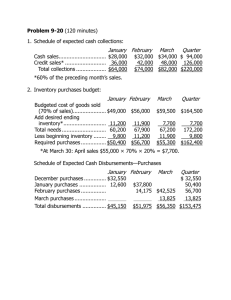
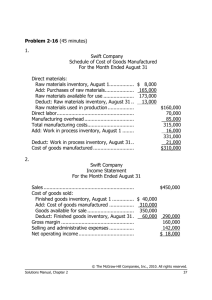
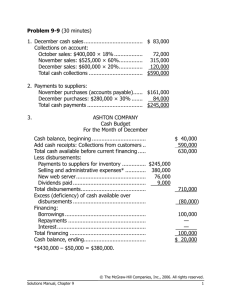
EXERCISE 9-21 (20 MINUTES) 1. The total required production is
advertisement
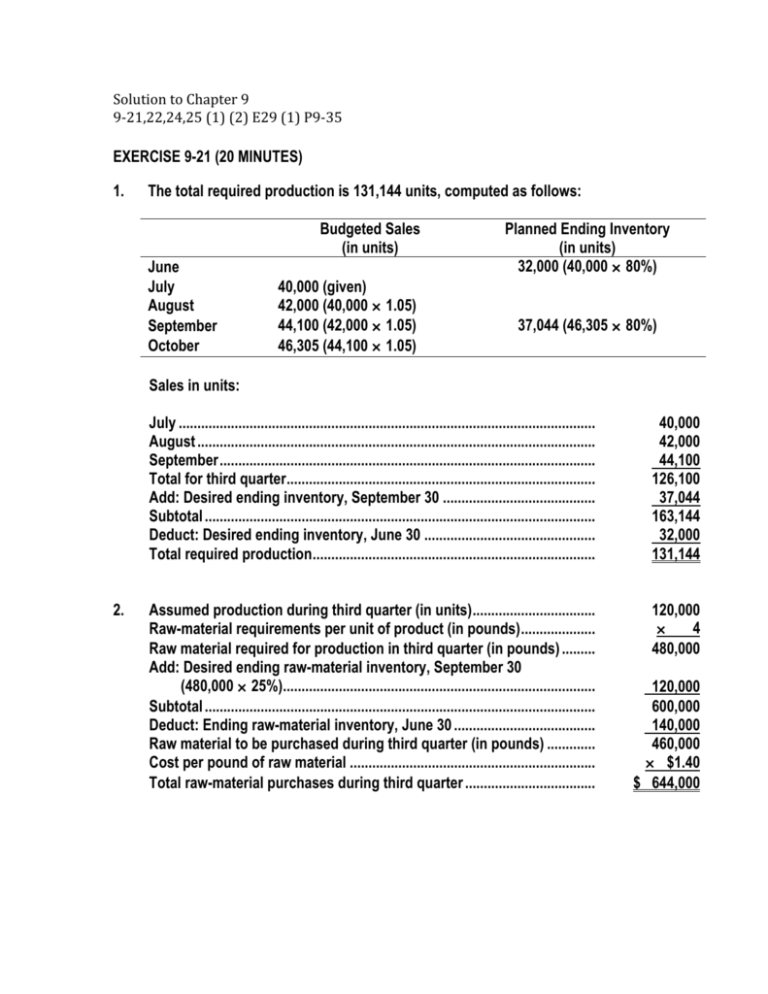
Solution to Chapter 9 9‐21,22,24,25 (1) (2) E29 (1) P9‐35 EXERCISE 9-21 (20 MINUTES) 1. The total required production is 131,144 units, computed as follows: Budgeted Sales (in units) June July August September October 40,000 (given) 42,000 (40,000 × 1.05) 44,100 (42,000 × 1.05) 46,305 (44,100 × 1.05) Planned Ending Inventory (in units) 32,000 (40,000 × 80%) 37,044 (46,305 × 80%) Sales in units: 2. July ................................................................................................................ August ........................................................................................................... September..................................................................................................... Total for third quarter................................................................................... Add: Desired ending inventory, September 30 ......................................... Subtotal ......................................................................................................... Deduct: Desired ending inventory, June 30 .............................................. Total required production............................................................................ 40,000 42,000 44,100 126,100 37,044 163,144 32,000 131,144 Assumed production during third quarter (in units)................................. Raw-material requirements per unit of product (in pounds).................... Raw material required for production in third quarter (in pounds) ......... Add: Desired ending raw-material inventory, September 30 (480,000 × 25%).................................................................................... Subtotal ......................................................................................................... Deduct: Ending raw-material inventory, June 30 ...................................... Raw material to be purchased during third quarter (in pounds) ............. Cost per pound of raw material .................................................................. Total raw-material purchases during third quarter ................................... 120,000 × 4 480,000 120,000 600,000 140,000 460,000 × $1.40 $ 644,000 EXERCISE 9-22 (25 MINUTES) 1. Cash collections in October: Month of Sale July............................................................... August ......................................................... September ................................................... October ........................................................ Total ............................................................. Amount Collected in October $150,000 × 4% $ 6,000 175,000 × 10% 17,500 200,000 × 15% 30,000 225,000 × 70% 157,500 $211,000 Notice that the amount of sales on account in June, $122,500 was not needed to solve the exercise. 2. Cash collections in fourth quarter from credit sales in fourth quarter. Amount Collected Month of Sale October ............................................ November ........................................ December ........................................ Total ................................................. Total collections in fourth quarter from credit sales in fourth quarter ......................................... 3. Credit Sales $225,000 250,000 212,500 October $157,500 – – $157,500 November $ 33,750 175,000 – 208,750 December $ 22,500 37,500 148,750 $208,750 $575,000 In the electronic version of the solutions manual, press the CTRL key and click on the following link: BUILD A SPREADSHEET EXERCISE 9-24 (15 MINUTES) 1. Production (in units) required for the year: Sales for the year ........................................................................................... Add: Desired ending finished-goods inventory on December 31.............. Deduct: Beginning finished-goods inventory on January 1 ...................... Required production during the year ........................................................... 2. 3,360,000 350,000 560,000 3,150,000 Purchases of raw material (in units), assuming production of 3,500,000 finished units: Raw material required for production (3,500,000 × 2) ................................ 7,000,000 Add: Desired ending inventory on December 31 ........................................ Deduct: Beginning inventory on January 1 ................................................. Required raw-material purchases during the year...................................... 315,000 245,000 7,070,000 EXERCISE 9-25 (20 MINUTES) 1. WHITE MOUNTAIN FURNITURE COMPANY EXPECTED CASH COLLECTIONS NOVEMBER Month September......................................... October ............................................. November.......................................... Total .............................................. 2. Sales $150,000 195,000 165,000 Percent 9% 20% 70% WHITE MOUNTAIN FURNITURE COMPANY EXPECTED CASH DISBURSEMENTS NOVEMBER October purchases to be paid in November................................................ Less: 2% cash discount ................................................................................ Net ............................................................................................................... Cash disbursements for expenses............................................................... Total ............................................................................................................ 3. Expected Collections $ 13,500 39,000 115,500 $168,000 $135,000 2,700 $132,300 36,000 $168,300 WHITE MOUNTAIN FURNITURE COMPANY EXPECTED CASH BALANCE NOVEMBER 30 Balance, November 1..................................................................................... Add: Expected collections ............................................................................ Less: Expected disbursements .................................................................... Expected balance....................................................................................... $ 55,000 168,000 168,300 $ 54,700 EXERCISE 9-29 (20 MINUTES) 1. Total Sales in January 20x5 $200,000 $260,000 $320,000 Cash receipts in January, 20x5 From December sales on account ........... From January cash sales .......................... From January sales on account ............... Total cash receipts .................................... $ 14,250* 150,000† 40,000** $ 204,250 $ 14,250 195,000 52,000 $261,250 $ 14,250 240,000 64,000 $318,250 *$14,250 = $380,000 × .25 × .15 †$150,000 = $200,000 × .75 **$40,000 = $200,000 × .25 × .80 2. Operational plans depend on various assumptions. Usually there is uncertainty about these assumptions, such as sales demand or inflation rates. Financial planning helps management answer "what if" questions about how the budget will look under various sets of assumptions. PROBLEM 9-35 (25 MINUTES) 1. Sales budget Sales (in sets).............................................. Sales price per set ...................................... Sales revenue.............................................. 2. August 6,000 × $60 $360,000 September 7,500 × $60 $450,000 July 5,000 1,200 6,200 1,000 5,200 August 6,000 1,500 7,500 1,200 6,300 September 7,500 1,500 9,000 1,500 7,500 Production budget (in sets) Sales ............................................................ Add: Desired ending inventory ................. Total requirements ..................................... Less: Projected beginning inventory........ Planned production .................................... 3. July 5,000 × $60 $300,000 Raw-material purchases Planned production (sets) ............................ Raw material required per set (board feet)................................................. Raw material required for production (board feet)................................................. July 5,200 × 10 52,000 August 6,300 × 10 63,000 September 7,500 × 10 75,000 Add: Desired ending inventory of raw material (board feet).................................. Total requirements ........................................ Less: Projected beginning inventory of raw material (board feet)........................... Planned purchases of raw material (board feet)................................................. Cost per board foot ....................................... Planned purchases of raw material (dollars) ...................................................... 6,300 58,300 7,500 70,500 8,000 83,000 5,200 6,300 7,500 53,100 × $.60 64,200 × $.60 75,500 × $.60 $ 31,860 $ 38,520 $ 45,300 July 5,200 × 1.5 7,800 × $21 $163,800 August 6,300 × 1.5 9,450 × $21 $198,450 September 7,500 × 1.5 11,250 × $21 $236,250 PROBLEM 9-35 (CONTINUED) 4. Direct-labor budget Planned production (sets) ............................ Direct-labor hours per set............................. Direct-labor hours required .......................... Cost per hour ................................................. Planned direct-labor cost.............................. 5. In the electronic version of the solutions manual, press the CTRL key and click on the following link: BUILD A SPREADSHEET