Master Budgeting
advertisement

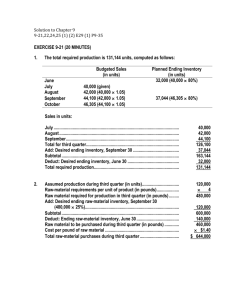
UYEN DINH Professor: STEPHEN BROWN ACC 2355 _ Managerial Accounting II_ Section 800 MASTER BUDGET ASSIGNMENT The 1st quarter master budget of Lim Corporation contains the following schedules, which are displayed and explained in the following pages: Schedule 1 2 3 4 5 6 Title of Schedule Sales Budget Expected Cash Collection Merchandise Purchasing Budget Cash Disbursement Budget Summary Cash Budget Absorption costing income statement Balance sheet as of March 31 Sales Budget The first step in developing Lim Corporation’s 1st quarter master budget is to prepare the sale budget. Let’s make assumption that the budget year is 20X1. Following is schedule 1, sale budget of Lim Corporation, based on the data b and c: LIM CORPORATION Sales Budget For the quarter Ending March 31, 20X1 20X0 20X1 (Budgeted Sales) December January February March (Actual) 60000 70000 80000 85000 Total Sales 1st Quarter April (1) 235000 55000 Cash Sales (2)= 40%*Sales 24000 28000 32000 34000 94000 22000 Credit Sales (3)= 60%*Sales 36000 42000 48000 51000 141000 33000 Schedule 1. Schedule of Expected Cash Collection Also based on the date b and data c, Lim Corporation’s cash receipts budget - schedule 1 detailed the expected cash collections during the 1st quarter: Cash Collection from: Cash Sales Credit Sales (5) 1 LIM CORPORATION Cash Receipt Budget For the quarter Ending March 31, 20X1 20X1 January February March 28000 32000 34000 36000 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March (ALWAYS) 2 ( ) Cash Sales = 40%*Sales January: 28000 = 40%*70000 February: 32000 = 40%*80000 3 ( ) Credit Sales = 60%*Sales January: 42000 = 60%*70000 February: 48000 = 60%*80000 4 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March 5 ( ) Credit Sales collection = 100% of previous month’s credit sales January: 42000 = 60%*70000 February: 48000 = 60%*80000 42000 48000 1st Quarter (4) 94000 126000 Total Cash Receipts (Cash Collection) (6) Schedule 2. 64000 74000 82000 220000 Merchandise Purchasing Budget This budget is based to the data a & d. LIM CORPORATION Merchandise Purchasing Budget For the quarter Ending March 31, 20X1 January February 49000 56000 20X1 March 59500 1st Quarter (7) 164500 11200 11900 7700 7700 (10) 60200 67900 67200 172200 Less: BEGINNING Inventory (12) (9800) (11200) (11900) (9800) (13) Required purchases (14) 50400 56700 55300 Budgeted Cost of Goods Sold(8) =70%*Sales Add: Desired ENDING inventory (9) =20%*next month’s COGS Total Needs (11) 6 162400 ( ) Total Cash receipt (Cash collection) =cash sales of current month + credit sales of prior month; OR Total Cash receipt =40%*sales + 60%*sales of prior month. For instant, January: 64000 =28000+36000 OR 64000 = 40%*70000 + 60%*60000 February: 74000 = 32000+42000 OR 74000 = 40%*80000 + 60%*70000 7 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March 8 ( ) Cost of Goods Sold =70%*Sales. For example, 49000 = 21000*70% 9 ( ) Desired ENDING inventory =20%*next month’s COGS January: 11200 = 20%*56000 February: 11900 = 20%*59500 10 ( ) Quarter’s Desired Ending Inventory is equal to the desired ending Inventory of March 31. 11 ( ) Total Needs = Cost of Goods Sold + Desired Inventory 12 ( ) expected beginning inventory of finished goods 13 ( ) Quarter’s beginning Inventory = the December ending inventory = the January beginning inventory 14 ( ) Required Budget = Total Needs – BEGINING Inventory Schedule 3. Expected Cash Disbursement The cash disbursement budget (schedule 3) details the expected cash payments during the 1st quarter for Lim Corporation. The pink-shaded top portion shows the schedule of cash payments for the merchandise purchases which based on data e and the required purchases from schedule 2. The Selling, general, and Administrative expense budget shows the planned amounts of expenditures for selling, general, and administrative expenses during the 1st quarter. Lim Corporation’s selling and administrative expense budget is displayed as the shaded bottom portion – part for selling and Administrative expense of schedule 3, based on the data f. LIM CORPORATION Cash Disbursement Budget For the quarter Ending March 31, 20X1 For Merchandise Purchases: Required purchases (From schedule 2) 20X1 December January February March 43400 (16) 50400 56700 55300 1st Quarter (15) 162400 32550 (18) 45150 51975 56350 153475 Commission Expense 12000 12000 12000 36000 Rent 1800 1800 1800 5400 Other expenses (19) 5600 6400 6800 18800 Total Disbursements for Expenses (20) 19400 20200 20600 60200 17 Total Disbursement for Purchases ( ) For Selling and Administrative Expenses: 15 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March 16 ( ) Required purchases of December = the account payable / 75% = 32550 / 75% = 43400 17 ( ) Cash Payments for Purchases = 25% of current month’s required purchases + 75% of prior month’s required purchases. For example: January: 45150=25%*50400 + 75%*43400 February: 51975=25%*56700 + 75%*50400 18 ( ) Beginning balance of the accounts payable 19 ( ) Other expenses = 8%*Sales (including $2400 Depreciation for the quarter) January: 5600=8%*70000 February: 6400=8%*80000 20 ( ) Total Cash payment for expenses (Total expenses ) = Commissions + Rent + Other expenses For Equipment 3000 8000 Total cash disbursements (21) 67550 80175 Schedule 4. 11000 76950 224675 Summary Cash Budget Analysis of short-term financing needs: In order to maintain cash balance of $5000 at the end of each month while we also need cash to pay for the equipment in data g, the following analysis table details the amount of cash we need to borrow from local bank. Cash balance at beginning of month Less: minimum cash balance LIM CORPORATION January February March 6000 0 0 (5000) (5000) (5000) Cash available for equipment purchases (22) Less: Cost of investment in Equipment (from schedule 3) Required short term borrowing (23) 1st quarter 6000 (5000) 1000 0 0 1000 (3000) 8000 0 (11000) (2000) (8000) 0 (10000) The cash budget details the expected cash receipts and disbursements during the 1st quarter. Lim Corporation’s completed cash budget is displayed as schedule 4. The pink shaded top portion pulls together the cash receipts and cash disbursements detailed in schedule 1 and 3. Also, based on the data showing the cash balance of $6000 as of December 31, 20X0. LIM CORPORATION Cash Budget For the quarter Ending March 31, 20X1 January February 21 20X1 March 1st Quarter (24) ( ) Total cash disbursement = cash disbursement for inventory + for operating expenses + for equipment 22 ( ) Cash available for equipment purchase = beginning cash balance – minimum cash balance required. (1000 = 6000-5000) (23 ) Based on the data h which local bank allows company to borrow from $1000 up to the total balance of $50000. 24 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March 6000 5000 6175 6000 64000 74000 82000 220000 70000 79000 88175 226000 Less: Total cash disbursements (from schedule 3) (67550) (80175) (76950) (224675) Excess (deficiency) of cash (25) (1175) 11225 Cash balance, January 1, 20X1 Add: Cash receipts (cash collection) (from schedule 1) Total cash available 2450 1325 Others (Financing) Add: Less: Proceeds from bank loan (26) (From analysis of financing needs) Quarter Interest on bank loan (27) (at March 31, 20X1) Repayment of bank loan (28) March 31, 20X1 10000 CASH BALANCE March 31, 20X1 25 10000 300 10300 1025 (29) ( ) Excess of cash when total cash receipts > total cash disbursements, and vice versa, it is decicency of cash when the cash receipts < total cash disbursement. (26) Based on the data h which local bank allows company to borrow from $1000 up to the total balance of $50000. Therefore, proceeds from bank loan= required short term borrowing. 27 ( ) Interest bank loan = 1%per month*borrowing loan=3months*1%*10000=300 28 ( ) based on the data h that we repay the loan plus interest at the end of the quarter 29 ( ) 1025 = 1325 + 10000 - 10300 Schedule 5. Absorption Costing Income Statement LIM CORPORATION Absorption – Costing Income Statement For the quarter Ended March 31, 20X1 Sales Revenue (from sale budget) 1st Quarter (30) 235000 Less: Cost of Goods Sold (from schedule 2) (164500) Gross Margin (31) 70500 Less: Selling & Administrative expenses (From schedule 3) Less: Interest on bank loan (from schedule 4) (60200) 10000 (32) NET INCOME Schedule 6. (300) Balance Sheet as of March 31 LIM CORPORATION Budgeted Balance Sheet March 31, 20X1 ASSETS Cash (from schedule 4) $ 1025 Account Receivable (33) $ 51000 Building and Equipment (34) $119485 Inventory (from schedule 2) TOTAL: 30 $7700 179210 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March 31 ( ) Gross margin = Sales revenue – Cost of Goods sold; OR = 30%*Sales (data a) 70500 = 235000 – 164500, OR 70500 = 235000*30% 32 ( ) net income before tax = 10000 = 70500-60200-300 33 ( ) Account Receivable Beginning Jan1 36000 + sale on account (sale budget) 141000 – cash collection from credit sales 126000 = 51000 34 ( ) balance 110885+cost of equipment acquired 11000-depreciation 2400=119485 LIABILITY + EQUITY Common shares 100000 Retained earnings (35) 40135 Account payable (36) 41475 Total: 35 181610 ( ) Beginning 30135 + net income 10000 =40135 36 ( ) beginning 32550 + purchase 162400-cash payments for purchases 153475 (Schedule 3) = 41475 APPENDIX After using all the data information, I created this condensed table to describe in detail where the numbers come from, as well as which data I used. Based on data b Sales 20X0 December (Actual) 60000 a Gross margin (38) =30%*Sales 18000 21000 24000 25500 70500 16500 a Cost of Goods Sold(39) =70%*Sales 42000 49000 56000 59500 164500 38500 c Cash Sales (40)= 40%*Sales 24000 28000 32000 34000 94000 22000 c Credit Sales (41)= 60%*Sales 36000 42000 48000 51000 141000 33000 64000 74000 82000 220000 73000 9800 11200 11900 7700 7700 (44) 51800 60200 67900 67200 172200 9800 11200 11900 9800 (47) Total Cash Receipts (42) d Desired ENDING inventory (43) 20X1 (Budget) January February March 70000 80000 85000 1st Quarter April (37) 235000 55000 =20%*next month’s COGS Total Needs (45) BEGINNING Inventory (46) 37 7700 ( ) Quarter = January + February + March 38 ( ) Gross margin =30%*Sales January: 21000 = 30%*70000 February: 24000 = 30%*80000 39 ( ) Cost of Goods Sold =70%*Sales. For example, 49000 = 21000*70% 40 ( ) Cash Sales = 40%*Sales January: 28000 = 40%*70000 February: 32000 = 40%*80000 41 ( ) Credit Sales = 60%*Sales January: 42000 = 60%*70000 February: 48000 = 60%*80000 42 ( ) Total Cash receipt (Cash collection) =cash sales of current month + credit sales of prior month; OR Total Cash receipt =40%*sales + 60%*sales of prior month. For instant, January: 64000 =28000+36000 OR 64000 = 40%*70000 + 60%*60000 February: 74000 = 32000+42000 OR 74000 = 40%*80000 + 60%*70000 43 ( ) Desired ENDING inventory =20%*next month’s COGS January: 11200 = 20%*56000 February: 11900 = 20%*59500 44 ( ) Quarter’s Desired Ending Inventory is equal to the desired ending Inventory of March 31. 45 ( ) Total Needs = Cost of Goods Sold + Desired Inventory Required purchases (48) 43400 (49) 50400 56700 55300 162400 e Total Disbursement for Purchases (50) 32550 (51) 45150 51975 56350 153475 f Commission Expense 12000 12000 12000 36000 f Rent 1800 1800 1800 5400 f Other expenses (52) 5600 6400 6800 18800 Total Disbursements for Expenses (53) 19400 20200 20600 60200 Equipment expenses 3000 8000 f, g 46 11000 ( ) expected beginning inventory of finished goods 47 ( ) Quarter’s beginning Inventory = the December ending inventory = the January beginning inventory 48 ( ) Required Budget = Total Needs – BEGINING Inventory 49 ( ) Required purchases of December = the account payable / 75% = 32550 / 75% = 43400 50 ( ) Cash Payments for Purchases = 25% of current month’s required purchases + 75% of prior month’s required purchases. For example: January: 45150=25%*50400 + 75%*43400 February: 51975=25%*56700 + 75%*50400 51 ( ) Beginning balance of the accounts payable 52 ( ) Other expenses = 8%*Sales (including Depreciation of $2400) January: 5600=8%*70000 February: 6400=8%*80000 53 ( ) Total Cash payment for expenses (Total expenses ) = Commissions + Rent + Other expenses