Final exam practice questions
advertisement

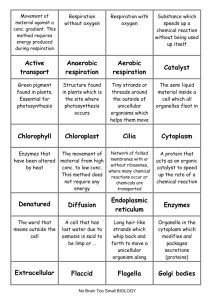
Final Exam Review Problems – Level 1 Cells: 1. Be able to compare the 3 types of microscopes in terms of the following: a. magnification and resolving power (which is best for each, not specific numbers). b. in general how each works. c. whether it produces a flat or 3D image. d. limitations of use. 2. Explain the relationship between a cell’s surface area and volume, and how those limit the size of a cell. 3. Be able to label the parts of a cell on a diagram. 4. How are plant cells similar and different from animal cells? 5. How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different from one another? Similar? 6. What is the endosymbiotic hypothesis? What types of evidence support this? 7. Be able to identify the function of each of the cell structures below, as well as explain any relationships that exist between organelles. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Plasma membrane Cell wall Nucleus (including chromatin, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pores) Ribosomes ER – smooth and rough Golgi apparatus Vacuoles Lysosomes Chloroplasts (including thylakoids and stroma within) Mitochondria (including cristae and matrix within) Centrioles (including microtubule composition) Cilia and flagella (including microtubule composition) Cell transport: 8. Be able to label a diagram of the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane. 9. Be able to identify the function/importance of each component of the plasma membrane. 10. Be able to compare active and passive transport in terms of each of the following: a. energy used. b. cell membrane components used. c. when each is used by the cell/examples of processes. d. concentration gradient followed. 11. Be able to compare isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions in terms of the following: a. solute to water ratio. b. movement of water across the cell membrane. c. be able to explain why water is moving in the direction that it is moving. 12. What causes turgor pressure to increase or decrease in a cell? 13. Be able to compare and contrast the following processes: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Enzymes and cellular respiration: 14. How are enzymes important to metabolic pathways and how do they affect the energy of activation for a reaction? 15. How are enzymes named, and why are they named this way? 16. Explain what happens when an enzyme binds with its substrate, and name the model used to describe this interaction. 17. Be able to explain how substrate concentration, temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, and inhibition affect enzyme activity. 18. If given a set of data or description of factors, be able to use enzyme functioning to explain the given data. 19. What do the terms oxidation and reduction mean? What enzymes are oxidized and reduced during the process of cellular respiration? 20. What is the overall equation for cellular respiration? Name the 4 phases involved in cellular respiration, and when each of the end products of cellular respiration are made. 21. What steps would a cell undergo to make ATP during both aerobic and anaerobic conditions? What kinds of organisms would undergo each type of respiration? 22. Where in the cell do each of the following occur: glycolysis, transition reaction, citric acid cycle, electron transport system, and fermentation? 23. What are the inputs and outputs of each of the following: glycolysis, transition reaction, citric acid cycle, electron transport system, and fermentation? 24. Be able to calculate the number of ATP produced during cellular respiration in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Be able to explain why there is a difference in terms of the amount of ATP for each. 25. Be able to label a diagram of the locations of all processes and products throughout cell respiration. Photosynthesis: 26. Be able to identify the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis (equation). 27. What is a producer? Name two examples. 28. Name 3 reasons why all life of earth is dependent upon the process of photosynthesis. 29. Be able to label a diagram of a leaf, and be familiar with the parts of a leaf. 30. Be able to label the parts of a chloroplast, and be familiar with where each of the steps involved in photosynthesis take place in a chloroplast. 31. Why are leaves green in the spring and summer, but red, orange and yellow in the fall (explain based on the pigments in leaves). 32. How are water, carbon dioxide, NADP+, and NADPH oxidized and reduced during the process of photosynthesis? 33. How are the light-dependent and light-independent phases dependent upon one another? 34. How do the cyclic and noncyclic electron pathways compare in terms of outputs? 35. What happens during the 3 phases of the Calvin Cycle? Be sure to include carbon dioxide, RuBP, G3P, NADPH, and ATP. 36. Be able to explain what happens to electrons when the sun hits the photosystems. Be able to explain the path of electrons, beginning with water, and ending with NADPH. Also be sure to mention the generation of ATP. 37. How does the process of photosynthesis compare with cellular respiration? Be able to compare and contrast the two in the following ways: types of organisms they occur within, organelle within the cell they occur within, products, reactants, and enzymes. Taxonomy: 38. Be able to identify, describe, and explain the significance of the following criteria used to classify organisms: a. level of organization b. type of body plan c. symmetry d. presence of coelom e. segmentation 39. Be able to describe the following animals based on the above characteristics: earthworms, clams, starfish, crayfish, grasshoppers, and frogs. In other words, be able to tell me the level of organization, type of body plan, symmetry, whether it is segmented or has a coelom. 40. Be able to make comparisons between the above animals in terms of the basic body plan characteristics (organization, body plan, symmetry, coelom, segmentation). 41. Be able to identify (in general) how each of the above animals perform the basic processes of life support, movement, response, feeding & digestions, reproduction, internal transport, respiration, and excretion. 42. Be able to make comparisons between the different animals in terms of how they perform the life processes listed above.