Acid base Titration
advertisement

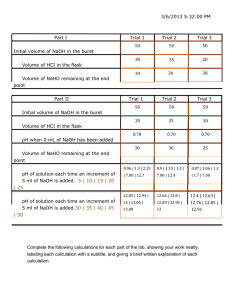
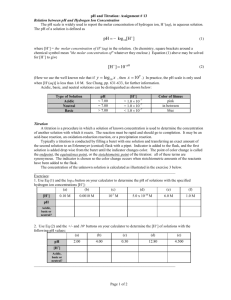
Acid base Titration Problem: How can the amount of acid in an unknown solution be determined? Materials: 125mL Erlenmeyer flask 100mL graduated cylinder Buret Ring stand Buret clamp Safety goggles NaOH HCl phenolpthalein distilled water Pre lab Questions: 1. If 24.3 mL of 0.085M NaOH solution are needed to completely neutralize 15.5 mL of an unknown acid, what is the concentration of the acid solution? 2. What is the H+ in each of the following acid solutions? a) 0.004 M HNO3? b) 1.33 M HClO4? c) 12MHI Procedure 1. Obtain a sample of unknown acid as directed by your teacher. Measure approximately 10mL of the acid solution into a clean graduated cylinder. Record the exact volume, and then place the acid in a clean 150-mL Erlenmeyer flask. 2. To the acid solution add six to eight drops of phenolphthalein indicator. Swirl to mix. Note: the solution should be colorless at this point. 3. Place the flask containing the acid under the tip of the buret. It maybe helpful in detecting the end point to place the flask on a piece of white paper. 4. Open the stopcock and allow the NaOH to flow slowly into the acid. As the NaOH drips into the acid, swirl the flask completely mix the acid and base together. Continue dripping the NaOH into the flask until the first persistent sign of pink appears. 5. Note and record the final volume of the base in the buret. 6. Repeat the titration with another 10.0mL of the same acid. Repeat the titration a third time. Each time be careful to record the initial volume and the final volume of the KOH in the buret. Analysis and Conclusions 1. For each of the three titrations, determine the number of milliliters of NaOH required to reach the end point 2. Calculate the molarity of an unknown acid in each of the three samples 3. Determine the average molarity of the unknown acid. Report your average answer to three significant figures. 4. a) What effect should each of the following on the molarity of your acid solution? rather than the desired light pink color, a bright magenta color marked the endpoint of the titration b) Ten drops of phenolphthalein, rather than 6-8 were used in the titration c) The flask was not swirled during the titration, and the experiment was stopped at the first sign of pink. 5. a) b) c) d) Using chemical resources, identify the primary acid found in each of the following: aspirin vinegar milk fruit juices Something Extra Repeat this experiment to compare the amount of acid present in lemon juice, apple juice, orange juice or grapefruit juice.( 10pts) Conclusion: (5pts) Rubric for the Activity: Acid base Titration Parts of the Lab Report Introduction Problem/ objectives Materials Procedure Data/table Pre lab Questions Analysis Conclusion Possible points 3pts Clearly stated objectives ( 3pts) Complete (2pts) Complete (3pts) Complete with proper labels (3 pts) 1.) 3pts 2.) a) 2pts b) 2pts c) 2pts 1) 3 points 2) 3points 3) 2points 4) a) 3 points b) 3 points c) 3points 5pts With clear calculations ( 10 pts) Something Extra Neatness and creativity of lab report(includes pictures of the experiment) Organization in performing the activity Total 5 points Participation of members / Follow procedures and clean working area 5 points 65 pts Points Earned Deductions -.5 for unclear objective -1 incomplete materials -1 incomplete procedure -1 without label -1 unclear answer -1 without solution -.5without unit -.5 without units -1 without solution -1 answer not in 3 significant digits - 1 unclear explanation -.5 every answer without unit -3 without showing calculations for solving the unknown concentration -1 ( every missing part of the lab-report) -1 not presentable work -1 no creativity -1 messy working area -1 always asking questions to the teacher without discussing it first with the group Common Ion Handout Cations +1 ammonium copper(I) or cuprous hydrogen hydronium lithium potassium rubidium silver sodium Anions -1 NH4+ Cu+ H+ H3O+ Li+ K+ Rb+ Ag+ Na+ 2+ barium Ba2+ cadmium Cd2+ calcium Ca2+ chromium(II) or chromous Cr2+ cobalt(II) or cobaltous Co2+ Copper (II) or cupric Cu2+ Iron (II) or ferrous Fe2+ Lead(II) or plumbous Pb2+ Magnesium Mg2+ Manganese Mn2+ Mercury (I) or mercurous Hg2+ Mercury (II) or mercuric Hg2+ Nickel Ni2+ Strontium Sr2+ Tin(II) or stannous Sn 2+ Zinc Zn2+ acetate bicarbonate bromide chlorate Chloride Chlorite cyanide fluoride hydride hydroxide hypochlorite Iodide Nitrate Nitrite Perchlorate Permanganate Thiocyanate C2H3O2HCO3BrClO3ClClO2CNFHOHClOINO3NO2ClO4MnO4SCN- 2carbonate chromate dichromate oxide peroxide selenide sulfate sulfide sulfite Thiosulfite CO32CrO42Cr2O72O2O22Se2SO42S2SO32S2O32- 3+ aluminum Chromium(III) Iron(III) or ferric Al3+ Cr3+ Fe3+ 3nitride phosphate phosphate N3PO43PO33-