Become the Crust of Earth11
advertisement

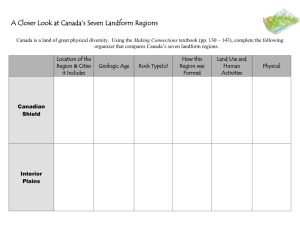
Become the Crust of Earth (student designed model) An assignment inspired by “The Zen Master” Objective: MLR - D2: Earth: Describe and analyze the effects of geophysical influences on the origin and changing nature of Earth Systems. Instructions: 1. Meditate for five minutes and imagine you are the Earth’s crust experiencing the always-changing physical and climatic forces that shape, sculpt, and deform the rock record leaving behind a history written in stone. 2. Create your own history that you record in one cross section (geologic column) of a rock record. Since you are now a portion of the Earth’s crust, you have a history and a story to tell to those who are willing to learn from you. As you imagine the events and forces that you experience over geologic time, design/construct rock layer by rock layer, and forceful event by forceful event, your own history. Your project can be a drawing or a model where you must: Include a key that describes each rock type and boundary. You must have at least 7 layers (including dikes / faults / unconformities) Use colored pencils (if drawn) or other materials approved by your teacher. You must include the following principles of Relative Dating: • Principle of Original Horizontality • Principle of Superposition (number the layers oldest to youngest) • Principle of Faunal Succession • Principle of Crosscutting Relations 3. Write an essay that puts your diagram into words. Write this essay in the first person as though you actually experienced the history you have created in your geologic column. Describe how each of the principles above became included in your geologic history as you discuss how each strata formed. For Example: “I am a geologic column with a fascinating history filled with drama and amazing energetic events. My story spans millions of years, and I’d like to tell you about it. I began as a layer of limestone rock under a shallow ocean. Sediments mixed with the broken skeletons of marine organisms (like crabs, clams, and snails) settled down in horizontal layers and became cemented and compacted into solid rock over thousands of years (a). Then, fish and shrimp died and became covered by sediments, while their soft body parts slowly decayed and became replaced by minerals from the water. They eventually turned into fossilized remains (b). I could see the minute evolutionary changes in these animals through the layers. This is an example of the process of faunal succession (b) within my crust...” Student:_________________________________________Period:____________ Become the Earth’s Crust Rubric Total Score:_________ Revised March 2014 Geologic Column – Model: _____ (7 pts.) At least 7 layers are shown in your geologic column. _____ (3 pts.) Key thoroughly describes each rock type & boundary _____ (3 pts.) Proper sequencing of layers from oldest to youngest is shown in the key (Principal of Superposition) _____ (7 pts.) Each layer & intrusion is neatly drawn/modeled and colored _____ (3 pts.) Principle of Original Horizontality is labeled correctly on model _____ (3 pts.) Principle of Superposition is labeled on the model, and layers are correctly numbered in order from oldest to youngest.) _____ (3 pts.) Principle of Faunal Succession is labeled correctly on model _____ (6 pts.) Principle of Crosscutting Relations is labeled correctly, and type of rock creating the intrusion is indicated on model _____ (35 pts. possible) Total Points Earned for this section Student:_________________________________________Period:____________ Essay: (This is your chance to make connections between the rock cycle, plate tectonics, and relative dating!) _____ (5 pts.) Essay is written in the first person. _____ (15 pts.) An introduction is written that thoroughly explains the main idea. _____ (15 pts.) A conclusion is written that supports the essay topic. _____ (15 pts.) Research Strata: ____ the formation of each layer of rock. ____ Under what conditions did the rock form? (deep ocean desert, fast river, calm water, convergent collision, convergent subduction, etc.) ____ What geologic processes (rock cycle) formed the rock? ____ Thorough description of how Principle of Original Horizontality came to be part of your geologic column. ____ Include any discussion of folding & unconformities here (Mountain building? Convergent subduction? River erosion? etc.) _____ (15 pts.) Research Fossils: ____ Thorough description of how Principle of Faunal Succession came to be part of your geologic column ____ Describe the geologic processes that created the fossils – What type of fossilization occurred to create the fossils? Trace? Mineralization? Etc. Discuss the fossilization process. _____ (15 pts.) Research Crosscutting: ____ Thorough description of how Principle of Crosscutting Relations came to be part of your geologic column. ____ What geologic processes occurred to turn the (igneous intrusion) magma into solid rock? ____ What kind of igneous rock was created? ____ Does the rock have crystals or no crystals? ____ Was the cooling slow or fast? ____ Is there contact metamorphism? (What is it and how does it affect the rock that it touches?) ____ If faulting occurred, what part of the geologic column is pushed up or dropped down? What strata are revealed or disappear from the fault movement? _____ (80 pts. possible) Total Points Earned for this section