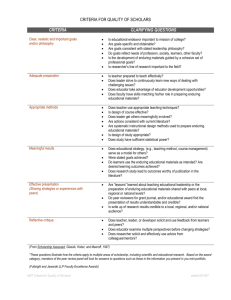
Integrated Science I Integrated Science I is a year long course that
advertisement

Integrated Science I Integrated Science I is a year long course that seeks to introduce students to basic chemistry, physical and earth science concepts. This course is designed to prepare students for college prep chemistry and physics. Topics include but are not limited to the physical and chemical properties of matter and energy, astronomy, geology, and meteorology. Enduring Understanding One: Science is a system of knowledge and methods for finding that knowledge. • What are the major branches of natural science and how do they overlap? • What are the main ideas of physical science? • What are the steps in the scientific method? • How are facts, scientific theories, and scientific laws the same and how are they different? Enduring Understanding Two: Much of the data scientist collect can be made into quantitative data. • How do you manipulate data that is in scientific notation? • How do you convert between metric units? Enduring Understanding Three: The composition of a material can be used to classify material and determine its physical and chemical characteristics. • How are substances classified? • What are the characteristics of an element and the symbols used to identify them? • What are the characteristics of a compound? • How are pure substances different from mixtures? • How do you classify mixtures as solutions, suspensions, or colloids? • What are the physical properties of matter? • What are the chemical properties of matter? • What is the difference between a physical and a chemical change? Enduring Understanding Four: Solids, liquids, and gases are common states of matter. Phase changes between these states of matter require energy to transfer between the object and the environment. The behavior of a gas is determined by its temperature, pressure, and volume. • What are the five states of matter? • How are materials classified as solids, liquids or gases? • What is gas pressure and what factors influence it? • What are Charles’s law, Boyle’s law, and the combined gas law? • What is a phase change? • What happens to the motion, arrangement, and average kinetic energy of molecules during a phase change? • What are the six types of phase changes? Enduring Understanding Five: Atoms are the basic unit of all matter and each has a specific structure. • What are the different models of an atom? • How has the model of an atom evolved over time? • What are the three subatomic particles? • What is the difference between the atomic number and the mass number of an element? • What is an electron cloud? • What are electron configurations? Enduring Understanding Six: The elements are arranged in the periodic table in such a way that their properties can be predicted based on where they are. • How did Mendeleev arrange the elements in his table? • How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table? • How is the atomic mass determined? • What are the general properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids? • How do the properties of elements change across a period in the periodic table? • How do the valence electrons relate to groups in the periodic table and to properties of elements in those groups? Enduring Understanding Seven: Elements bond in different ways to form compounds and molecules. • How do ionic bonds form? • How do covalent bonds form? • How are ionic and covalent bonds named? • How are the formulas for ionic and covalent bonds written? Enduring Understanding Eight: Chemical equations are used to describe the different types of chemical reactions. • What are chemical equations? • How do you balance chemical equations? • How do you convert between moles and mass? • What are the different types of reactions? • How does energy change during a chemical reaction? Enduring Understanding Nine: Solutions are created by dissolving one substance into another. Each solution has its own unique qualities and characteristics. • What are dissociation, dispersion, and ionization? • How are the physical properties of a solution can different from those of its solute and solvent? • What are the factors affect the rate at which a solute dissolves in a solvent? • What is solubility and what factors affect it? • What does it mean to be unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated? • What are properties of an acid? • What are properties of a base? • • • • • • What is a neutralization reaction? How can acids and bases be defined as proton donors and acceptors? What is the pH scale? What makes a strong acid or base? What is a buffer? What is an electrolyte? Enduring Understanding Ten: Displacement is the straight line distance between two points. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement, and acceleration is the change in velocity. • What are frames of reference and how are used to measure motion? • What are the appropriate SI units for measuring distance? • What is the difference between distance and displacement? • How do you calculate displacement using vector addition? • What are the appropriate SI units for measuring speed? • What is the difference between average speed and instantaneous speed? • How do you calculate speed using an object using slopes? • How do you combine velocities? • How changes in motion that produce acceleration? • What are some examples of constant acceleration? • How do you calculate the acceleration of an object? • How do you classify acceleration as positive or negative? • What is instantaneous acceleration? Enduring Understanding Eleven: A force is a push or pull and is the cause of acceleration. Friction is the opposing force that acts on objects that touch when they pass by each other. Newton’s Laws describe how force and accelerations are related to each other. • What are examples of forces and what SI units measure them? • How is the motion of an object affected when balanced and unbalanced forces act on it? • What are the four different types of friction? • How do gravity and air resistance affect falling objects? • What does the path of a projectile look like and what forces produce it? • What are Newton’s three laws of motion? • How is mass different from weight? • What is momentum? Enduring Understanding Twelve: A fluid behaves differently from a solid or a liquid because of the atoms are weaker. Fluids respond differently to forces and pressures. • What is pressure and what SI units do you use to measure it? • What is the relationship between depth and pressure? • How are forces from pressure distributed at a given level in a fluid? • How does altitude affect air pressure? • • • • • How is pressure transmitted in a fluid? According to Pascal’s principle how are the speed and pressure of a fluid related? How does buoyancy affect the apparent weight of an object? What is the relationship between the volume of a fluid displaced by an object and buoyant force acting on an object? What causes objects to float? Enduring Understanding Thirteen: Work and power depend on the amount of force applied and the time that force was exerted. Machines can help reduce the amount of forced needed to do work. • What conditions must exist for force to do work on an object? • How do you calculate the amount of work done? • How do you calculate power? • What is a machine and how does it make work easier? • How do you calculate a machine’s efficiency? • What is mechanical advantage? • What are six types of simple machines? • What are compound machines? Enduring Understanding Fourteen: The total mechanical energy of a system is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy, as the energy converts from on to another it is conserved. • What is the relationship between work and energy? • How is kinetic energy related to mass and speed? • How is potential energy related to an objects’ position? • How does energy convert from one form to another? • What is the law of energy conservation? • How is energy converted between kinetic and potential energy? Enduring Understanding Fifteen: The internal energy of an object is the total energy of all the atoms and molecules within it. This energy can be transferred by convection, radiation or conduction, and this energy follows the three laws of thermodynamics. • How do heat and work transfer energy? • How do you calculate thermal energy, temperature change, or mass using the specific heat equation? • What are conduction, convection, and radiation? • What is the difference between thermal conductors and thermal insulators? • What are the three laws of thermodynamics? Enduring Understanding Sixteen: Waves carry energy through a medium, and these waves can be reflected or refracted. • What are three different types of mechanical waves? • How do waves carry energy through a medium? • What are the parts of these waves? • • • • • • What are frequency, period, wavelength, and wave speed? How do reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference affect waves? What factors affect the amount of refraction, diffraction, or interference? What is the difference between construction and destructive interference? What are the properties of a sound wave? How does relative motion determine the frequency of sound? Enduring Understanding Seventeen: All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in empty space. Their speed through a medium depends on the medium and on the frequency of a wave. These waves will also reflect and refract as they interact with different mediums. • What are the characteristics of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum? • How do you calculate the wavelength and frequency of an electromagnetic wave given its speed? • How are electromagnetic waves classified? • What are the uses for different waves of the magnetic spectrum? • How are materials classified? • What happens with light is reflected, refracted, polarized, or scattered? Enduring Understanding Eighteen: When light rays reflect from any mirror, the angle of incidence equals the angle or reflection. A lens is a curved piece of transparent material that is used to focus light. • What is the law of reflection? • What is the difference between real and virtual images? • What are the physical characteristics of a plane, convex, and concave mirror, and what types of images do they form? • What causes light to refract? • What is the index of refraction? • What are the physical characteristics of a concave and convex lens and what images do they form? Enduring Understanding Nineteen: Electricity is the flow of charges which can flow to create different types of circuits. • How do electric charges transferred and why do electric discharges occur? • What is an electric charge? • What are electric currents and what are two different types? • What are electrical conductor and insulators? • What are the factors that affect resistance? • How does voltage produce current? • How do you calculate voltage, current and resistance using Ohm’s law? • What is a circuit and what are the two different types? Enduring Understanding Twenty: Magnetic fields are produced whenever an electric charge is in motion. When a magnetic field moves through a closed loop of wire a current is produced. • What are the effects of magnetic forces and magnetic fields? • How does Earth’s magnetic field affect a compass? • How does a moving electric charge create a magnetic field? • How is an electric current generated by electromagnetic induction? Enduring Understanding Twenty one: The earth is composed of layers; the top layer is created by plates that move. When movement occurs different geologic incidences occur. By studying rocks and minerals we can determine under what conditions they were formed, thus revealing the geologic history of an area. • What is geology? • What are the main layers of earth’s interior? • What are the differences between a rock and a mineral? • How do you identify rocks and minerals? • What are the different classes of rocks? • What is the rock cycle? • What is continental drift? • How does the theory of plate tectonics explain sea floor spreading, subduction, and the formation of mountains? • What are the causes and effects of stress in the earth’s crust? • Why do earthquakes occur? • How are earthquakes measured? • What is the internal structure of a volcano? • What are the different types of volcanic eruptions? • What are the different types of volcanoes? Enduring Understanding Twenty two: The earth’s oceans are divided into different layers, each with their own unique characteristics. The ocean water is also constantly in motion, impacting the shoreline. • How do the properties of ocean water change with depth? • What are the different features found on the ocean floor? • What is the difference between surface currents, deep currents, and upwelling? • What is the process by which waves and currents cause erosion and deposition? Enduring Understanding Twenty three: The earth’s season are created by the tilting of the planet. This also creates unique convection cells within the atmosphere which impacts our weather and climate. • What is an atmosphere and why is it essential to life? • What are the different layers of our atmosphere and what are their properties? • What causes the seasons? • Why do different latitude zones have different average temperatures? • What are local and global winds and how are they produced? • How are clouds and precipitation formed? • • • How are air masses formed and classified? What are the four types of fronts and what type of weather is associated with each? What are the major types of storms and how are they formed? Enduring Understanding Twenty four: Our solar system is made up of several unique plants that orbit around our sun. • What are the difference and similarities between the geocentric and heliocentric model of the solar system? • How do the planets orbit the sun? • How was our moon formed? • What are the characteristics found on the surface of the moon? • Why do the phases of the moon, eclipses, and tides occur? • What are the unique characteristics of the terrestrial planets? • What is an asteroid and how are they formed? • What are the unique characteristics of the gas giants? • What is the difference between a comet and meteoroids? • How did our solar system form? Enduring Understanding Twenty five: Our sun is one of billions within the universe, each going through its own life cycle. • How does the sun produce energy? • What are the interior and atmospheric features of the sun? • How can you measure the distance between stars? • How can you classify stars? • How do stars form? • What is the life cycle of a star? • How are stars distributed in space? • What are the basic types of star clusters? • How do you classify galaxies? • What is the big bang theory? • What is dark matter and what is its importance of its effects on the expanding universe?