Hemostasis
advertisement

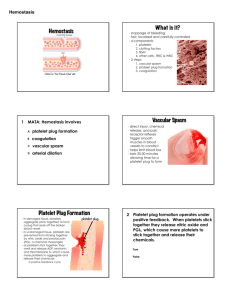
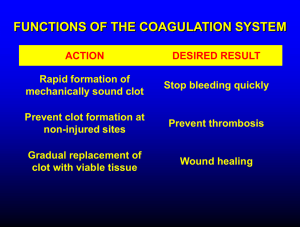
Dr Mere Kende MBBS, MMED (Path), MACTM, MAACB, MACRRM Lecturer: SMHS, UPNG What is Hemostasis? Factors Involved in Hemostasis? Role of Blood Vessel in Hemostasis Role of Platelet in hemostasis Fibrin in thrombus Coagulation Cascade Extrinsic and Intrinsic Pathway Fibrinolysis & Tissue Repair List of Disorders of Hemostasis & Investigation STOP BLEEDING Prevent entry of micro-organisms Initiate Repair & Healing of damaged tissue Vessel Wall (collagen) Platelets Coagulation Factors 1. Blood Vessels Contract 2. Platelet Activation 3. Fibrin Clot Formation Vessel Wall Damage & Contract Temporary Platelet Plug Activation of coagulation system Stabilisation Clot of Fibrin Clot Retraction Fibrinolysis & Repair Damaged Blood Vessel Injury: trauma, Cholesterol plug,/Hypertension//smoking, Vasoconstriction Compression Collagen (serotonin, TXA2, adrenaline) (spilled blood/tissue swelling) exposed Activation of platelet (exposed collagen) Adhesion (vWF, GpIb/IX) Activation Aggregation via fibrinogen links (gp IIb & IIIa) Glansman’s Thromboaesthenia) Secretion (ADP, TXA2, serotonin, thrombin) Activation of more platelets/initiate clot Formation Fibrinogen In a normal individual, coagulation is initiated within 20 seconds after an injury occurs to the blood vessel damaging the endothelial cell. Platelets immediately form a haemostatic plug at the site of injury. This is called primary haemostasis. Time required for ceiling of bleeding by ‘platelet plug’ after vessel damage Normal: 2-6 minutes Replaced by more firm fibrin clot Extrinsic & Intrinsic Pathways I(fibrinogen) II (prothrombin) Tissue factor 3/Tissue Thromboplastic Calcium V(proaccelerin, labile factor) VI VII (stable factor) VIII(antihemophilic factor) IX(Christmas factor) X(Stuart-Prower factor) XI(plasma thromboplastin antecedent) XII(Hageman factor) XIII(fibrin-stabilizing factor) von Willebrand factor Prothrombin Xa Va Thrombin Fibrinogen Fibrin Extrinsic Pathway TF3 (Endothelium) Prothrombin VIIa Xa Va Thrombin Fibrinogen Fibrin Intrinsic pathway Kallikrein & HMW Kininogen cofactors Activated by PLT phospholipids & exposed collagen XIIa Extrinsic Pathway TF3 (Endothelium) XIa Prothrombin IXa VIIIa VIIa Xa Va Thrombin Fibrinogen Fibrin Intrinsic pathway Kallikrein & HMW Kininogen cofactors Activated by PLT phospholipids & exposed collagen XIIa Extrinsic Pathway TF3 (Endothelium) XIa Prothrombin IXa VIIIa Fibrinogen VIIa Ca++ Xa Va Thrombin Soft clot Fibrin XIIIa Fibrin Hard clot Extrinsic-7 (PT) Intrinsic 12,11,9,8 (aPTT-) Sequential Activation of inactive Proteases Common Path (TT) FX FXa Prothrombin Thrombin Fibrinogen Fibrin For Purposes monitoring PT- tests extrinsic pathway aPTT-tests intrinsic There are many points of interaction between 2 pathways Thrombin activated via extrinsic pathway is cofactor for VIII (intrinsic pathway) activation Thrombin enhances V & VIII, plaletlet & endothelial activity Factor VIIa (extrinsic) can activate XI (intrinsic) Factor XIa, XIIa, Xa, and thrombin (IIa) can activate VII (extrinsic) Kallikrein /HMWK Collagen/PLT phospholipids (Tissue) Factor III PF-3 PF-3 Platelet &endothelium Thrombin enhances PLT & endothelium cells Fibrin monomer (unstable, non-covalent) Fibrin Polymers (stable, covalent bond) Stabilization Factor (XIII) Liver epoxide reductase Fibrinogen Thrombin Fibrin Mononer Fibrin Polymer F-XIIIa Cross Linked Fibrin Within minute-hours of clot formation Large fraction of serum is extruded during the process Requires Platelet Prevents clot breakdown and enhances healing Pro-coagulants Vessel Endothelium Platelets Clotting Factors Anti-coagulants Prostacyclin Anti-thrombi III Protein C & S Plasminogen/Plasmin Tissue Plasminogen Activator Tissue Plaminogen Activator Protein C & S (enhances fibrinolysis) Anti-thrombin III Heparin is cofactor Inactivates Enhances Thrombin (V,VII indirectly) Fibrinolysis Inactivates Va & VIIIa Binds endothelial thrombomodulin ----- Activates Protein C Protein C + cofactor (protein S) Enhances Fibrinolysis/Proteolysis via inactivation of Va & VIII & Inhibiting TPA inhibitor Endothelial cell proliferation & differentiation Fibroblast cells (Fibroblast Growth factor) Smooth muscles cells Growth factors (VEGF, PDGF) Angiogenesis OPERATES TO: LIMIT CLOTS TO SITE OF INJURY & PREVENT ABNORMAL CLOTS (THROMBOEMBOLYTIC DISEASE) MAINTAINS PHYSIOLOGICAL BALANCE BREAKS DOWN CLOT FORMED TO ENHANCE HEALING PROCESS (proliferation, differentiation of endothelium, fibroplast) Disordered BLEEDING regulatory system DISORDERS (HAEMOPHILIA) THROMBOTIC DISORDERS (DVT/PE/STROKE) Vascular disorders – Platelet disorders Scurvy, easy bruising, Henoch-Schonlein purpura, vasculitis. Quantitative - Thrombocytopenia Qualitative - Platelet function disorders – Glanzmans Coagulation disorders Congenital - Haemophilia (A, B), Von-Willebrands Acquired - Vitamin-K deficiency, Liver disease Mixed/Consumption: DIC Thromboembolic Diseases (PE/DVT) SKIN BRUISES/EASY BRUSING: A bruise (layman's term), also called a contusion (medical term), is a type of hematoma of tissue in which capillaries and sometimes venules are damaged by trauma Ecchymosis ->10mm Purpura (bleeding disorders) purple/red discolouration, do not blanch (3mm-10mm) (typical vascilitis) Petechiae <3mm (typical Platelet disorder) BLANCHES on pressure Capillary dilatation Eg contact dermatitis/allergy /sunburn Easy Bruising Menorrhagia Generalised mucosal Bleeding (nose bleeds) FBE/PLATELET BLEEDING COUNT TIME PROTHROMBIN ACTIVATED TIME (PT) PARTIAL THROMBOPLASPTIN TIME (aPTT/PTT) Coagulation VWF Factor Assay (VIII) Assay Snake Venom Tests Thrombophilia Screen (Protein C, S, factor V Leiden, Ant-thrombin III activity, Phospholipid Asssay) Condition PT PTT Bleeding Time Platelet Count Vitamin K deficiency prolonged prolonged normal normal Warfarin Rx Prolonged Prolonged Normal Normal DIC Prolonged Prolonged Prolonged decrease vWD normal Prolonged Prolonged Normal Liver Disease (early) Prolonged Normal Normal Normal Uremia (low PLT) Normal Normal Prolonged Normal Thromobocytopenia Normal Normal prolonged decreased Hemophilia A & B Normal prolonged Normal Normal Factor V & X deficiency Prolonged Prolonged Normal Normal Glasmans Thromboasthenia (GPIIb/IIIa) Normal Normal prolonged Normal Bernard Soulier Syndrome (GPIb) Normal Normal prolonged decreased BV Injury Tissue Factor Neural Blood Vessel Platelet Coagulation Constriction Activation Activation Primary hemostatic plug Reduced Blood flow Plt-Fusion Thromibn, Fibrin Stable Hemostatic Plug Harrisons Principle of Internal Medicine 17th Edition PJ. Gallagher, GA Tanner. Medical Physiology, 2nd edition A. Despopoulous, S. Silbenagl. Colour Atlas of Physiology, 5th Edition