Learning Targets For Ninth Grade Career Planning Five Week Unit
advertisement

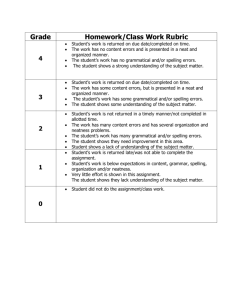
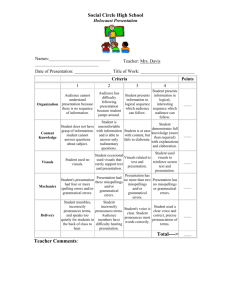
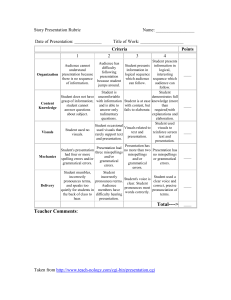
FDN-5560 Classroom Assessment Develop an Assessment Exercise Chris Sardler Feb 10, 2005 Learning Targets for Ninth Grade Career Planning Five Week Unit Learning Target: Students will be able to select a future career that matches their interest and aptitudes then be able to explain to an audience their selection of a future career(s). After participating in the career planning process, students taking the course Career Management, will be able to list the steps in the process, describe the process components by using a chart, table or thinking map demonstrate their knowledge of the process through a class presentation of their search and their findings and explain the process by writing a letter to their parents describing the steps of the process and their conclusion about a possible career. The levels of learning were determined by using Blooms and Marizano. Steps of the career planning process include: (1) Self Evaluation (2) Research the possibilities (3) Select an appropriate career (4) Be able to justify your selection Week One Knowledge Base (Low Level Learning Target): Students will participate in the career planning proces As an introduction to the course, students will participate in the career planning process by engaging in activities that establish base knowledge. These activities will explore various careers through the use of individual, small group research, and classroom discussion, accompanied by videos and guest speakers. Assessment of this target would be accomplished by having the students develop their own list of question for the research, video or speaker. After participating in the exploration they will know where to find the answer. Students will receive one point for each question designed a minimum of 5 is required. Students can earn a maximum of 10 points. Student Career Survey Directions: To learn more about a career(s) please design a minimum of 5 questions you need to know before selecting a future career. As you find the answers to your questions Sardler 2 record them on this sheet. You will receive 1 point of each answered question up to a maximum of 10 pts. Example: Student question: What is the average salary range for an Architect? Correct Answer can be found in the Occupational Outlook Handbook or Speaker Student question: How many years of education beyond high school does an Architect need to begin a career? Correct Answer can be found at CFNC.org or Video Base knowledge is the first level of learning targets. This activity is necessary to establish the knowledge needed about possible future careers. Recall would be another descriptor of this target. Week Two Analysis or Application (Middle Level Learning Target): Students will use the steps of the process Using a handout, overhead or power point, students will be given the steps of the process and refer to the steps as they complete the process. Their career choice(s) at this time will be used later to compare to their final choice(s). Students will answer the question, “What would happen if the process started with step 4?” by using a table, chart or think map to evaluate the outcome. They will present their findings in an oral presentation. Comparing the process to an alternative is the analysis level of learning. This is a foundation for the explanation of their choice of a career. This target will be assessed through a writing rubric. Using the Steps of the Process Directions: For this part of the unit of study you will need to design a chart, graph or thinking map to evaluate the outcome if the steps were conducted in the opposite order. You will then present you conclusion to your assigned small group. Upon conclusion place the finished product in your portfolio. You make receive 9-0 points for this activity. Oral Presentation Rubric Name: Content Eye Contact Date: 3 points 2 points 1 points Student demonstrates full knowledge (more than required) of content with explanations and elaboration Student holds the attention of the audience with the use of direct eye contact Student demonstrated knowledge of content but fails to elaborate Student is uncomfortable with the information and can answer only rudimentary questions Student displays consistent use of eye contact with the audience Student displays minimal eye contact with the audience Point Value Sardler 3 Creativity Student work demonstrates a unique level of originality Student work demonstrates originality Student work lacked originality TOTAL Teacher Comments: Student Comments: Analysis would be an appropriate descriptor for this learning target. Students are ask to describe and organize the steps. They will make decisions about the way to arrange the information. Week Two and Three Learning Target: Students will make comparisons between their interest, aptitude and values inventories results and possible careers. Students will use John Holland’s Self-Directed Search and Piney Mountain on-line values and aptitude inventories. They will file the results in their career portfolio. Students will use the inference level in this activity which is middle to high learning level. They will infer from the inventories future careers that match their inventories. The students will be assessed by writing an essay about their career(s) selection. A rubric will be used to evaluate the writing. Comparison of Future Career Possibilities Directions: For this part of the unit you will write an essay about your findings and then place it in your career portfolio. You may receive 16-0 points for this activity. Writing Rubric Name: Date: 4 points All Paragraph Construction paragraphs Quality of Information include introductory sentence, explanations or details, and concluding sentence. Information clearly related to the main topic. It includes several supporting details 3 points 2 points 1 points Most paragraphs include introductory sentence, explanations or details and concluding sentence. Information clearly relates to the main topic. It provides 1-2 supporting details Paragraphs included related information but were typically not constructed well. Paragraphing structure was not clear and sentences were not typically related within the paragraphs. Information clearly relates to the main topic. Not details and/or examples are given. Information has little or nothing to do with the main topic. Point Value Sardler 4 Mechanics Sources and/or examples. No grammatical, spelling or punctuation errors. All sources are accurately documented in the desired format. and/or examples. Almost no grammatical, spelling or punctuation errors. All sources are accurately documented, but a few are not in the desired format. A few grammatical, spelling or punctuation errors. All sources are documented, but many are not in the desired format. Many grammatical, spelling or punctuation errors. Sources are not accurately documented TOTAL Comments By Student: Comments By Teacher: Week Three and Four Learning Target: Students will demonstrate their knowledge of the process and their findings through individual presentations. Students will share with the class or in small groups the results of their findings through an electronic presentation or other visual presentation means. Students will be evaluated using a rubric. The rubric will be designed with sections for self-evaluation, peer evaluation and teacher evaluation. Presentation of Findings Directions: Using a presentation media of your choice prepare a presentation for your classmates about your findings. Once presented, place the presentation in your portfolio. You may receive 20-0 points for this activity. Visual Presentation Rubric Name: Organization Date: 4 points 3 points 2 points 1 points Student presents information in logical, interesting sequence which the audience can follow. Student presents information in logical sequence which audience can follow. Audience has difficulty following the presentation because student jumps Audience cannot understand presentation because there is no sequence of information Points for Self Points by Peers Points by Teacher Sardler 5 Content Knowledge Student demonstrates full knowledge (more than required) with explanations and elaboration Student is at ease with content, but fails to elaborate Visuals Student used visuals and animation to reinforce text and presentation Visuals related to text and presentation Mechanics Presentation has no misspelling or grammatical errors Presentation has no more than two misspellings and/or grammatical errors Delivery Student used a clear voice and correct, precise pronunciation of terms Student’s voice is clear. Students pronounces most words correctly around. Student is comfortable with the information and is able to answer only rudimentary questions. Student occasionally used visuals that rarely support text and presentation Presenation had three misspellings and/or gramaatical errors. Student incorrectly pronounces terms. Audience members have difficulty hearing presentation Student does not have a grasp of information; student cannot answer questions about the subject. Student used no visuals. Presentation hd four or more spelling errors and/or grammatical errors Student mumbles, incorrectly pronounces terms and speaks too quietly for student s in the back of the class to hear. Comments: Learning target is at the evaluation/synthesis level which is a high learning level. Students should select the means of presentation and evaluate their work and the work of others. Comparison would also be addressed as students compare their work with others in the class. Students will make judgments about their work and the work of others. Week Five Learning Target: Students will demonstrate their knowledge of the process and explain the outcomes. Sardler 6 Students will write a letter to their parents explaining the process they used to come to their conclusion of a future career. They will also be encouraged to have their parents respond to the letter with a written reply. Students would be able to reflect on the replies and discuss their reactions. This activity includes the learning outcomes of application and analysis a middle to high level of learning. Students should apply the knowledge gained to justify to their parents their possible career(s). This activity would be assessed by using the writing rubric. Final Assessment At the end of the unit a VOCATS multiple choice item test will be given. The items will be evaluated to best practices in multiple choice item writing by the Kehoe method. Each correct item will have a point value of one. The test is a total of 25 items for a maximum of 25 points. Sample Item from the VOCATS test for this unit: Which of the following jobs is NOT dependent upon a person working with people and influencing them? A. Teacher B. Lawyer C. Farmer D. Salesperson Better item using Kehoe approach: Which job is dependent upon a person working with people and influencing them? A. Cattle Farmer B. Truck Driver C. Sales Clerk Alternate question: T or F A sales clerk must work with people and influence their decisions? Testing Blueprint and Scoring Plan Each assessment carries point values. The points for each assessment will the tallied at the end of the unit and a grade assigned to the total points acquired for the Learning Target. Assessment 1: Assessment 2: Assessment 3: Assessment 4: Assessment 5: Questions Developed carries 5-0 points Oral Presentation carries 9-0 points Essay carries 16-0 points Visual Presentation carries 20-0 points Letter carries 16-0 points Sardler 7 Assessment 6: Multiple Choice Test carries 25-0 points TOTAL Points = 91-0 91-61 points=Mastery Below 61 indicates lack of mastery and reteaching and re-assessing would need to occur. Grades could be assigned as follows: 91-81=A, 80-71=B, 70-61=C, 60-51=D, 50-0=F Or points could be earned throughout the class to earn course mastery. This would be a novel way to evaluate and possibly difficult for students, parents and administration to understand. The 100 point scale is heavily ingrained. References Kehoe, Jerard (1995). Writing multiple-choice test items. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation, 4(9). Retrieved November 7, 2003 form http://PAREonline.net /pare/getivn.asp? v=4&n=9. NCDPI Division of Career and Technical Education, VOCATS Item Bank, Career Management, 1999. Olson, George H. (2005). FDN 5560-376 Syllabus, www.lesn.appstate.edu/olson. Popham, W. James (2005). Classroom Assessment: What teachers need to Know, 4th Edition Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.