C:\CLASSES\101\Exams\review sheet 1.wpd
advertisement

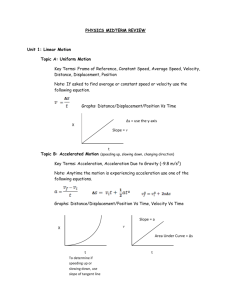
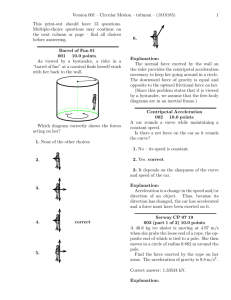
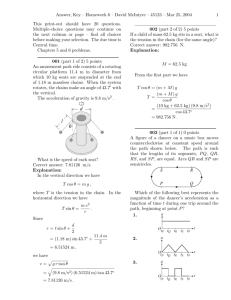
Review topics for Physics 101 Exam 1 Chapter 1. Measurements – Why are measurements necessary in physics? Units – What units do physicists use and how do you convert between units? Scope of Physics – what are the different areas of physics and how are they related? Chapter 2. Average and instantaneous speed – what are their definitions and how are they used? Vectors and scalars – what is the difference? Velocity – what is velocity and how is it related to speed? Acceleration – what is it and what is its relationship to velocity? Changing what produces an acceleration? Graphing Motion – how are velocity and acceleration related to the graphs of different quantities? Uniform Acceleration – how are position, velocity and acceleration all related when the acceleration is constant? Chapter 3. Acceleration due to gravity – how do objects move when subjected to gravity? Falling objects – how do you describe the motion of a falling object? Throwing a ball upward – what are the similarity and differences between a dropped object and a thrown object? Projectile Motion – independence of horizontal motion and vertical motion. How the two motions work together. Chapter 4. Newton’s First Law – understand the law of inertia. This is a special case of the second law (for the case of no forces.) Newton’s Second Law – How forces are related to changes in motion. Mass and Weight – What are the differences between the two. How are they mathematically related? Newton’s Third Law – forces come in pairs. They always act on different objects. They are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. The horse and cart ‘paradox.’ Chapter 5. Uniform Circular Motion – be able to describe the motion and know when is an appropriate time to use it. Centripetal acceleration – what direction is it and what is its magnitude? When does it occur? Centripetal forces – be able to apply Newton’s second law to centripetal accelerations. Newton’s law of universal gravitation – what things affect ths size of the force of gravity and what direction does it point? Chapter 6. Work – what is the definition of work? When does it show up? What sign is it? Power – how is power different from work? When is it important? Kinetic Energy – how is Kinetic Energy related to the work done on an object? What is its mathematical form? This is called the work-kinetic energy theorem. Potential Energy – What is Potential Energy? How is it related to work done by a force? What different types of potential energy are there? Conservation of Energy – When is mechanical energy conserved? How do you use conservation of energy to understand what is happening in a system? Friction – When friction is present, how does that change conservation of energy? Oscillations – What factors affect the frequency of oscillation of a spring-mass system? What factors affect the frequency of oscillation of a pendulum? How does conservation of energy relate to oscillating systems?