Exam 3 Review Sheet
advertisement

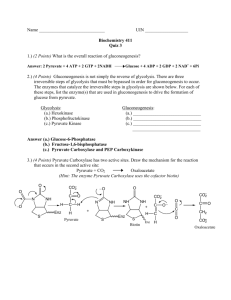
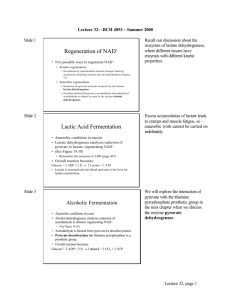
CH339K: Biochemistry 1 Fall 2013 Dr. Ready What's covered on Exam 3 This sheet is to give you a concrete idea of what I expect you to know. As always, it is intended as a study guide and not as an exhaustive list of topics covered nor as an answer key. Introduction to Metabolism (Chapter 12) Read it if it helps Glycolysis and associated stuff (Chapter 13) Glycolytic pathway: Location Reactions Enzymes Net Products Regulation at phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase steps What if you don't have O2? Lactic acid fermentation / lactate dehydrogenase Ethanol fermentation / pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase Glycogen metabolism Glycogen phosphorylase a and b: regulation by phosphorylase kinase, phosphorylase phosphatase Debranching enzymes for amylose and glycogen The Krebs' cycle and stuff (Chapter 14) Oxidation of pyruvate by pyruvate dehydrogenase Location Big 3-enzyme complex Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Proper / Thiamine Pyrophosphate Dihydrolipoamide Transacetylase / Lipoic Acid Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase / FAD Pyruvate + NAD+ + HSCoA --> CO2 + NADH + AcCoA Krebs' / Citric acid / Tricarboxylic acid cycle Location Reactions Enzymes Net Products Anaplerotic reactions Pyruvate carboxylase PEP carboxylase Malate dehydrogenase Glutamate dehydrogenase -Oxidation of fatty acids (Chapter 18) Liposome Activation Blood transport by Serum Albumin Activation: fatty acyl - CoA ligases Transfer to mitochondria: linkage to carnitine -Oxidation Location Net Products Odd-number fatty acids Processing of propionyl-CoA Unsaturated fatty acids Enoyl CoA Reductase (2 double bonds to 1) Enoyl CoA Isomerase (cis-3,4 to trans-1,2) Activation of Glycerol Electron Transport (Chapter 15) Standard reduction potentials: Eo' Predicting the direction of a redox reaction Real vs standard reduction potentials E' E' o RT [Oxidant] ln nF [Reductant ] Free energy, equilibrium constants and the reduction potential G o ' -nFE' o Keq exp( nF E' o) RT The electron transport chain: Location Pathway NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) Coenzyme Q Succinate dehydrogenase (Complex II) Coenzyme Q - cytochrome C reductase (Complex III) Cytochrome C Cytochrome Oxidase (Complex IV) Electron carriers FMN, Coenzyme Q, heme, FeS complexes Action - generating proton gradient ATP Synthase: F0/F1 ATPase Chemiosmotic coupling 3-state model of activity: L/T/O conformations Anabolic Pathways: Glyoxylate cycle (Chapter 14) Net synthesis of oxaloacetate from AcCoA Oxaloacetate can be used in gluconeogenesis 'Short-circuited' Krebs' cycle Reactions Products Gluconeogenesis (Chapter 16) Reversal of glycolysis except for: Glucose + ATP G-6-P + ADP F-6-P + ATP F-1,6-bisP + ADP PEP + ADP Pyruvate + ATP PEP formation via: Pyruvate carboxylase to OAA to Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) Cost in NTPs? F-6-P formation via fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase Glc formation via glucose-6-phosphatase Remaining rxns driven by mass action Substrates lactate pyruvate alanine oxaloacetate other aa's oxaloacetate (except leu, lys) glycerol glycerol-3-P dihydroxyacetone phosphate propionate + CO2 methylmalonyl-CoA succinyl-CoA Regulation by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate Cori cycleLactose formation favored in NADH - rich tissues Lactose transported to liver in bloodstream Reconversion to pyruvate / gluconeogenesis favored in NAD+ rich liver Glucose transported to tissues in bloodstream








![Anti-Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E2 antibody [4A4-B6-C10]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012091494_1-06ee5bc2ead8554d75205b5759bd552b-300x300.png)