GCF, LCM, and Distributive Property
advertisement

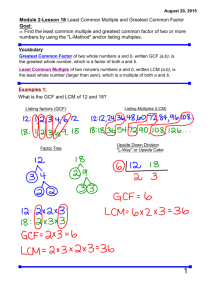
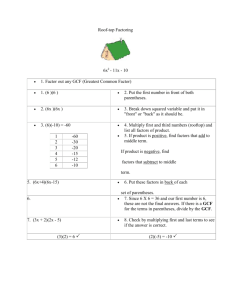
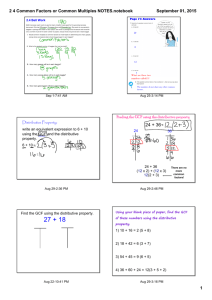
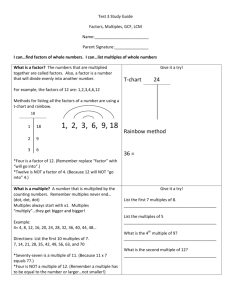
GCF, LCM, and Distributive Property Common Core Standard: Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1-100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. Factors- are numbers that when multiplied together equal a number (i.e., the factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, and 10) Greatest common factor – is the largest factor two or more numbers have in common o Least common multiple- is the smallest number that is a multiple of 2 or more numbers o This is noted as GCF This is noted as LCM Example: An artist can order paint brushes in bunches of one dozen and canvases in bunches of 5. Last month she ordered the same number of paint brushes as canvases. If she ordered no more than 100 paintbrushes, what is the smallest number of bunches of each that she could have ordered? o 1st: Determine if this is LCM or GCF o This is LCM, because the artist is ordering more or multiples 2nd: Determine the multiples of each number, until there is a number in common (sometimes, you might know the LCM from the very beginning) o Multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 ( I know that 5 times 12 is 60, and so I can stop now) Multiples of 5 are 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 3rd: Which multiple in common is the smallest? o 60 This means that the artists could have ordered 60 bunches of each. Example: At a party, Nylan’s mom is making treat bags. She has 24 noise makers and she has 32 boxes of candy. Nylan’s mom wants to use all the noise makers and candy. She wants all the treat bags to be the same. What is the largest number of treat bags she can make? o 1st: Determine if this is LCM or GCF o This is GCF, because there can’t be more treat bags than there are items to fill them 2nd: Determine the factors of each number Factors of 24 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 Factors of 32 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 o 3rd: Which factor in common is the largest? o 8 This means they can make 8 treat bags Distributive Property – states that multiplying a number by a group of numbers added together or subtracted is the same as doing each multiplication separately o Example: 4(2 + 3) You could add 2+3 first then multiply it by 4 2+3=5 5 ● 4 = 20 You could use the distributive property Multiply each term in the parenthesis by the number outside the parenthesis then add (or subtract) 4●2 + 4●3 8 + 12 = 20 You can use distributive property to break apart an addition or subtraction problem by determining the GCF of the numbers being multiplied Example: 36 + 48 o o o What is the GCF of 36 and 48 Factors of 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36 Factors of 48 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 48 The GCF is 12 Divide out 12 from the terms 36 ÷ 12 = 3 48 ÷ 12 = 4 Rewrite using the distributive property 12(3 + 4)