ALE #7
advertisement

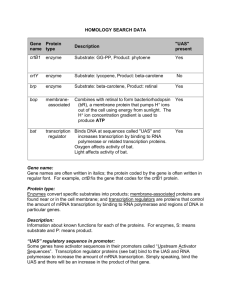
ALE #7 Ch.11 & 12: Gene Regulation & DNA technology Name__________________________________________ 1. Please define the following important players in eukaryotic gene regulation: a. transcription factors – regulatory proteins that help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter. Thus they promote transcription. b. Activators - regulatory proteins that bind to enhancer sequences, interacting with transcription factors to promote transcription. c. Silencers - regulatory proteins that inhibit transcription. d. Promoters – a section of DNA that indicates the start of a gene. When RNA polymerase binds to a promoter, transcription occurs e. Enhancers – these are sections of DNA that play a role in the regulation of gene expression. When activator proteins bind to enhancers, they assist other transcription factors to bind to RNA polymerase. This helps to promote transcription 2. Please describe how each of the following processes exerts control over eukaryotic gene expression: a. DNA packing –during prophase of mitosis and meiosis, chromatin becomes tightly packed by wrapping itself around histone protein and coiling into tight helical fibers and supercoils. In this highly packaged state, transcription is nearly impossible. RNA polymerase will be blocked from binding to promoters b. X chromosome inactivation – early in embryonic development of female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes in each cell becomes highly compacted and (permanently?) inactive, preventing transcription of genes on the inactive X chromosome. c. alternative RNA splicing – removal of some exon (coding) material along with the non-coding introns can result in the production of different kinds of proteins from one gene. d. RNA interference – small, complementary RNA strands bind to mRNA transcripts, thus blocking the translation of a gene. 3. Read the short article attached from AICR (American Institute for Cancer Research) Science Now titled Epigenetics: A New Frontier in Cancer Research from the Spring 2007 Issue then answer a-c below 1 a. What are the two most widely known epigenetic processes? 1.DNA methylation – adding methyl groups to DNA to turn genes on or off without mutating the gene itself. 2. Histone modification – loosens the DNA coils to enhance transcription of genes. b. How does lunasin kill cancer cells? It modifies histones in cancers cells, and this prevents DNA coil unwinding. This has the effect of killing the cancerous cell. c. How did the four nutrients given to pregnant agouti mice change their babies chance of obesity, cancer and diabetes? The nutrients cause methyl groups to attach to the agouti gene, thereby silencing it (turning off transcription). This had the effect of changing fur coat color and decreasing appetite. 4. What is the difference between reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning? Reproductive cloning involves implanting a cloned embryo into a surrogate mother for the purpose of creating an entire new organism. The purpose of this would be to create domestic animals with desired traits or to reintroduce extinct or endangered organisms. Therapeutic cloning involves the creation on an embryo clone in culture in order to induce the stem cells to create new tissues or organs, etc for the individual from which DNA was derived. This could be used to cure many diseases and to fix damaged body parts, without having to grow an entire new organism just for harvest. 5. In the table below, list the pros and cons of cloning. Be prepared to share these in class. Pros Cons Agriculture: produce livestock or Clones are not really clones! crops with desirable traits, Epigenetics tells us that even potentially decreasing the need for though the genes of two organisms antibiotics, herbicides, pesticides, might be the same, that does not increasing crop yield, etc. mean their gene expression will be the same. Medicine: create animals that would secrete certain desired In fact, we see that many cloned proteins in their milk animals have reduced viability. Increasing the population of a rare Cloning reduces genetic variability, or endangered plant or animal which many reduce the population’s ability to adapt to its Therapeutic cloning has the environment potential to cure almost any disease, and to eliminate the need for organ Disadvantages of therapeutic donation. Patients could be given cloning? For humans, some people stem cell transplants without any will always object to the use of chance of rejection. human embryos for scientific research (controversial). However, 2 if scientists are trying to induce other kinds of stem cells (cord blood, bone marrow) to grow into various tissues. 6. List the pros and cons of genetically modified (transgenic) organisms in the table below. Be prepared to share these in class. Pros Cons Plants: create plants that are Plants: transgenes can be resistant to bugs or disease, thus transferred into the environment reducing the need for herbicides and hybridize with native plants. and pesticides This could create invasive weeds, which are extremely harmful to our Improved nutritional quality of environment and economy crops can save millions of malnourished people worldwide. Once the transgenes have “escaped”, there is not way to get Improved water use efficiency and them back. nitrogen use efficiency can reduce our environmental (and carbon!) Could introduce new allergens into footprint on the earth. nature or our food supply. Animals: Easy creation and harvest of pharmaceuticals – especially beneficial would be the production of human proteins needed for medicine (insulin). Creation of domestic animals/livestock with superior traits, reducing the need for antibiotics, etc. 3