FLEX (Foreign Language Exploratory) Courses
advertisement

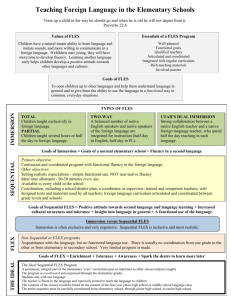
FLES or FLES – What will students learn? FLEX (Foreign Language Exploratory) Courses Curriculum Recommendations for FLEX summarized from A Celebration of FLES: Sequential FLES, FLEX and Immersion, Gladys Lipton, editor. National Textbook Company, 1998 What is FLEX? FLEX (Exploratory) programs are an introduction to one or more foreign languages, with few language skills expected. There may be limited development of fluency with a once- or twice— a-week program over several years that emphasizes limited language acquisition and cultural awareness. Choice of Language: Children receive paramount benefit not so much from the particular language chosen for instruction, but from the experience and process of learning a language. This experience develops the intellectual flexibility necessary for subsequent language acquisition. (p. 155, Armstrong) FLEX programs goals: Introduce students to languages and cultures Develop limited awareness of language relationships In FLEX programs, students will: Learn to say several basic expressions in the target language, such as - Greetings - Counting - Colors and other descriptors - Foods - Geographic names (the sophistication of these items being affected by student age Recognize the language when it is seen and heard Participate in limited imitative writing in context, depending on the nature of the target language (alphabetic or non-alphabetic). Experience music and songs from the target culture Identify the areas of the world where the language is spoken Acquire basic knowledge about the culture Hear or read a representative folktale or legend of the culture (can be in English) Acquire the above skills and knowledge as a reinforcement of social studies skills and as an expansion of linguistic development. FLES(Foreign Language in Elementary School) Sequential Courses FLEX programs are usually followed by a Sequential FLES program in subsequent grades or in middle school. FLEX teachers work in close collaboration with grade level teachers to augment the interdisciplinary learning of subjects such as social studies, arts, science, math, & reading. Sample FLEX lessons (two – four instructional periods over four to six weeks): Greetings and names (practiced orally in meaningful exchanges0 New vocabulary, phrases, and geographic names introduced through thematic topics, Family, numbers, food, clothing, etc. Folktales and songs that students listen to and participate in Other interesting cultural material that is particularly student-oriented. Sample Thematic progression: Greetings and presentations (names, countries, numbers, ages, you and me) How are you? Action verbs, body parts Where are you going? Taking a trip, places, geography, flags, colors What time is it? Schedules - school, typical day, transportation (i.e. buses, trains) I’m hungry! – At the restaurant, eating habits, foods, etiquette, foods. Prepare a special lunch, with entertainment, authentic music and art Outings – places to go, i.e. market Examples of ongoing performance assessments: The following activities can be used to assess student progress (oral or written language): Make a list of terms in a category (e.g. colors, people) Ask and respond to questions about a theme or situation Express preferences Describe familiar object or person Retell a story or an experience Describe a meal, meal plan or menu Record a message Write a letter, or a short message, a poem, or a greeting card Tell how to do something Make an announcement Write an email message Create questions for a quiz Prepare questions for a guest speaker Tell a folktale Plan a travel itinerary Make a collage on a theme Draw and label a cartoon Create a “Concentrations” game Make a calendar (weather, activities, sports, etc) Role-play shopping in a specific kind of store Sing authentic songs Create the family tree of a famous person (real or fictitious) Create a poster about (themes, culture, stories, etc.) Create directions for a class treasure hunt. Make a shopping list for a specific purpose Create a language game Role-play a cultural/historical skit Draw and label vocabulary Follow directions Match words/Phrases and pictures Complete sentences. Present a conversations Write dictation Instructional methods: All students actively participate - individual, small group, whole-class activities Students are given the opportunity to use the foreign language in functional situations Students use the language in all four abilities of listening, speaking, reading and writing and in higher order thinking activities. Teachers plan a variety of activities in short segments Teacher review and reinforce activities as well as present new work in each lesson Teachers use a wide variety of auditory and visual materials of interest to students Teachers use ongoing evaluation for purposes of diagnosis, grouping Cultural topics woven into each lesson. Teachers uses effective classroom routines so that everyone is on task during the lesson The teacher explains new homework clearly and checks homework The teacher and students use the foreign language consistently in class (using English only to briefly when necessary TPR (Total Physical Response): teacher uses commands to teach vocabulary, such as “Stand”, “Walk”, “Point to”. TPR Storytelling: teacher uses TPR to introduce new vocabulary and structures, then creates a story in the target language by asking personalized and reiterative questions to reinforce language acquisition (Natural Approach). Cooperative groups: various groupings and cooperative tasks that allow students to interact in the language and to reinforce language learning and cultural discussions.