Ionic Bonding
advertisement

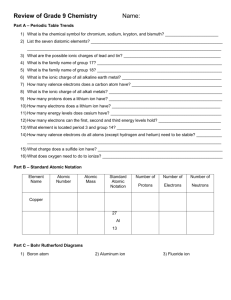
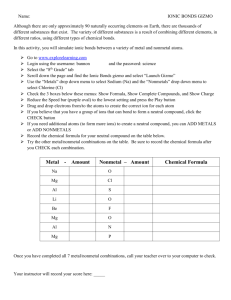
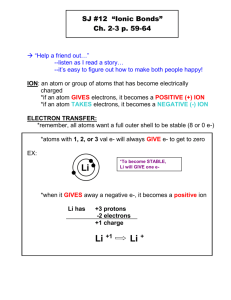
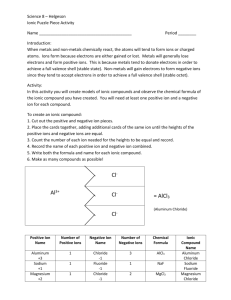
IONIC BONDING 2014-2015 Science 8 TERMS TO KNOW Ion: an atom or atoms with an electric charge Polyatomic ion: an ion made of more than one atom Ionic bond: chemical bond between two oppositely-charged ions Compound: the product of the bond between the ions Subscript: a number in a chemical formula that tells the ratio of elements in an ionic compound. Chemical formula: the symbols and subscripts showing the elements in a given compound. IONS Atoms without full valence shells can gain or lose electrons. Cations are atoms that have lost electrons (lost negative energy) and are therefore positive ions. Anions are atoms that have gained electrons (gained negative energy) and are therefore negative ions. IONS Consider Lithium and Bromine and answer the following questions. 1) Circle. Lithium is a (metal/nonmetal) and Bromine is a (metal/nonmetal). 2) Lithium has valence electrons. Bromine has valence electrons. 3) How many valence electrons make an atom feel “full”? 4) It takes a lot of energy to hold onto valence electrons in a nearempty shell. Which element is more likely to lose their valence electron? 5) What type of ion will Lithium become? IONS Consider Lithium and Bromine and answer the following questions. 1) Circle. Lithium is a (metal/nonmetal) and Bromine is a (metal/nonmetal). 2) Lithium has 1 valence electrons. Bromine has 7 valence electrons. 3) How many valence electrons make an atom feel “full”? 8 4) It takes a lot of energy to hold onto valence electrons in a nearempty shell. Which element is more likely to lose their valence electron? 5) What type of ion will Lithium become? Positive (+1) cation IONS Because metals do not have many valence electrons and their shells are relatively empty, they will tend to lose their electrons and become cations. Nonmetals, on the other hand, tend to have almost full valance shells, and therefore will gain electrons and become anions. Cations and anions are oppositely charged, and because of that, they are attracted to each other. This is a chemical bond called an ionic bond, because it is a bond between two ions. IONIC BOND PROPERTIES Ionic compounds are generally: Hard, brittle crystals that have high melting points, conduct electricity and are dissolvable in water. IONIC COMPOUNDS – FORMULAS AND NAMES Compounds are often written by their chemical formula, or the symbols that also show the ratio of atoms needed to make the compound. To find the formula, you need to find the charge of the ion, then balance them. IONIC COMPOUNDS – FORMULAS AND NAMES Practice: Find the ionic charges, then balance. A) Na B) Mg C) Rb O Cl N IONIC COMPOUNDS – FORMULAS AND NAMES Practice: Find the ionic charges, then balance. A) Na B) Mg C) Rb O Cl N Na 0 MgCl Rb N IONIC COMPOUNDS – FORMULAS AND NAMES To write the name of an ionic compound, you write the positive ion (metal) first, and then the negative ion. If the negative ion is a sign element, and not a polyatomic ion (an ion with many atoms), then you change the suffix to –ide. It does not matter how many atoms you have of each. Write the names of the three examples below: Na20 MgCl2 Rb3N IONIC COMPOUNDS – FORMULAS AND NAMES To write the name of an ionic compound, you write the positive ion (metal) first, and then the negative ion. If the negative ion is a sign element, and not a polyatomic ion (an ion with many atoms), then you change the suffix to –ide. It does not matter how many atoms you have of each. Write the names of the three examples below: Na20 sodium oxide MgCl2 magnesium chloride Rb3N rubidium nitride REVIEW QUESTIONS Review Questions: Ionic compounds are formed mostly between: When an atom loses a valence electron, it becomes a(n) . In an ionic compound, the total positive charges of all the positive ions the total negative charge of all the negative ions. REVIEW QUESTIONS Review Questions: Ionic compounds are formed mostly between: metals and nonmetals When an atom loses a valence electron, it becomes a(n) anion. In an ionic compound, the total positive charges of all the positive ions equals the total negative charge of all the negative ions. Ionic Bonding Terms to know: Ion: an atom or with an charge Polyatomic ion: an ion made of more than atom Ionic bond: chemical bond between two charged ions Compound: the of the bond between the ions Subscript: a number in a chemical formula that tells the of elements in an ionic compound. Chemical formula: the symbols and showing the elements in a given compound. GLUE THIS SIDE DOWN IN YOUR NOTEBOOK Page # A) Na O B) Mg Cl C) Rb N To write the name of an ionic compound, you write (metal) first, and then the negative . the If the negative ion is a sign element, and not a many atoms), then you change the suffix to It does not matter atoms you Write the names of the three examples Na20 MgCl2 Rb3N (an ion with . have of each. below: Review Questions: 1) Ionic compounds are formed mostly between: 2) When an atom loses a valence electron, it becomes a(n) . 3) In an ionic compound, the total positive charges of all the positive ions the total negative charge of all the negative ions.