The Urinary System
advertisement

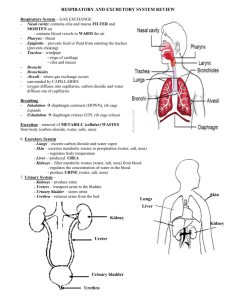
THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary or excretory system functions to control the volume and composition of the blood. It filters waste products from the blood and expels them from the body in the form of urine. The Kidneys The kidneys are two bean shaped organs found just above the waist on either side of the vertebral column. Blood passes through the kidneys and waste products and excess fluid is taken from it. The cleaned blood then returns to the circulatory system. Nephrons are the filtration units of the kidney. Each nephron contains a cluster of blood capillaries called glomeruli (singular is glomerulus). This is where the blood is actually filtered. The renal cortex is the outer area of the kidney, the middle is called renal medulla and the inner section is called the renal pelvis. Ureters Once urine is filtered through the nephrons, it drains into the renal pelvis. From the renal pelvis, urine is transported away from the kidneys is tubes called ureters. The ureters join the urinary bladder. Urinary Bladder The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine. When urine is expelled from the bladder it is called micturition, voiding or urination. The bladder can also be referred to as a vesicle. Urethra The urethra is a small tube leading from the bladder to the exterior of the body. The female urethra is about 4cm long while the male urethra is 20cm long. Urine Urine is composed of 95% water the rest is made up of waste products. Root Ren Nephr Pyel Combining form Ren/o Nephr/o Pyel/o Ureter Cyst Vesic Urethr Ureter/o Cyst/o Vesic/o Urethr/o Urin Urin/a, urin/o, urin/i Ur Lith Ur/o, -uria Lith/o URINE Meaning Kidney Kidney Refers to the space inside the kidney Urinary canal Bladder Bladder Tube through which urine leaves the body from the bladder Urine, the excretory product of the kidneys Urine Stone 1 Prefix/suffix -ptosis Hydr/o Olig/o Meaning Falling/displacement Water Deficiency/few/little Activity 1 Write the meaning of the following words; 1. renogram 2. nephrolithotomy 3. glomerulitis 4. pyelonephrosis 5. vesicocele 6. urethrostenosis 7. urinalysis 8. oliguria 9. dysuria 10. lithotripsy Activity 2 Build words which mean; 1) Surgical fixation of a kidney 2) Condition of pain in a kidney 3) Surgical repair of the renal pelvis 4) x-ray picture of the renal pelvis 5) Instrument to view the bladder 6) Specialist who studies the urinary tract 7) Abnormal urination at night URINE 2 Diseases and disorders of the urinary system The urinary system has two major types of disorders that affect it. One is when the filtration of urine from the blood is disturbed, the other is when the flow of urine either from the kidneys to the bladder, or from the bladder to the outside of the body, becomes blocked. If the filtration of blood does not take place, then the blood quickly becomes toxic. If the patient is not treated they will die. This condition is commonly known as renal failure. Interventions to save the patient can be artificial filtration of the blood by a process called dialysis; another approach may be a kidney transplant. Renal failure is caused by damage to the kidneys, which can include infections, trauma, cancer, or damage caused by toxic (poisonous) agents, such as certain drugs. Blockages in the ureters, bladder and urethra can be caused by inflammation from infections, cancers and tumours, and mineral deposits that form stones or calculi – these are known are kidney stones or renal calculi, and sometimes they have to be surgically removed. If a blockage occurs in the renal tract then the urine begins to build up. If the blockage is not removed, the urine will quickly backup into the kidneys and cause damage. Other disorders involve the composition of urine, the amount of urine that is passed from the body, and the ability of the body to control the bladder. Diseases and disorders include: Disease Anuria Cystitis (cyst/o means bladder) Dysuria Haematuria Nephritis Nocturia Proteinuria Polyuria Renal calculi Urethritis Urinary alkaliniser Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Urinalysis Definition An inability to pass urine, or an absence of urine Inflammation of the bladder Painful or difficult urination Blood in the urine Inflammation of the kidney Abnormal urination during the night Above normal levels of protein in the urine, usually indicating a urinary tract infection Large amounts of urine, of frequent urination A stone in the urinary tract Inflammation of the urethra A medication to reduce acid content of urine A general term meaning an infection in the ureters, bladder and/or urethra A test to analysis the composition of the urine Activity 3 Read the following paragraph and rewrite it using lay terms. A 26 year old woman presented with a two day history of severe dysuria. She has been passing small amounts of urine with increasing frequency. A urinalysis was performed with the results showing moderate proteinuria and haematuria. There was no indication of nephritis or kidney involvement on physical examination, and a diagnosis of cystitis was made. The patient was prescribed a urinary alkaliniser and antibiotics. URINE 3