38- Antiviral and antifungal drugs
advertisement

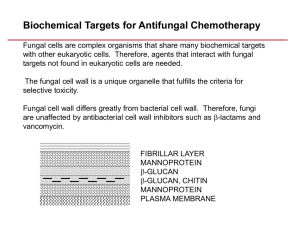
Antiviral and antifungal drugs Anti-HIV agents Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors(NRTIs, 核苷类逆转录酶抑制剂) Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs, 核苷类逆转录酶抑制剂) Protease inhibitor(PI, 蛋白酶抑制剂) 1. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) Zidovudine (齐多夫定,AZT, ZDV)/Lamivudine(拉米夫定,3TC)/Stavudine(司他夫定, d4T), Zalcitabine (扎西他宾, ddC)/Didanosine (去羟肌苷, ddI)/Abacavir (阿巴卡韦, ABC) (1) Zidovudine (齐多夫定,AZT, ZDV) The first reverse transcriptase inhibitor for treatment of AIDS Treatment of AIDS and HIV-associated dementia and thrombocytopenia Mechanism: Toxicity: myelosuppression (2) Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors Delavirdine(地拉韦定)/Nevirapine(奈韦拉平)/Efavirenz (依法韦恩茨) Mechanism: different with NRTIs Used in combination with NRTIs and PI / Toxicity: rash (3) Protease inhibitor Drugs :saquinavir(沙奎那韦), ritonavir(利托那韦),indinavir(英地那韦), nelfinavir(奈非 地韦) Mechanism: inhibit precursor molecules convert to mature virions during HIV replication Clinical uses: in combination with other agents to treat AIDS Toxicity: abnormality in metabolism include altered body fat distribution, insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia Other Antiviral agents Acyclovir (ACV) Active against HSV-1 , HSV-2 Convert to ACV triphosphate and inhibit viral DNA polymerase Treatment of a variety of herpes infections include primary and recurrent genital herpes (one of the most effective) 2. Valacyclovir (伐昔洛韦) Higher blood concentration 3.Ganciclovir CMV 4.Vidarabine (Ara-A) Convert to Ara-A triphosphate and inhibit DNA polymerase Active against HSV, VZV, CMV, HBV etc/ Toxicity : neurotoxicity Idoxuridine(IDU) Inhibit DNA synthesis by blocking thymidylic acid synthetase Topical use for treatment of HSV infections of the eyelid, cornea and skin High toxicity 6. Ribavirin (virazole) Inhibit replication of both DNA and RNA viruses Treatment of influenza A and B infections Teratogenesis Lamivudine (3TC) NRTIs: HIV-1/ One of the most effective drugs on HBV infection Amantadine and rimantadine Inhibit penetration of virus to cells and the uncoating of certain virus Prevent diseases caused by influenza A 7. Foscarnet 8. Interferon 9. Polyinosinic polycytidylic acid ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS 1. Fungal infection Topical infection/ Systemic infection 2. Antifungal drugs Antifungal antibiotics/ Azole: imidazole and triazole/ Others: terbinafine and flucytosine 3. Antifungal antibiotics (1)Griseofulvin ①Antifungal activity Inhibit the growth of dermatophytes include epidermophyton, microsporum and trichophyton No effect on bacteria and systemic infections of fungi ②Mechanism of action: interfere with fungal nucleic acid synthesis ③Clinical use only used in the systemic treatment of dermatophytosis include skin, hair and nails ④Adverse effects Nausea, vomiting ,headache/ Allergic reaction: fever, skin rash and leukopenia (2)Nystatin Has the same mechanism with amphotericin B Only used topically for suppression of local candidal infection (3)Amphotericin B ①Antifungal activity: Has the broadest spectrum of antifungal action, Active against candida albicans, cryptococcus neoformans, histoplasma capsulatum , bastomyces ②Mechanism of action Bind to ergosterol on fungal cell membrane and alter the permeability of the cell by forming amphotericin B-associated pores in the cell membrane, allow the leakage of intracellular ions and macromolecules leading to cell death ③Clinical uses Drug of choice for nearly all life-threatening mycotic infections include severe fungal pneumonia, crypotoccal meningitis or sepsis syndrome ④Adverse reactions Infusion-related toxicity: fever, chills, muscle spasm, headache, hypotension Renal damage: azotemia, K+ ,Mg2+ wasting Others: Liver damage, arrhythmia, anemia 4. Azole (1)Drugs : Imidazole: Clotrimazole, miconazole, ketoconazole Triazole : Fluconazole, itraconazole (2)Mechanism of action Reduction of ergosterol synthesis by inhibition of fungal cytochrome P450-dependent 14-α -demethylase (3)Clinical uses Broad spectrum: candida species, cryptococcus neoformans, dermatophytes (4)Topical azoles: clotrimazole and miconazole Poorly absorbed / Broad spectrum/ Too toxic for systemic uses/ Topical use in treatment of dermatophytosis (5)Ketoconazole The first broad-spectrum oral azole introduced into clinical use Treatment of mucocutaneous candidiasis and dermatophytosis Major toxicity: Endocrine disturbance: infertility, gynecomastia and menstrual irregularity Hepatoxicity: hepatitis (6)Fluconazole Can be administered orally and intravenously, high bioavalibility Least effect on hepatic microsomal enzyme Drug of choice in the treatment of cyrptococcal meningitis and other systemic fungal infections (7)Itraconazole Can not penetrate BBB Choice in the treatment of dermatophytosis and onychomycosis 5. Other antifungal agents (1)Terbinafine Inhibit fungal enzyme- squalene epoxidase and interfere with ergosterol biosynthesis Treatment of dermatophytosis especially onychomycosis (2)Flucytosine Convert to 5-FU, inhibit DNA synthesis Synergism with Amphotericin B, Effective against cryptococcus and candida species