Print › 3.D Cell Signaling Without Pictures | Quizlet | Quizlet
advertisement
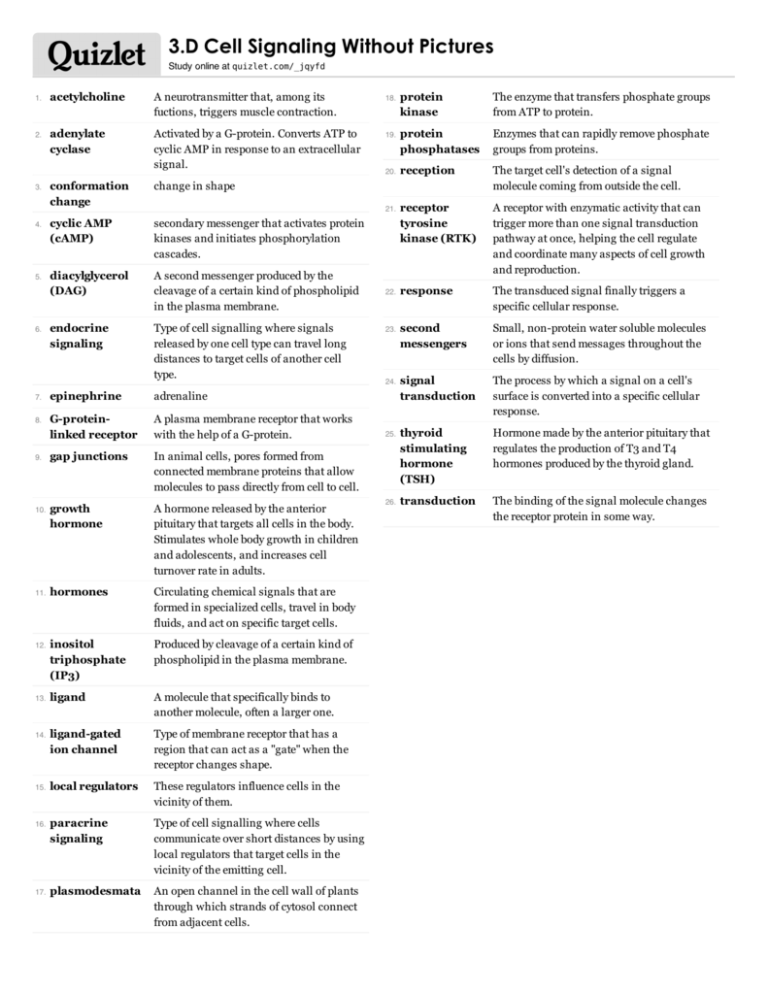
3.D Cell Signaling Without Pictures Study online at quizlet.com/_jqyfd 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. acetylcholine A neurotransmitter that, among its fuctions, triggers muscle contraction. adenylate cyclase Activated by a G-protein. Converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to an extracellular signal. conformation change change in shape cyclic AMP (cAMP) secondary messenger that activates protein kinases and initiates phosphorylation cascades. diacylglycerol (DAG) A second messenger produced by the cleavage of a certain kind of phospholipid in the plasma membrane. endocrine signaling Type of cell signalling where signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell type. epinephrine adrenaline G-proteinlinked receptor A plasma membrane receptor that works with the help of a G-protein. gap junctions In animal cells, pores formed from connected membrane proteins that allow molecules to pass directly from cell to cell. growth hormone A hormone released by the anterior pituitary that targets all cells in the body. Stimulates whole body growth in children and adolescents, and increases cell turnover rate in adults. hormones Circulating chemical signals that are formed in specialized cells, travel in body fluids, and act on specific target cells. inositol triphosphate (IP3) Produced by cleavage of a certain kind of phospholipid in the plasma membrane. ligand A molecule that specifically binds to another molecule, often a larger one. ligand-gated ion channel Type of membrane receptor that has a region that can act as a "gate" when the receptor changes shape. local regulators These regulators influence cells in the vicinity of them. paracrine signaling Type of cell signalling where cells communicate over short distances by using local regulators that target cells in the vicinity of the emitting cell. plasmodesmata An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect from adjacent cells. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. protein kinase The enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to protein. protein phosphatases Enzymes that can rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins. reception The target cell's detection of a signal molecule coming from outside the cell. receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) A receptor with enzymatic activity that can trigger more than one signal transduction pathway at once, helping the cell regulate and coordinate many aspects of cell growth and reproduction. response The transduced signal finally triggers a specific cellular response. second messengers Small, non-protein water soluble molecules or ions that send messages throughout the cells by diffusion. signal transduction The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response. thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Hormone made by the anterior pituitary that regulates the production of T3 and T4 hormones produced by the thyroid gland. transduction The binding of the signal molecule changes the receptor protein in some way.