ANTACID NEUTRALIZATION Claudia Zimmerman
advertisement
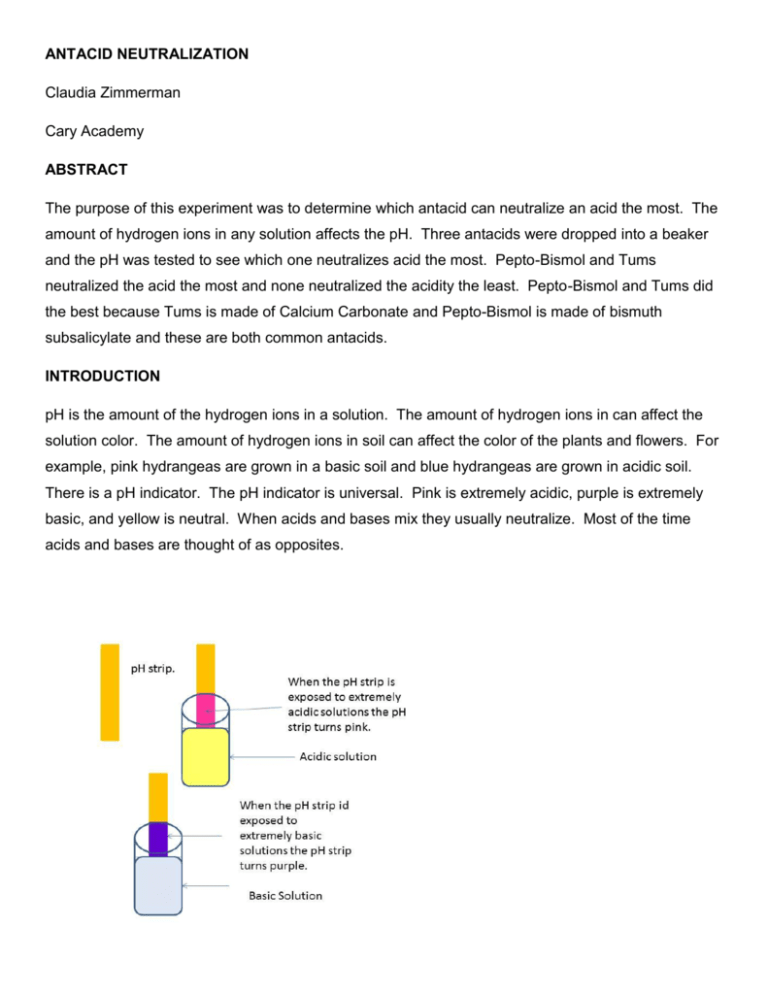
ANTACID NEUTRALIZATION Claudia Zimmerman Cary Academy ABSTRACT The purpose of this experiment was to determine which antacid can neutralize an acid the most. The amount of hydrogen ions in any solution affects the pH. Three antacids were dropped into a beaker and the pH was tested to see which one neutralizes acid the most. Pepto-Bismol and Tums neutralized the acid the most and none neutralized the acidity the least. Pepto-Bismol and Tums did the best because Tums is made of Calcium Carbonate and Pepto-Bismol is made of bismuth subsalicylate and these are both common antacids. INTRODUCTION pH is the amount of the hydrogen ions in a solution. The amount of hydrogen ions in can affect the solution color. The amount of hydrogen ions in soil can affect the color of the plants and flowers. For example, pink hydrangeas are grown in a basic soil and blue hydrangeas are grown in acidic soil. There is a pH indicator. The pH indicator is universal. Pink is extremely acidic, purple is extremely basic, and yellow is neutral. When acids and bases mix they usually neutralize. Most of the time acids and bases are thought of as opposites. Figure 1. The pH strip turns pink when extremely acidic and turns purple when extremely basic. The more hydrogen ions the stronger the acid and the fewer the hydrogen ions the less acidic the solution is. In chemistry the word “acid” has a specific and precise definition. The definition is a chemical compound that dissociates in solution, releasing hydrogen ions and lowering the solution pH (a proton donor). A pH of one and two are strong acids. Things in nature also have pH, such as a bee sting. The sting of a bee is acidic. Ammonia is a household cleaner that is a base. When hydrangeas are grown in a basic soil they turn pink. pH’s above 7 are considered acids. pH’s below 7are considered bases. Lead battery acid is an extremely acidic solution. Soda lye is an extremely basic solution. An antacid is any substance that neutralizes acidity. Antacids are used to neutralize acids. Antacids that come over the counter usually neutralize the acidity. In many over the counter antacids the main ingredient is baking soda. Other common ingredients in antacids are aluminum hydroxide, bismuth subsalicylate, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium hydroxide, and calcium carbonate. Experiments like this have been done in the past by Coleman Mitchell. He is from Cary Academy. He tested which type of soda an Alka-Seltzer tablet would dissolve in fastest. He used 7up, Sprite, Ginger Ale, and water. 250 mL were put into a beaker and the pH was tested and recorded. He found out that Ginger Ale was the most acidic with a pH of 3. Another experiment that he did was measuring how long it took for an Alka-Seltzer tablet to dissolve. He found out that an Alka-Seltzer dissolves fastest in water. The Alka-Seltzer dissolved in water with a time of 66 sec. With his third experiment that he did was measuring Alka-Seltzer tablets in different amounts of water. He found that an Alka-Seltzer tablet will dissolve fastest in 150 mL of water. It took 60 sec for the Alka-Seltzer tablet to dissolve in 150 mL of water. For his fourth experiment, he tested different amounts of AlkaSeltzer in 7up. He found that one tablet dissolved in the least amount of time. One tablet dissolved in 7up in 90 sec. Coleman did this experiment again but this time using Ginger Ale. Again one tablet dissolved in Ginger Ale the fastest. One tablet dissolved in 65 sec. Coleman’s final experiment was like his fifth and sixth. This time he used sprite. Again, one tablet dissolved the fastest. One tablet in sprite dissolves in 85 sec. These were experiments done by Coleman Mitchell. The idea or concept of pH was first introduced by a Danish chemist. He was named Søren Peder Lauritz Sørensen. In 1909, he introduced the idea of pH at the Carlsberg Laboratory. From 1901 to 1938 he was head of the prestigious Carlsberg Laboratory in Copenhagen. When he was working at the Carlsberg Laboratory he studied the amount of ion concentration on proteins and the effect that it had. In 1909 he explained the pH scale as a simple and basic way of expressing the amount of hydrogen ions in a solution. MATERIALS AND METHODS In these experiments beakers, water, lemon juice, Tums, Prevacid, Pepto-Bismol, baking soda, vinegar, stopwatches, and a pill cuter were used. 100 mL of water and 60 mL of lemon juice were added into a beaker. Different Ant-Acids were added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after adding the tablet was recorded. This process was repeated three times. 100 mL of water and 60 mL of lemon juice were added to a beaker. Different amounts of PeptoBismol were added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after adding the tablet was recorded. This process was repeated three times. 100 mL of water and 60 mL of lemon juice were added to a beaker. Pepto-Bismol was added for different times and the pH before and after were recorded. This process was repeated three times. 60 mL of lemon juice was added to a beaker. Different amounts of water were added and the pH before and after the water was added was recorded. This process was repeated three times. 100 mL of water and 60 mL of lemon juice were added to a beaker. Different consistencies of Tums were added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after were recorded. This process was repeated three times. 100 mL of water and 60 mL of lemon juice were added to a beaker. Different amounts of baking soda were added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after were recorded. This process was repeated three times. 100 mL of water and 60 mL of lemon juice were added to a beaker. Different colors of Tums were added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after were recorded. This process was repeated three times. 50 mL of different Acid Liquids were added to a beaker. A Tum was added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after were recorded. This process was repeated three times. 100 mL of water and different amounts of lemon juice were added to a beaker. A Tum was added and left in for 60 sec. The pH before and after were recorded. This process was repeated three times. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 7 6 5 pH of Before and After 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 None Prevacid Pepto Bismal Tums Type of Antacid Figure 2. How well different ant-acids can turn an acid into a base. Pepto-Bismol and Tums got the lowest pH of 6 and none got the highest pH of 2. Pepto-Bismol has an active ingredient of bismuth subsalicylate. Bismuth subsalicylate is found to what makes PeptoBismol work. Bismuth subsalicylate is found in most antacids, and is a powerful antacid. In Tums Calcium Carbonate USP is the active ingredient or what makes it work. Calcium Carbonate is also found in many antacids. Both of these active ingredients begin working immediately. In Prevacid, there is lansoprazole. Lansoprazole makes the capsule have a delayed reaction so there for the capsule did not work in one min. This is why Tums and Pepto-Bismol neutralized more than Prevacid. 7 pH Before and After 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 Amount of Pepto-Bismol Figure 3. The amount of Pepto-Bismol that works better 4 Three tablets of Pepto-Bismol got the lowest pH of 6 and one and two tablets got the highest pH of 5. In one and two tablets, there isn’t as much bismuth subsalicylate as in three tablets. When there is more bismuth subsalicylate the more the pH is able to go down. Figure 4. Three Pepto-Bismol Tablets have more bismuth subsalicylate than one tablet does. 7 The pH Before and After 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 Amount of Time (sec) Figure 5. The amount of time that the Pepto-Bismol was in the water and lemon juice 90 sec got the lowest pH and 30 sec got the highest pH. 90 sec got the lowest pH because the bismuth subsalicylate had more time to neutralized the acid. 30 sec got the highest pH because the bismuth subsalicylate didn’t have much time to work. 60 sec got a lower pH than 30 sec but not as low as 90 sec because the bismuth subsalicylate had less time neutralize the acid. 7 pH Before and After 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Amount of Water (mL) Figure 6. The amount of water added to the lemon juice The 50 mL of water got the highest pH and the 80 mL and 100 mL got the lowest pH. The 50 mL of water got the highest pH because the water was not able to dilute the lemon juice as much as the 100 mL of water was able to. When the water was able to dilute the lemon juice the Calcium carbonate had an easier time making the acid to a base. 7 pH Before and After 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 Crushed Cubed Whole Texture of Tums Figure 7. The crushed and cubed Tums did better than whole The crushed and cubed Tums got a pH of 6 and whole Tums got a pH of 5. The crushed and cubed did better because when the tums was cubed it was able to neutralize the acidity in four places. This meant that it was able to neutralize almost four times as much. The whole tum was only able to neutralize the acidity in one place, so not as much as crushed or cubed. The crushed tums was able to neutralize the acidity in many places. 8 pH Before and After 7 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 0 5 10 15 20 Amount of Baking Soda (mL) Figure 8. The pH before and after adding the baking soda The 15 mL baking soda and 5 mL baking soda got a pH of 7 and 1 mL of baking soda got a pH of 6. In baking soda, the main ingredient is sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate is the only ingredient in baking soda. Other ingredients such as flavoring in Tums and Pepto-Bismol can help reduce the how well the antacid can neutralize the acid. 7 pH Before and After 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 Blue Purple Pink Color of Antacid Figure 9. Blue Tums lowers the acidity more than pink and purple. Blue got a pH of 6 and purple and pink got a pH of 5. Blue didn’t need any dyes whereas pink and purple did. The dyes can make the antacid not work as well. This is why blue worked better than purple and pink. 9 pH Before and After 8 7 6 5 4 Starting pH 3 Ending pH 2 1 0 Vinegar Lemon Juice Water Acid Liquid Figure 10. Tums lowers the acidity with vinegar more than lemon juice. Water got the lowest pH of 8 but the starting pH was 7 so the tum did not have much of an effect. Vinegar can help lower blood sugar spikes. Vinegar has a negligible amount of magnesium but still has some. Magnesium can lower the pH temporarily, so adding the tums help lower the pH even more. This is why the vinegar got a lower pH than lemon juice. 6 pH Before and After 5 4 3 Starting pH 2 Ending pH 1 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 Amount of Lemon Juice (mL) Figure 11. Different amounts of lemon juice have different effects on the pH 20 mL of lemon juice got the lowest pH of 5 and 80 mL got the highest pH of 2. With 20 mL of lemon juice, the water was able to dilute the lemon juice. Therefor the pH was low. With 80 mL of lemon juice, the water could not dilute the lemon juice. There was so much acidity that the tums could not work well and it did not lower the pH. CONCLUSION It was found that Pepto-Bismol and Tums neutralize acidity better than Prevacid. When there is acidity in a stomach people will want to take Pepto-Bismol or Tums to help relieve pain fast. The outcome was unsurprising because it was expected that antacids with active ingredients that are popular in most antacids would do the best. In the future another follow up experiment would be if either newer or older antacids work better. CITATIONS "Antacid." Encyclopedia Britannica. Encyclopedia Britannica Online School Edition. Avraham, Regina. “Antacids.” The Digestive System, Chelsea House Publishers, 1989 Challoner, Jack. Acids and Bases. The Visual Dictionary of Chemistry, DK Publishing 1996 Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 2013. Web. 16 Jan. 2013. Karen Vaughan “Vinegar, Muscle Cramps, Blood Sugar and Acids.” SelfGrowth. 17 Feb. 2013 Mitchel, Coleman 2012 ISP Mitchell, Coleman Cary Academy 2012 Newmark, Ann. “Acids and Bases.” Chemistry, New York: DK Publishing, 1993 “pH.”Wikipedia February 17, 2013 Web. 17 Feb. 2013