science Ch4-cell processesStudyGuide
advertisement

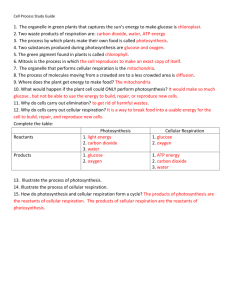
Name______________________________________Date_____________Class_______ Chapter Four Study Guide Key Cell Processes 1. In order to survive… Cells need to obtain raw materials and energy and get rid of wastes. Cells need water because they are made mostly of water. Cells need to be able to replace worn out or dead/lost cells. 2. How cells obtain raw materials and get rid of wastes What organelle that surrounds the cell allows materials to move in and out of the cell? Cell membrane When a membrane allows certain materials to move in and out, it is called semi-permeable or selectively permeable. Cells move materials in and out in two ways (define the terms): 1. Passive Transport: The movement of particles across the cell membrane without the use of energy EX: Osmosis and Diffusion 2. Active Transport: The movement of particles across the cell membrane with the use of energy EX: Endocytosis and Exocytosis No energy is required in passive transport. Two types of passive transport are listed below. Define these terms: 1. Diffusion: The movement of particles from areas of high concentration (crowded) to areas of low concentration (less crowded). 2. Osmosis: The movement of water from areas of high concentration (crowded) to areas of low concentration (less crowded). Example – When it rains, wilted plants will become rejuvenated because of the movement of the water from a higher concentration in soil to the lower concentration in the wilted plant, which is called osmosis. Energy is required in active transport. Two types of active transport are listed below. Define these terms: 1. Endocytosis: The active-transport process by which a cell surrounds a large particle, such as a large protein, and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell. 2. Exocytosis: The active-transport process by which large particles, such as wastes or proteins, travel to the cell membrane in a vesicle, the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and the large particles exit the cell through the cell membrane. 3. How cells get energy Plant cells get energy from the sun and animal cells get energy from glucose (food). Photosynthesis – Making FOOD 1. Where do plant cells get energy to make food? From the sun 2. What organelle in the plant cell traps the sun’s energy and turns it to food (glucose)? Chloroplast 3. What pigment is stored in the chloroplast that allows photosynthesis to take place? Chlorophyll 4. What gas does a plant need from the atmosphere to make food (glucose)? And what is one source of this gas? Carbon Dioxide; Humans 5. The building block of cells that is made during photosynthesis is carbohydrates. One of the chemical forms of this building block is called glucose. 6. What is the end result of photosynthesis (write the whole formula in words)? carbon dioxide + water + sunlight glucose + oxygen 7. What happens (2 things) to the food made by plants? 1. It is used by the plant for energy 2. It is used by animals that eat plants for energy Cellular Respiration/Fermentation - making ENERGY Once an organism eats a source of food (plant or other organism) it has to break this food down to make energy. The processes that make energy are cellular respiration and fermentation. 1. In which organelle does cellular respiration and fermentation take place? Mitochondria 2. What gas is needed in order for cellular respiration to take place? Oxygen 3. What waste product (or gas) is released during cellular respiration? Carbon Dioxide 4. Where does this gas go when it is released? Into the atmosphere 5. What is the importance of releasing this gas back into the atmosphere? It is then used to start the process of photosynthesis in plant cells 6. What is the scientific name for food? Glucose 7. Sometimes energy is produced without oxygen. This process is called fermentation. * When this process occurs in muscle cells, the waste product given off is lactic acid, which causes the muscles to cramp. **The processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis work together. The end products of photosynthesis (oxygen and glucose) are the ingredients needed for cellular respiration to begin (oxygen and glucose/food). 4. Cell Division Cells replace worn out or dead cells through a process of cell division. 1. What chemical that makes up chromosomes controls the activities of the cell? DNA 2. When a cell reproduces or divides, what has to be copied before the cell can split? DNA 3. In a cell cycle, the cell spends four phases, or steps, reproducing. This process of cell reproduction is called mitosis. 4. During the last phase of the cell cycle, the cell actually becomes two cells. The cytoplasm splits in this step. This phase is called cytokinesis. 5. Which type of cell has a simpler cell division: eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Prokaryotic 6. The simpler type of cell division found in prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) is called binary fission. This means splitting into two parts. 7. Eukaryotic cells have more chromosomes that are arranged in pairs that have similar structure and sequence. These pairs are called homologous chromosomes. Other items to study in order to prepare for the test: 1)Cell Processes Poster, 2)Naked Egg Lab, 3)Diffusion & Osmosis WS, 4)Skits WS, 5)Recipes for making energy & food WS