when the firm needs flexibility in business portfolio for countering vulnerability - when unusually large number of opportunities come up in the environment & firms are strongly tempted towards diversifications. - Uncertain environment propels the firm towards diversification. - There is scope for higher profitability - When the firm has surplus strength & resources exceeding the requirements of existing business it may be sensible to diversify. - It has synergies that would be relevant in trapping emerging opportunities - When a change enlarges the firms mission. Q31. Is diversification a resource intensive strategy? Discuss? A. Yes, diversification is a resource intensive strategy. The diversifying firm should have the required resources. Getting into new business-whether through startup route, acquisition or joint venture- necessitates high investment. The entry as well as day to day battle for scanning market in the new business is resource intensive processes. Intrinsically new businesses, in particular, may need strong staying power as they often involve longer gestation. The firm has to carry out thorough stock taking of current status of its competitive, strength & resources. It has to decide whether the strengths & resources needed for handling the risk & lower synergies inherent in diversification. Relevant core competence is a key resource required for diversification. Diversification needs support of competitive advantage unique to the business & building each competitive advantages is a resource-intensive job. Q32. Why is divestment strategy adopted? A. If the corporation has multiple business lines & it chooses to sell off a division with low growth potential, this is called divestment. Divestment strategy is adopted: - when a firm funds that some of its businesses have become unattractive, unprofitable & unviable. 19 - Obsolescence of product/ process. Firm is unable to compete successfully When the business is in the decline stage of the PLC. When a firm perceives some environmental threat As a matter of policy the firm decides not to be present in business where it is not a major player holding no.1 or no.2 position. When the firm sees alternative opportunities in some business while its resources are locked up in certain unprofitable business, it can consider divestment of better. a redefinition of company’s business or a rearrangement of the priorities of the business takes place. Q33. Explain what is concentric diversification? A. When an organization takes up a new business in such a manner that it is related to the existing businesses through process, technology or marketing it is called concentric diversification. The new product is a spin-off from existing facilities & products/ processes. Thus in concentric diversification there are benefits of synergy with current operation. In concentric diversification, the product is only connected in a loop-like manner at one or more points in the firm’s existing process/ technology/ product design. The firm may choose to diversify concentrically through either internal or external means. Q34. Explain what is backward & forward integration? A. The degree to which a firm operates vertically in multiple locations on an industry’s value chain from extracting raw materials to manufacturing to retailing is known as Vertical integration. It is of two typesbackward & forward integration. Backward integration:- assuming a function previously provided by a supplier is called backward integration (going backward on an industry’s value chain). It occurs when the organization moves towards the source of raw materials for its existing product by entering into a new business which involves supplying the raw material, for its existing product, to itself as well as others. Backward integration strategy is adopted by the organization: - when the organization present supplier are specially expensive or unreliable or uncapable of meeting the company’s need for parts, components or raw materials. - When the no. of suppliers is few & the number of competitor’s is many. - When an organization has capital in an industry that is growing rapidly. - When the organization has capital & human resource to manage new business of supplying its own raw material. - When the advantage of stable prices are very important. Stabilize the cost of raw material & the associated price of the product through backward integration. - When present supplier have high profit margin which suggests that entering the business is a incant venture. - When the organization needs to acquire a needed resource quickly. Forward integration:- assuming a function previously provided by a distributor.(going forward on an industry’s value chain) is labeled forward integration. It involves activities that will bring the organization closer to the customer i.e. by budging the gap between the product produced by it & the fural product the customer receives. Q35. Can a combination strategy be adopted simultaneously? A. Combination strategy is followed when the firm adopts mixture of stability, expansion & retrenchment either at the same time in the different businesses or at different time in the same business with the aim of improving its performance. A firm adopting a combination strategy may apply the combination either simultaneously i.e. across the different businesses or sequentially. The sequented operation may relate to one particular business or several businesses. It is basically the question of phasing the combination over time. Q36. How can the concept of experience curve help in exercising strategic choice? A. The experience curve suggests that unit production costs decline by some fixed percentage (commonly 2030%) each time the total accumulated volume of production in units doubles. The actual percentage varies by industry & is based on many variables; the amount of time it takes a person to learn a new task, scale 20 economies, product & process improvements, & lower raw materials costs, among others. Management commonly uses the experience curve in estimating the production cost of (1) a product never before made with the present techniques & processes or, (2) current products produced by newly introduced techniques or areas in strategic management. For Ex- experience curve is considered as a barrier for new firm contemplating entry in an industry. It is also used inn building market share & discouraging competition. By leveraging the position, a firm can decide which strategy to follow so as to harness its competitive advantage to its maximum. Q37. Explain how customers benefit through competition? A. Competition benefits to number of benefits : a) Improved product:- due to competition every manufacturer would like to sell a product which is one of the best. Hence the customer gets the luxury to choose form top of the line products. b) Wide variety:- due to fierce competition firm want their product to be a little different from others & hence incorporate some small additional features there by creating a wide variety for the customer to enjoy. c) Competitive pricing:- due to competition the pricing is determined by the market dynamics & not as firm wants. The firm cannot increase its price least it looses market share & customer base. Hence the customer gets a competitive priced product. d) Better services:- to retain its customer base the strategy adopted by the firm to counter competition is to provide a better after sales services so that the customer remains happy. Q38. Explain the effect of liberalization of imports on Indian business? A. Effects of liberalization of imports:- Manufacturers could now themselves import by passing the analysing agencies like, STC etc. this made considerable savings. - Lowering of import tariffs - Abolition of import licenses - A more open exim regime - Encouragement to exports - Encouragement to foreign investment - Integrating Indian economy with the global economy. Q39. Explain how entry of MNC’s has increased corporate vulnerability? A. MNC (Multinational Corporation) is a company with significant assets & activities in multiple countries conducts in marketing, financial, manufacturing, & other functional activities. The entry of MNC’s into the Indian business scene has increased the corporate vulnerability in following manner:- Capital/ financial inadequacy has been a major dimension of vulnerability of the Indian firms. Indian firms had to become bigger & expand to remain effective players, this called for heavy investments which most firms did not have nor did they have the clout to raise the reqd. capital thus getting marginalized in business. - With increased MNC presence in Indian firms financial weakness were exposed leading to (a) takeover threat, (b) unequal battle,(c) subdued position in joint venture. - Indian firms were generally weak when it comes to products, process & brands. - PSU’s became vulnerable as they were pushed into unfamiliar waters as government protectionism, funding was removed & they had to compete with MNC’s head to head. - Total dependence on a single product made many firms vulnerable - Loss of monopoly also made many firms vulnerable. Q40. Explain how analyzing the consumer can help build a successful business strategy? A. Successful business strategy involves designing the product & marketing programme that incorporates attributes which are important to consumer’s changes in consumption pattern & buying habits of consumers play an important aspect in planning business strategy. Consumer preferences & tastes keeps changing very fast & all the time. Consumer analysis involves finding - who are the consumers - what basic needs the product is serving (as per firm) 21 - what need is served by the product (as per consumer) - priorities of [reference of benefits of product. Analyzing the consumer can lead to the knowledge of his - purchasing power - buying motives - buying habits - attitudes - lifestyle & needs; present positions & trend - brand awareness & brand loyalty - reasons/ motives for customer’s patronage of specific brands - who among the competition remains closest to customer’s & - every reactions of customers to company’s & competing products. - Analysis of customer value The above knowledge gained helps in formulating a successful business strategy. Q41. List the techniques used to conduct environmental surveys? A. - Econometric models - Trend analysis - Regression analysis - Delphi technique - Scenario writing - Problem-situation model - Benchmarking - Espionage/ spying - MIS of the firm. Q42. Explain how objectives & strategy together constitute the firms concept of business? A. Objectives represent a managerial commitment to producing specified results in a specified firm frame. They spell out how much of what kind of performance by when. Strategy is a comprehensive general plan of major actions through which a firm intends to achieve its long term objectives in a dynamic environment. So while objectives lay down the destination or where the business/ organization wants to reach, strategy charts out a plan-a blueprint-as to how to reach there & thus both together constitute the concept of business. Q43. In what way does the concept of product life cycle help in making strategic choice? A. The product life cycle is a concept that attempts to describe a products sales, profits, customers, competitors, & marketing emphasis from its beginning until it is re3moved from the market. It serves as a conceptual base for examining product growth development. The life cycle is nothing more than the pattern of demand for the product over time. A typical product life cycle has the four stages:- Introduction:- A stage of introducing the product into the market characterized by slow sales growth & negligible profits because of heavy expense of product introduction & promotion. - Growth:-The most profitable stage for the marketer. A period of rapid market acceptance & substantial profit improvement. The stage is supposed to be the shortest stage. - Maturity:- A stage of constant sales & slowing declining profits. A period of slow down of sales growth because the product has achieved acceptance by most potential buyers. Profit stabilizes or decline because of increased expenses to defend the product in the market against the competitors. - Decline:- The stage of declining sales &profits. Hence particular attention to be paid to the stage at which the business (or product) is and keeping that in mind strategies are made. Q44. Explain how growth in revenue, profits & assets are the main objectives of the firm? A. A firm has to set growth targets specifically in revenue, profits & assets. Growth in just one of these parameters is not enough. It is possible that sales revenue increase but the firms profits decline. The firm needs 22 good growth in sales revenue & profits & at the same time growth in assets as well. When desired growth levels in sales, profits & assets are ensured a major condition of growth of the firm is ensured. Q45. Under what condition is market penetration the main strategy of the firm? A. Market penetration is the main strategy of the firm when it tries to sell more of its present product to its present markets. It is effective when the market is matured but not saturated. Firms believe that higher sales volume will lead to lower unit costs & higher long-run profits. They set the lowest price, assuming the market is price sensitive or increase in expenditure for advertising & personal selling, intensive distribution & competitive pricing. In other words, the firm tries to increase the market share through penetrating the market further, staying with the same products & same markets. Q46. Explain how value chain analysis help identify a company’s strength or weakness? A. A value chain is a linked set of value-creating activities beginning with basic raw materials coming from suppliers, moving on to a series of value-added activities involved in producing & marketing a product or service, & ending with distributors getting the final goods into the hands of the ultimate consumer. The focus of value chain analysis is examine the corporation in the context of the overall chain of value-creating activities, of which the firm may be only a small part. Typical value chain for manufactured product: Raw material Primary Manufacturing Fabrication Product producer Distributor Retailer. Each corporation has its own internal value chain of activities. Porte proposes that a manufacturing firms ‘primary-activities usually begin with inbound logistics (raw materials handling & warehousing), go through an operations process in which a product is manufactured, & continue on tooutbound logistics (warehousing, repair & sales of parts). Several support activities such as procurement (purchasing), technology development(R & D), human resource management, & firm infrastructure (accounting, finance, strategic planning), ensure that the primary value-chain activities operates effectively & efficiently. A corporation’s value chain Support Activities Firm Infrastructure Human Resource Management Technology Development Procurement Profit Inbound Operati- Outbound Marketin Service Logistics ons logistics g&sales Margin Primary Activities Primary activities The systematic examination of individual value activities can lead to better understanding of a corporation’s strengths & weaknesses. According to porter “ Differences among competitor value chains are a key source of competitive advantage.” Corporate value chain analysis involves following three steps: - Examine each product line’s value chain in terms of the various activities involved in producing that product or service: which activities can be considered strengths (core competencies) or weaknesses (core deficiencies)? 23 Examine the linkages within each product line’s value chain: linkages are the connections between the way one value activity (for eg. Marketing) is performed & the cost performance of another activity (for eg. Quality control). - Examine the potential synergies among the value chain of diff. product lines or business units. Q47. Explain whether a firm should continue to invest in current known technology or in new but untested technology. A. Technology is the main source of core competence of the firm & business history shows that firms with technological strength alone are able to enjoy sustainable competitive advantage. In the present scenario of break neck competition new technologies gives the pioneer a competitive edge over existing players. But these technologies are tested i.e. they have undergone various costs & R & D experiments & only after the tests have been found successful, has a firm accepted this technology. Under no circumstances would a firm like to make a heavy investment in a new untested technology. It might make a small investment initially & test the technology & its feasibility in the firm’s process & also its acceptance by customer. Although being the first to implement a technology is important as it gives a firm tremendous competitive advantage & no firm would like to jump the gun & be first & get it wrong. This would have a tremendous negative impact on the business of the firm & might even shake its very existence. Hence major investments in the field of new but untested technology does not make sense but at the same time continuing with current technology will not give a firm sustainable competitive advantage, hence the firm should be on the lookout/ or develop new technologies in them-but invest in them only after the technology has been tested & accepted. Q48. List the conditions which could cause a firm to retaliate aggressively against a new entrant in the active industry? A. Marketing Factors: - If the new entrant is operating in more routes i.e. covering more destinations than the existing player. - When the new entrant is offering better facilities e.g. in terms of on flight food & refreshments, better entertainment mediums, pick & drop facility. - When a new entrant has a stronger brand image then the existing player - If the new entrant has larger number of ticketing counters - If the new entrant is following aggressive sales promotion / advertising activities. Finance Factors: - If the new entrant is financially more sound than existing player - If the new entrant has higher resources or higher surplus capital than existing player - If the new entrant has other business/ businesses which have an integrating effect on airline business e.g. catering business, petrochemical business e.g. reliance. Service factors - If the new entrant has a large no. of online fleet Customer satisfaction: - when the new entrant provides services which the customers feel are added value Eg. Offering discounts for stay in 5 stars for customers flying by a particular flight. Miscellaneous: - If the new entrant gets concession form the government or gets made new rules by the government which favour him - If the new entrant poaches the staff of the existing player - If the working conditions in the new entrant company are much better than the existing player - Causes a high employee turnover in the firm of existing player - If the new entrant has an already well established customer base. - Q.49. What are the traditional & emerging motives for a firm to expand internationally? A. Traditional motives: -To expand sales volume - To tap new markets - When domestic competition is too hot to handle - When there are lack of domestic investment opportunities 24 - When there is domestic stagnation - To gain government incentives - To circumvent tariff wall. Emerging Motives: - Building an international image - Having a global brand - It is a part of its objectives or vision to have global presence - To avail the cost advantage –cheap labor & raw material - To utilize its core competence & or competitive advantage & increase its market share & market growth. - Expand its customers base - To have technological advantage - To benchmark the best - Wants to pursue expansion strategy. Q50. Why does the need for developing contingency strategies arise? A. Contingency strategy outlines the steps that management would take in response to specific adverse developments, such as price wars or strikes. The purpose of contingency planning is to encourage managers to give prior thought to difficulties that might lie ahead. Strategic decisions/ choices are made on the basis of certain conditions, assumptions & premises. Strategy being eventually a firm’s response to environment, changes in environmental factors will naturally have a bearing on strategy choice, changes in the mega environment, changes in consumer factors & changes in competition are the main elements of the environmental flux. If the environment is highly uncertain the choice of strategy becomes very difficult & risky. The drastic changes in the environment would evarscent a rehashing of company mission, objectives & strategies. Contingency strategies need to be formulated to deal with these uncertainties that are a natural part of the business. 25 CASE STUDY THE TWO-WHEELER COMPANY IN INDIA Synopsis of the case The case is about the strategic decision choices being faced by Rahul Bajaj CMD of Bajaj Auto Ltd. (BAL) due to the changes in the environment & the government policies & an all pervasive competition. The case describes how Baja Auto Ltd. which had carved out a virtual monopolistic position for itself before the policy changes, was facing a serious challenge. The case goes on to tell us that how during the 80’s there were only a few players in the two-wheeler industry & Bajaj faced virtually no competition & how customers had to wait for years to buy a two wheeler, & that too after having made an advance payment. After the economic reforms in the early 90’s the government had liberalized technology import policies & import of internal components. Foreign direct investment was encouraged & fuel efficient vehicles were being promoted. The oil stock & the fact that oil imports constituted the largest item in country’s import portfolio, the government realized the need for fuel efficient vehicles for the next generation. Since the industry was not technologically competent to produce such vehicles the government liberalized its technology import policy, eased restrictions on foreign collaborations & then opens the doors for foreign participation in the two wheeler industry. These environmental & policy changes led to the entry of HONDA, YAMAHA, SUZUKI, PIAGGIO, KAWASAKI, in the Indian two wheeler market with modern technologies & popular models thereby creating tough competition for Bajaj Auto. There was a challenge of being price competitive since the scenario had changed from the ‘sellers market’ to the ‘buyers market’. Instead of receiving advance the industry had started attracting customers by offering incentives in the form of discounts & easy installment payment scheme. After years of being undisputed leader BAL saw its sales decline, market share shrinking & profitability going down. Rahul Bajaj the CMD of BAL was worried about competition, inspite of severe recession in the market he ahd started to rebuild the company for the future with the objective of becoming a global player. He was thinking about an offer of a alliance form Piaggio, the Italian scooter giant. BAL’s competition had opined that since the Italian had themselves not kept pace with the technological changes, BAL’s tie up with PIAGGIO would not make much difference. Now it was up to Rahul Bajaj to make a decision. Q1. How did environmental & policy changes affect the fortunes of the two wheeler industry in India? A. The environmental & policy changes affected the Indian two wheeler industry in the following ways: 1) Earlier the customers had to wait for years to buy a two wheeler that too after making in advance an initial down payment or they had to purchase form grey market at a premium of 15-20% than showroom price. But with policy changes the customers now had more choice & he became fickle & finicky. The waiting line disappeared & Indian two wheeler companies had to woo customers by offering incentives, discounts & attractive installment payment schemes. The factories & dealer warehouses were full with unsold vehicles. 2) From a monopolistic market, dominated by Bajaj Auto Ltd. the Indian two wheeler market became a global play field with every major player in the two wheeler industry like Honda, Yamaha etc. pitching in to acquire a majority share of the market. As a result of this the competition increased, the number of players in the Indian two wheeler industry increased. 3) With the advent of new players eg. Honda, Suzuki etc. came in new technology & new models offering better specifications & features. Thus the customer now had a slew of models to choose from. The technological & price advantage (due to parent company being financially stronger than the Indian counterparts) that the global players had given a high competition to the Indian two wheeler firms. 4) The market share of the leader of the Indian two wheeler industry for the first time started to decline due to competition from foreign players & MNC’s that came to India after the environmental & policy changes. Q2. Suggest the strategic option Rahul bajaj should consider to rebuild his company to regain its eminent position in the two wheeler industry? 26 A. the strategic option that Rahul Bajaj should consider are: a) PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY: From the case it is evident that Bajaj has somehow lagged behind in technological competence vis a vis its Japanese counterparts. It makes sense for bajaj to introduce new superior specifications which deliver a better performance in order to counter the competition provided by the foreign two wheeler companies. The customer will thus get more choice from Bajaj itself & hence buy Bajaj product. b) MARKET DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY: - Bajaj can tap newer market & or new market segments. It can go & expand its market territory in those areas where the foreign players find it difficult to reach due top geographical or language or cultural etc. constraints. Bajaj can also look into the finding new users for the products or find new customer segments eg. Army, security forces.etc. Bajaj can also look at tapping rural markets which represent 70% of Indian population. c) MARKET PENETRATION STRATEGY: - Bajaj can penetrate the market deeper by expanding its production capacity. Capacity expansion will result in higher stock thus allowing higher market penetration. Capacity expansion will also yield lower production cost per unit advantage to Bajaj Auto. d) PRICING STRATEGY: - This would be fallout of the capacity expansion strategy as there would be reduction in per unit production cost. Hence Bajaj can adopt a competitive pricing strategy by keeping the price of its models below those of the nearest competitor. e) PRODUCT PROTFOLIO EXPANSION STRATEGY:- Rahul Bajaj should seriously think of expanding the product portfolio of Bajaj Auto Ltd. instead of relying only on the scooter as the major bread earner for Bajaj, he should consider a stronger presence in the other segments like motorcycle, scooteretts, moped etc. This would prevent Bajaj from relying only on a single product and shield it against any fluctuations or cyclic variations in that occur in one product segment. f) CONCENTRIC DIVERSIFICATION STRATEGY:- Rahul Bajaj can also think of adopting concentric diversification strategy by entering into the financial business & thus provide the all important finance scheme for the customer wanting to buy a two wheeler. This by entering into a totally new business he can strengthen the existing two wheeler business by providing low interest schemes to customers who purchase Bajaj two wheeler. g) STRATEGIC ALLIANCE:- Since technology is what in lacking the two wheeler industry & also Bajaj Auto Ltd. what Rahul Bajaj can do is enter into strategic R&D and technological alliance like Tokyo R&D Japan, etc. & source superior technology from them on royalty basis & hence improve the technological competence of Bajaj’s Products. Alternatively Bajaj can also enter into strategic alliance with any of the major two wheeler firms from Japan to source technology from them to churn out improved products. h) JOINT VENTURE: - Bajaj can also think about having a joint venture with the major players like Kawasaki, Yamaha etc. & thereby get technology from them & upgrade its product or introduce new products with superior technology. Rahul bajaj can think of a combination of any of these above mentioned strategies rather than a single strategy for regaining his preeminent position in the two wheeler industry. Q3.Does Rahul Bajaj possess the potential of baking BAL a global player in the two wheeler business? Give reason’s for your viewpoint? A. – Rahul Bajaj the CMD of BAL, one of the countries few potential global players is not averse to acquiring LML - He is also not worried about recession but what he is worried about is competition. He wants to take steps in order to have competitive advantage. - Till now Bajaj has been the largest & dominating player in the two wheeler industry in India having a virtual monopoly in the market. - Profitability as a percentage of non profit to sales turnover is as high as 22% (generally it is around 1015%). - Rahul Bajaj has started planning to rebuild the company for the future with the object of becoming a global player. 27 From the above we feel that Rahul Bajaj does have the potential of making BAL a global player especially with PIAGGIO showing its intention for alliance with BAL. But at the same time if we see that Rahul Bajaj had not been proactive & had not taken steps to be technologically competent when there was no competition from foreign firms. Also the fact that even now Rahul Bajaj instead of focusing on improving in-house technological competence & capability is thinking of outsourcing them by having an alliance. What he should be doing in strengthening & improving in-house R&D efforts so that he can compete globally by having a better in-house or self developed technology & thus have a major competitive advantage globally. Thus Rahul Bajaj does have the potential of making BAL a global player provided he thinks & focuses on the right direction & adopts a right strategy. Q4. What Strategy is BAL’s competitors are likely to follow in order to eat into BAL’s market share? A. The strategy that Bajaj’s competitor’s are likely to follow are: a) PRODUCT PORTFOLIO EXPANSION:- The competitor’s are likely to expand their product portfolio to have different products to attract the Bajaj scooter customers. Eg. Honda coming out with scooters, LML & Kinetic with motorcycles etc. Thus they will attract the existing or future customers of Bajaj & thus eat into Bajaj’s market share. b) JOINT VENTURE OR STRATEGIC ALLIANCE:- The competitor’s can form a joint venture or have a strategic alliance with a major global two wheeler firm or with a global technology supplier etc. Thus they will get access to better & superior technology & hence offer better products to attract potential & existing Bajaj Customer’s. c) PRICING STRATEGY:- The global competition like Honda, Yamaha etc. that are present in India can adopt aggressive pricing strategy whereby they can afford to price their products at costs lower than that of Bajaj’s product & thus attract customers. They can also even afford to sell at a nominal loss to gain the competitive advantage if the parent company is financially very strong. d) PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY:- The competitor’s can also come out with new products to attract customers by providing better features or specifications, hence better value for money to customers & thus eat into Bajaj’s market share. e) PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION STRATEGY:- The competitor’s can aim for a product differentiation strategy thereby providing products which are totally different from those offered by Bajaj & also unique in their own way. 28