doc
advertisement
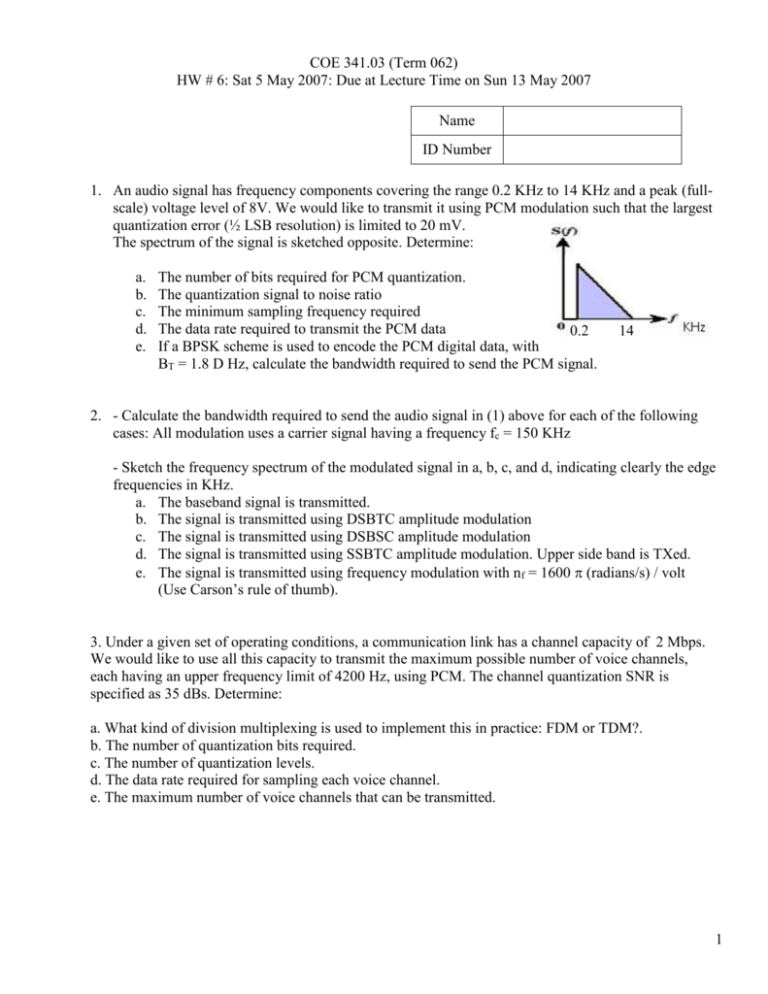
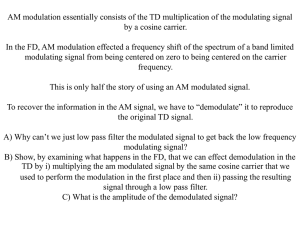
COE 341.03 (Term 062) HW # 6: Sat 5 May 2007: Due at Lecture Time on Sun 13 May 2007 Name ID Number 1. An audio signal has frequency components covering the range 0.2 KHz to 14 KHz and a peak (fullscale) voltage level of 8V. We would like to transmit it using PCM modulation such that the largest quantization error (½ LSB resolution) is limited to 20 mV. The spectrum of the signal is sketched opposite. Determine: a. b. c. d. e. The number of bits required for PCM quantization. The quantization signal to noise ratio The minimum sampling frequency required The data rate required to transmit the PCM data 0.2 If a BPSK scheme is used to encode the PCM digital data, with BT = 1.8 D Hz, calculate the bandwidth required to send the PCM signal. 14 2. - Calculate the bandwidth required to send the audio signal in (1) above for each of the following cases: All modulation uses a carrier signal having a frequency fc = 150 KHz - Sketch the frequency spectrum of the modulated signal in a, b, c, and d, indicating clearly the edge frequencies in KHz. a. The baseband signal is transmitted. b. The signal is transmitted using DSBTC amplitude modulation c. The signal is transmitted using DSBSC amplitude modulation d. The signal is transmitted using SSBTC amplitude modulation. Upper side band is TXed. e. The signal is transmitted using frequency modulation with nf = 1600 radians/s / volt (Use Carson’s rule of thumb). 3. Under a given set of operating conditions, a communication link has a channel capacity of 2 Mbps. We would like to use all this capacity to transmit the maximum possible number of voice channels, each having an upper frequency limit of 4200 Hz, using PCM. The channel quantization SNR is specified as 35 dBs. Determine: a. What kind of division multiplexing is used to implement this in practice: FDM or TDM?. b. The number of quantization bits required. c. The number of quantization levels. d. The data rate required for sampling each voice channel. e. The maximum number of voice channels that can be transmitted. 1 4. A modulating signal x(t ) 12 cos 2 103 t is used to amplitude-modulate a carrier signal y (t ) 20 cos 2 106 t . A DSBTC signal is generated. Give: (show all calculations) a. The AM modulation index na b. An equation for the modulated signal as a carrier signal plus two side band components c. The total power in the transmitted modulated signal. d. What is the maximum amplitude allowed for the modulating signal that ensures correct recovery of the signal at the receiver. e. The minimum modulation index that ensures that the carrier transmitted power does not exceed 50% of the total modulated signal power (Hint: Use power equation on page 161 of the textbook) 5. An angle-modulated signal is given as: s(t ) 13 cos[2 106 t 9 sin 2 103 t ] a. Considering the wave as phase modulated, determine the peak phase deviation in radians. b. Considering the wave as frequency modulated, determine the peak frequency deviation, f, in KHz. - Hint: obtain an expression for the instantaneous frequency: 1 d (total phase) fi i 2 2 dt c. Given that the modulating cosine/sin has a peak amplitude of 0.1 V, calculate the modulation index np and nf in both cases above. Note: Ensure correct dimensions (units) for each index. 6. The figure below shows an analog signal to be transmitted using Delta Modulation (DM). The signal spectrum has significant components up to a maximum frequency of 800 Hz and a peak amplitude of 3V. The square grid represents the sampling interval Ts in time and the step size, , in amplitude. Shown also are the initial parts of the staircase waveform and the digitization DM output waveform. a. Calculate the maximum allowed sampling interval Ts in ms. b. Calculate the amplitude step size in volts. c. Calculate the minimum data rate required to transmit the DM data. d. Complete the two waveforms. e. Mark one area where slope overhead noise exists (where needs to be large) f. Mark one area where conventional quantization noise exists (where needs to be small). Ts 2