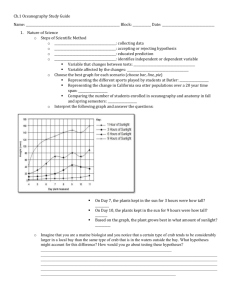
File
advertisement

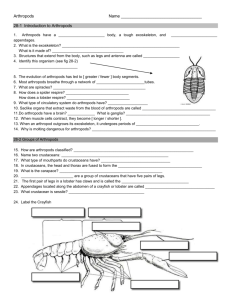
Phylum Arthropoda (Crustacea) Worksheet 1. Marine Crustaceans normally have how many major body regions? 2. Define the term 'Tagmata': 3. Define the term 'Tagmosis': 4. The exoskeleton of Arthropods and Marine Crustaceans is secreted by what structure? 5. The exoskeleton of Marine Crustaceans is composed of what material? 6. How do Arthropods move their appendages? 7. Explain 'Molting' (Ecdysis): 8. Molting occurs most frequently during what stage in a Marine Crustaceans life cycle? 9. What type of body symmetry do Arthropods have? 10. What class contains the "Horseshoe Crab"? 11. The head and thorax of a Horseshoe Crab are fused to form what body region? 12. Where is the mouth located on a Horseshoe Crab? 13. What are the first and second pair of appendages called on a Horseshoe Crab? 1st Pair: 14. 2nd Pair: What are the two functions of the 'Telson' on a Horseshoe Crab? a. b. 15. What are the flat leaf-like respiratory organs called on a Horseshoe Crab? 16. When and where do the female Horseshoe Crabs lay their eggs? a. When b. Where – Sea Spiders are found in which Class of Arthropods? 17. 18. Explain how a Sea Spider obtains food? 19. Lobster, Crab, Crayfish, Shrimp, Copepods, and Barnacles are all found in what Sub Phylum (Class) of Arthropods? 20. What are the four methods or feeding techniques used by Crustaceans? a. c. b. d. 21. Why are Decapods so important to humans? 22. What two regions of a lobster, shrimp or crayfish are fused to form the first body segment (Cephalothorax)? a. b. 23. Why is the Carapace so important to Crustaceans? 24. How many cell layers make up the carapace? 25. Which layer of the carapace contains chromatophores? 26. The legs of Decapods attached to what body segment? 27. What are 'Chelipeds'? 28. What is the second body region (segment) of the lobster, crab or shrimp called? 29. List and describe the function of each of the three pairs of mouth parts contained on Decapods: Pair of mouth parts Function a. b. c. 30. Describe the two advantages of the exoskeleton found on Decapods? a. b. 31. Describe the two disadvantages of the exoskeleton found on Decapods? a. b. 32. What are two factors which help to partially control the molting process in Marine Crustaceans? a. 33. b. Crayfish have a two-part stomach. List and Describe the function each stomach: a. b. 34. The gills of most crustaceans are attached to what part of their body? (This allows for maximum ventilation) 35. Where are the excretory and osmoregulatory organs (Green Glands) located on marine crustaceans? 36. On what side of the crustacean body are the nerve cords generally located? 37. What is the most common type of reproductive strategy in Marine Crustaceans? 38. Where on the female’s body are the fertilized eggs of the majority of Decapods carried? 39. What protects the abdomen of the Blue Crab? 40. Is the taking of spiny lobster during certain months of the year prohibited? 41. What is 'Autotomy'? 42. 43. In what Subclass are Barnacles found? What are the two types of Barnacles? a. b. 44. What is the larval form of the Barnacle called? 45. With what structures do Barnacles feed? 46. How do Barnacles attach themselves to a substrate? 47. What 'Subclass’ contains the Copepods? 48. Why are Copepods important in the Marine Environment?