REPRODUCTION – IB TEST REVIEW
advertisement

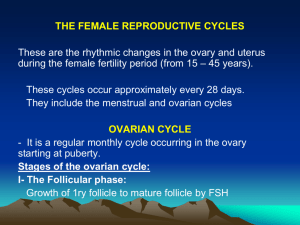
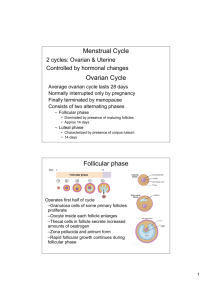
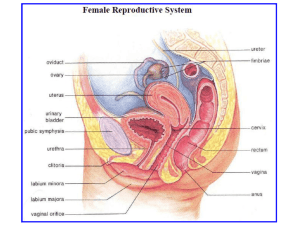
REPRODUCTION TEST REVIEW – A&P II 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. What are the organs of reproduction in a female? Draw and label a picture of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and vagina. What are the organs of reproduction in a male? Draw and label a picture of the main male reproduction organs. Write out the pathway of sperm. Trace the pathway on your diagram from number 4. What does FSH and LH stand for? Where are each of these hormones made? Where is testosterone made? Outline the role of RH, FSH, LH, and Testosterone in a male. What is negative feedback? Explain how negative feedback plays a role in controlling male hormone production. The female menstrual cycle is approximately how long? What are the two different perspectives of the menstrual cycle? (what 2 organs are involved?) What are the two phases of the ovarian cycle? What is the immature ovum, or egg cell, called early in the ovarian cycle? Where is the immature ovum located in the first half of the ovarian cycle? What surrounds this egg cell while it is in the ovary? What is the main hormone involved in the first half of the ovarian cycle? Outline the role of FSH and LH in the control of the follicular phase. Where is estrogen made? What is estrogen’s purpose during the follicular phase? What occurs at the end of the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle? Why does the uterine lining need to become thicker? What causes ovulation? At about what day in the menstrual cycle does ovulation occur? What is the second phase of the ovarian cycle called? Why is it called this? What is the main hormone involved with the second half of the ovarian cycle? What is the corpus luteum? Where is the corpus luteum? Why is the corpus luteum important? (what is its purpose?) What is the main hormone that the corpus luteum secretes? What causes the corpus luteum to be reabsorbed? What does progesterone prevent happening? (other than FSH & LH production!) Explain the path of the egg after ovulation. Describe the main stages of the egg AFTER it is fertilized. Where are sperm produced? What is the difference between ovulation and fertilization? What does implantation mean? What does the word morula mean? Approximately what day after fertilization does implantation occur? What are the chorionic villi? What structure will they become a part of? What hormone does the growing embryo secrete? What is the purpose of this? Approximately what week is the embryo called a fetus? Describe the main stages of embryonic development in the womb. What is placenta previa? What are main functions of the placenta? What is spermatogenesis? Oogenesis? (Look these up if you must!) Where does spermatogenesis occur? Diagram the location of the testes, seminiferous tubules, epididymis, and vas deferens. What is the general purpose of the prostate Cowper’s, and bulbourethral glands and seminal vesicles? What happens in mitosis, generally? What happens in meiosis, generally?