Solutions to Test #3
advertisement

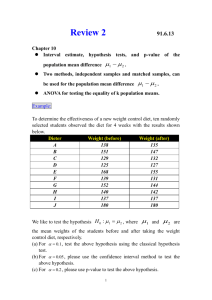
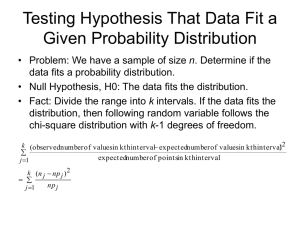
Elementary Statistics Fall, 2006 Name: Dr. D. P. Story Test 3 Instructions: (100 points) Solve each problem without error, feel free to use the probability tables provided, or use your calculator to compute probabilities. (14pts ) 1. Multiple choice/fill-in the blank/True-False questions. (a) (2 pts) Given the same sample statistics, which level of confidence would produce the widest confidence interval? 90% 95% 98% ✔ 99% (b) (2 pts) What is the effect on the width of the confidence interval when the sample size is increased? the width increases ✔ the width descreases No effect (c) (2 pts) You wish to construct a 95% confidence interval for a population mean of a normal population using a sample size of n = 18. Your confidence interval will be based on the t -distribution with 17 degrees of freedom. (d) T (True/False, 2 pts) If you reject the null hypothesis, you can support the alternate hypothesis. (e) (3 pts) A statistician takes a random sample of size n = 20 from a normal population and plans on using a left-tailed t -test with α = 0.10. In this case, the rejection region is t < −1.328 . (The answer has the form: t < −a or t > a, where a is the critical value for the test. Of course, you need to determine the value of a.) (f) (3 pts) Of the 848 children surveyed, 102 plan to join the armed forces in the future. The point estimate for the true population proportion of children who plan to join the armed services is p̂ = 0.12 . Confidence Intervals. The problems #2–6 concern the topic of confidence intervals. (7pts ) 2. Find the margin of error for the given values of c = 0.90, s = 2.5 and n = 36. Margin of Error = 0.6854 Solution: 2.6 E = (1.645) · √ = 0.6854 36 (10pts ) 3. A random sample of 56 American beech trees has a mean height of 10.452 meters and a standard deviation of 2.130 meters. Construct a 99% confidence interval for the the population mean height. 99% C.I. = 9.719 , 11.185 Solution: 2.13 E = (2.575) · √ = 0.7329 56 Calculate the endpoints of the confidence interval: x̄ − E = 9.719 x̄ + E = 11.185 Stats/T3 (7pts ) – Page 2 of 4 – Name: 4. Determine the minimum required sample size if you want to be 95% confident that the sample mean is within 0.5 unit of the population mean given σ = 4.8. n= 355 Solution: We plug the information into the formula: z · σ 2 1.96 · 4.8 2 n= = = 354.04 E 0.5 (10pts ) 5. In a random sample of 9 microwaves, the mean repair cost was $75.00 with a sample standard deviation of s = $12.50. Assuming the population is normally distributed, construct a 95% confidence interval for the mean cost of repair of microwave ovens. (Does one construct this interval based on the z-distribution or the t -distribution?) 95% C.I. = 65.39 , 84.61 Solution: From the t -tables, for 95% confidence interval and degrees of freedom of 8 we have tc = 2.306. 12.50 E = (2.306) · √ = 9.61 9 Calculate the endpoints of the confidence interval: x̄ − E = 65.39 x̄ + E = 84.615 (10pts ) 6. In a survey of 1024 adults from the United States, 122 of them said they were not confident that the food they eat in the United States is safe. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the proportion, p, of people that are not confident that the food they eat in the United States is safe. 95% C.I. = Solution: 0.099 , 0.139 p̂ q̂ (0.12)(0.88) E=z = (2.306) · = 0.0199 ≈ 0.02 n 1024 Calculate the endpoints of the confidence interval: p̂ − E = 0.099 ≈ 0.10 p̂ + E = 0.139 ≈ 0.14 Hypothesis Testing. The problems #7–10 concern the topic of confidence intervals. (12pts ) 7. A car dealer claims that at least 24% of its new customers will return to buy their next car. Let p denote the true population proportion of new customers that will return to buy a new car. (a) (6 pts) Based on the claim of the dealer, set up the hypotheses using the rules introduced by the text. ⎧ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨H0 ! p ≥ 0.24 ⎪ ⎪ ⎩H ! a p < 0.24 Stats/T3 – Page 3 of 4 – Name: (b) (6 pts) Write sentences describing type I and type II errors for this test of hypothesis. type I error ! Reject the dealer’s claim, when it is, in fact, true. type II error ! Accept the dealer’s claim, when it is, in fact, false (10pts ) 8. A light bulb manufacturer guarantees that the mean life of a certain type of light bulb is at least 750 hours. A random sample of 36 light bulbs has a mean life of 745 hours with a standard deviation of 60 hours. Do you have enough evidence to reject the manufacturer’s claim? Use α = 0.05. Test the hypotheses and show all details. ⎧ ⎪ ⎨H ! μ ≥ 750 (Claim) 0 ⎪ ⎩H ! μ < 750 a (a) Rejection Region. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region. Solution: Reject if… z < −1.645 (b) Calculations. Find the value of the standardized test statistic. Solution: 745 − 750 z= √ = −0.5 60/ 36 (c) Conclusions. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Solution: Cannot reject H0 . There is insufficient data at α = 0.05 to refute the claim. (10pts ) 9. An environmentalist estimates that the mean waste recycled by adults in the United States is more than 1 pound per person per day. You want to test this claim. You find that the mean waste recycled per person per day for a random sample of 12 adults in the United States is 1.2 pounds and the standard deviation is 0.3 pound. At α = 0.05, can you support this claim? ⎧ ⎪ ⎨H ! μ ≤ 1 0 ⎪ ⎩H ! μ > 1 a (Claim) (a) Rejection Region. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region. Solution: For α = 0.05 and d.f. = 11, we have t > 1.796 (b) Calculations. Find the value of the standardized test statistic. Solution: 1.2 − 1 √ = 2.31 z= 0.3/ 12 (c) Conclusions. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Solution: Reject H0 . There is sufficient evidence to support the environmentalist’s claim that μ > 1. Stats/T3 (10pts ) – Page 4 of 4 – Name: 10. A medical researcher says that at least 23% of U.S. adults are smokers. In a random sample of 200 U.S. adults, 22.5% say they are smokers. At α = 0.01, do you have enough evidence to reject the researcher’s claim? Test, ⎧ ⎪ ⎨H ! p ≥ 0.23 (Claim) 0 ⎪ ⎩H ! μ < 0.23 a (a) Rejection Region. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region. Solution: z < −2.33 (b) Calculations. Find the value of the standardized test statistic. Solution: 0.255 − 0.23 −0.075 z= = −0.168 = 0.0298 (0.23)(0.77)/200 (c) Conclusions. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Solution: Fail to reject H0 . There is insufficient evidence to deny the claim.