Worksheet

Worksheet
Lesson: Ionic and Covalent Bonding
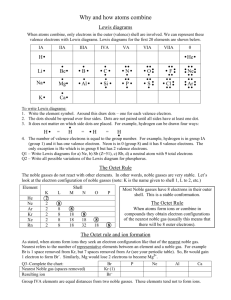
1. Lewis symbol and the Octet Rule
1.1 Write the Lewis symbol for each of the following atoms: a. H b. Na c. Cl d. Mg e. N
1.2 The electronic configuration of a carbon atom in its ground and excited states is 1s
2
2s
2
2p
2
and
1s
2
2s
1
2p
3
respectively. a. Draw the Lewis symbol for the carbon atom in the ground state. b. Draw the Lewis symbol for the carbon atom in the excited state. c. How could a carbon atom conform to the octet rule?
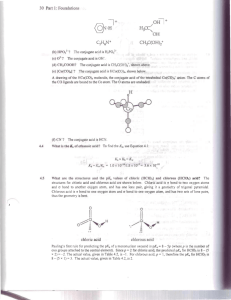
1.3 The valence orbital diagram for S atom in sulphur hexafluoride is: a. Draw the Lewis symbol of S in sulphur hexafluoride. b. Does the sulphur atom conform to the octet rule? Explain your answer.
2. Ionic bonding
2.1 Determine the charge on the ion formed when each of the following atoms is ionised to form a stable ion. Explain your answer: a. calcium b. zinc c. oxygen d. sulphur
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. 1
2.2 Write the chemical formula of the ionic compound formed when each of the following pairs of elements react : a. magnesium and nitrogen b. zinc and oxygen
3. Simple covalent bonding
3.1 Deduce the type of chemical bond in each of the following compounds. a. HI b. NaF c. Cl
2
O d. CaO
3.2 Draw the Lewis structure of each of the following molecules: a. BF
3 b. Cl
2
O
4. Properties of substances with ionic and covalent bonding
4.1 Sodium chloride has a high melting point. Give an explanation for this observation.
4.2 Electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide gives aluminium at the cathode and oxygen at the anode. Explain this observation.
© 2003 Ministry Of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. 2