Tutorial
advertisement

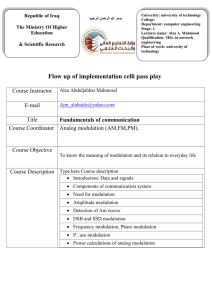
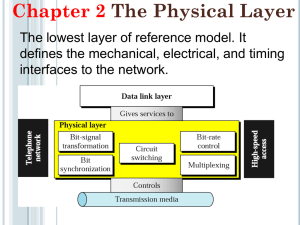
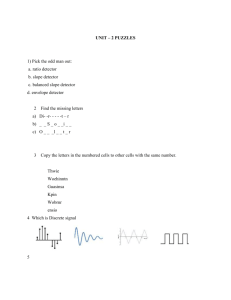
TELE 201 Tutorial – Week 4 21st March 2002 Java tutorial with Zhiyi Huang. A look at the following encoding techniques using the ‘Baudline’ computer program and the oscilloscope : Ethernet signal PCM ( Pulse Code Modulation ) FSK ( Frequency Shift Keying ) ASK ( Amplitude Shift Keying ) AM ( Amplitude modulation ) FM ( Frequency modulation ) Tutorial questions. 1. Name some of the advantages and disadvantages of twisted pair cable used in a building enviroment. 2. Explain the difference between baseband and broadband. 3. What characteristic of coaxial cable makes it less susceptible to noise and interference than twisted pair cable. 4. Name some of the advantages of using fibre optic cable for undersea telecommunication cables. 5. Given a 100 watt power source, what is the maximum allowable length for the following transmission media if a signal of 1 watt is to be received ? Use the attenuation chart in slide 11 of lecture 5 Stallings. a) b) c) d) e) 24 – gauge twisted pair operating at 300 kHz. 24 – gauge twisted pair operating at 1 Mhz. 9.5mm coax operating at 1 Mhz. 9.5mm coax operating at 25 Mhz. Optical fibre operating at its optimal frequency. 2. 6. Explain the differences and give some advantages and disadvantages of the following unguided wireless transmission media : a) Terrestial microwave. b) Satellite microwave. c) Broadcast radio. 7. How does QAM ( Quadrature Amplitude Modulation ) convey more bits of information than other forms of modulation. 8. Why are signals modulated. 9. Explain the difference between Pulse Code Modulation and Delta Modulation. 10. A digital telephone voice channel has a data rate of 64Kb. Why is this speed necessary. 11. Andrew Tiffany in his fibre optics talk said optical fibre could transmit an analogue signal. How do you think this would be done.