Kinetics Review Ans Key1
advertisement
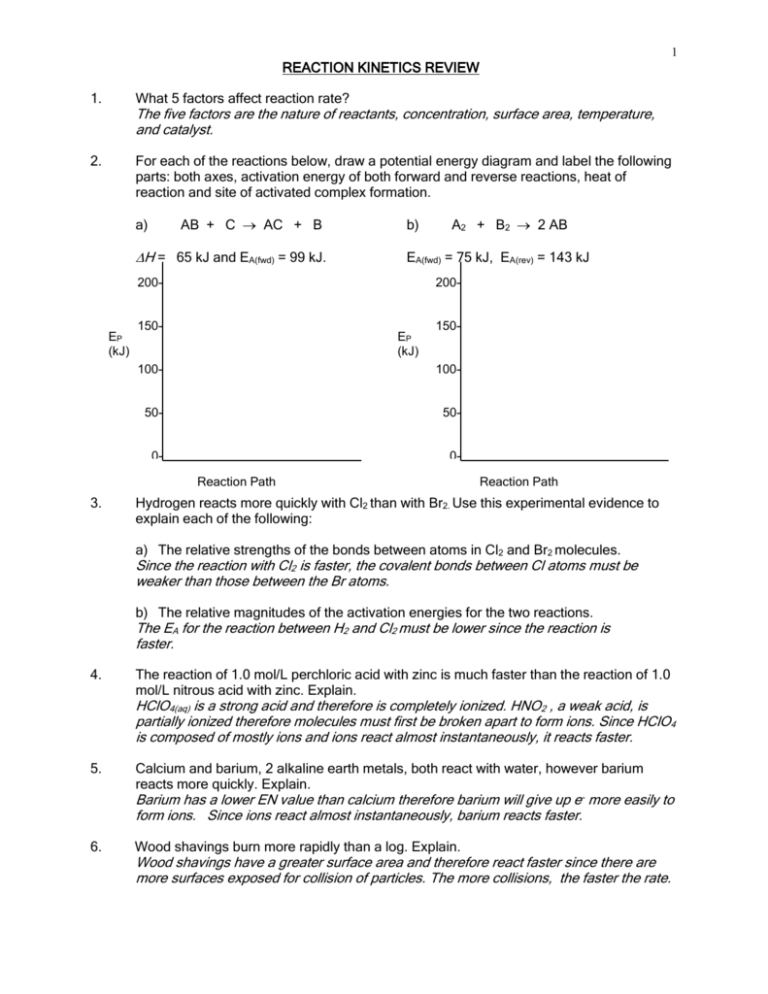
1 REACTION KINETICS REVIEW 1. What 5 factors affect reaction rate? 2. For each of the reactions below, draw a potential energy diagram and label the following parts: both axes, activation energy of both forward and reverse reactions, heat of reaction and site of activated complex formation. The five factors are the nature of reactants, concentration, surface area, temperature, and catalyst. AB + C AC + B a) H = 65 kJ and EA(fwd) = 99 kJ. b) EA(fwd) = 75 kJ, EA(rev) = 143 kJ 200- EP (kJ) A2 + B2 2 AB 200- 150- EP (kJ) 150- 100- 100- 50- 50- 0- 0Reaction Path 3. Reaction Path Hydrogen reacts more quickly with Cl2 than with Br2. Use this experimental evidence to explain each of the following: a) The relative strengths of the bonds between atoms in Cl2 and Br2 molecules. Since the reaction with Cl2 is faster, the covalent bonds between Cl atoms must be weaker than those between the Br atoms. b) The relative magnitudes of the activation energies for the two reactions. The EA for the reaction between H2 and Cl2 must be lower since the reaction is faster. 4. The reaction of 1.0 mol/L perchloric acid with zinc is much faster than the reaction of 1.0 mol/L nitrous acid with zinc. Explain. HClO4(aq) is a strong acid and therefore is completely ionized. HNO2 , a weak acid, is partially ionized therefore molecules must first be broken apart to form ions. Since HClO4 is composed of mostly ions and ions react almost instantaneously, it reacts faster. 5. Calcium and barium, 2 alkaline earth metals, both react with water, however barium reacts more quickly. Explain. Barium has a lower EN value than calcium therefore barium will give up e- more easily to form ions. Since ions react almost instantaneously, barium reacts faster. 6. Wood shavings burn more rapidly than a log. Explain. Wood shavings have a greater surface area and therefore react faster since there are more surfaces exposed for collision of particles. The more collisions, the faster the rate. 2 7. Consider 2 gases, A and B, in a container at room temperature. What effect will the following changes have on the rate of the reaction between these 2 gases? a) The volume is decreased __________________ b) The number of moles of gas is decreased ________________ c) The temperature is increased at constant volume _________________ d) A catalyst is added to the reaction mixture _________________ 8. Zinc metal reacts much more quickly in 5.0 mol/L HCl(aq) than in 1.0 mol/L HCl(aq). Explain. 5.0 mol/L has a greater concentration than 1.0 mol/L. The greater the concentration, the more particles in a given volume there are to collide. The more collisions there are the faster the reaction. 9. Baking powder, containing a mixture of a solid acid (tartaric acid) and a solid base (sodium bicarbonate), does not react when dry, but reacts rapidly when dissolved in water. Explain. When dissolved in water the compounds form ions which react almost instantaneously. 10. Given the reaction: 4 HBr + O2 2H2O + 2Br2 a) Would you expect this reaction to take place in a single step? Why or why not? No, it would require the collision of 5 particles all at once, which is not likely to occur. Each step usually involves 2-particle collisions. b) This reaction is thought to take place by means of the following mechanism: Step 1: HBr + O2 HOOBr Step 2: HBr + HOOBr 2HOBr (slow) (fast) Step 3: 2HBr + 2HOBr 2H2O + 2Br2 c) Identify the intermediates (fast) HOOBr and HOBr d) A catalyst is discovered which increases the rate of Step 3. How will this affect the rate of the overall reaction? Explain your answer. No effect since it’s not in the RDS. e) A catalyst is discovered which increases the rate of Step 1. How will this affect the rate of the overall reaction? Explain your answer. Increase the rate since step 1 is the RDS (slowest step). f) Which step has the greatest activation energy? Explain. Step 1 = RDS = Slowest step. g) How many "bumps" will the PE diagram for the reaction mechanism have? It will have 3, one for each step. h) Sketch a potential energy diagram to show the shape of the curve you might expect for the reaction in this question. The overall reaction is exothermic! Make sure you get the "bumps" the correct relative sizes.








