Grade Level Expectations
advertisement

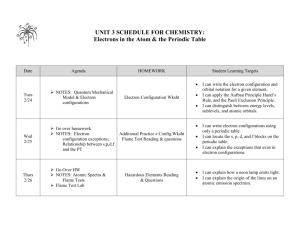
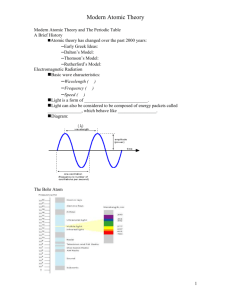
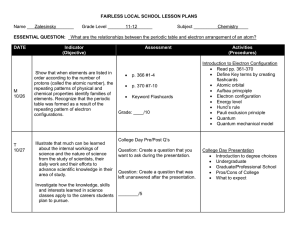
Chemistry Grade Level Expectations Unit 1 Understand: 1. The model of the atom explains experimental observations. 2. An atom’s electron arrangement determines its chemical properties. 3. Variations in atomic structure cause properties and periodicity in elements. 4. Substances have unique chemical and physical properties. 5. The classification and nomenclature of compounds are based upon the elements they contain. 6. Changes can occur within a substance without altering its identity. 7. Changes can occur within a substance that changes its identity. 8. Changes within a substance can be measured. Know: 1. The scientists, experiments, observations and conclusions that lead to the development of the atomic theory. 2. The number and properties of sub-particles in an atom of a given element. 3. How the sub-particles of an atom give an element its mass properties. 4. The different types of elements on the periodic table. 5. Difference between and ion and an isotope. 6. Charges of ions. 7. The scientists, experiments, observations and conclusions that lead to the development of the quantum theory. 8. Quantum numbers and their interpretations. (If time allows) 9. Valance electrons and the octet rule. 10. How to relate electron configurations to the periodic table and periodic properties. 11. How to write and interpret electron configurations. 12. Observations that led to the discovery of periodicity. 13. How properties differ in a periods and families. 14. How trends are periodic in periods and families. 15. Families of elements. 16. Types of mixtures ( heterogeneous/ homogeneous) 17. How to separate components of a mixture. 18. Methods used to identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. 19. A substance’s properties determine its function. 20. All substances have unique chemical and physical properties. 21. Differences between chemical and physical properties. 22. How to classify a substance as ionic, molecular, acidic, or basic by the elements it contains. 23. How to name and write the formulas for a. ionic b. binary molecular c. acids and bases 24. Relationship of bonding to the periodic table. 25. Know seven diatomic molecules 26. Precision and accuracy in measurements 27. How to make a measurement 28. How to do calculations 29. How to do calculation with significant figures Be Able to: 1. List the scientists, experiments, observations, and conclusions that led to the atomic theory. 2. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons for atoms, ions, and isotopes of a given element. 3. Determine atomic mass and average atomic mass of isotopes. 4. Write electron configurations for elements 5. Identify and element by its atomic absorption (flame test). 6. Use the periodic table to write condensed electron configurations 7. Give property similarities and differences for series and families. 8. Map periodic trends. 9. Explain relationship between the periodic properties and properties of the families of elements. 10. Classify and locate metals, nonmetals, and semimetals. 11. Write dot diagrams. 12. Distinguish between and chemical and physical property. 13. Separate components of a mixture. 14. Identify compounds using chemical and physical properties. 15. Explain how electrolytes conduct electricity. 16. Identify parts of a solution. 17. Name compounds and write chemical formulas. 18. Identify compounds. 19. Identify by properties the bonding types (ionic, covalent, and metallic). 20. Identify bonding types by elements present in the substance. 21. Identify the seven diatomic molecules. 22. Measure and calculate using the correct number of significant figures. 23. Solve dimensional analysis/factor label problems. 24. Convert between moles, mass, volume, number of particles, and number of atoms. 25. Balance chemical equations 26. Write word and symbol equations. 27. Identify reaction types. Unit 2 Understand: 1. Solutions have unique properties. 2. Changes can occur within a substance that changes its identity. 3. Changes within a system can be measured. 4. There are driving forces that determine how and why a chemical reaction takes place. Know: 1. a. States of matter are controlled by forces and energy (temperature and pressure). b. Variables that affect gases. c. Colligate properties * 2. a. How to balance chemical equations. b. How to identify chemical reactions. c. How to predict products. 3. a. Stoichiometric relationships of moles, mass, volume, and joules 4. a. 3 laws of thermodynamics* b. The relationship between Gibb’s free energy and the spontaneity of reactions.* c. Exothermic vs. Endothermic Be Able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Interpret phase diagrams. Solve gas law problems. Solve concentration problems. Solve dilution problems. Work with colligate properties.* Explain how electrolytes conduct electricity. Identify the parts of a solution. Predict products of chemical reactions. Use an activity chart and solubility rules to determine if a reaction will form and what the products will be. 10. Solve stoichiometry problems. 11. Solve titration problems. 12. Solve calorimetric problems. 13. Give examples from the world around you of the 3 laws of thermodynamics.* 14. Interpret variables of Gibb’s free energy equation.* 15. Looking at sign of ∆H to determine if reaction is exothermic or endothermic.