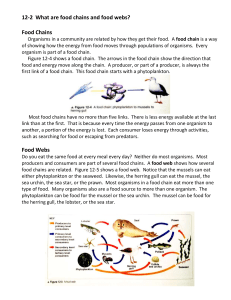
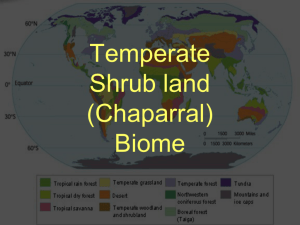
Food Chains and Food Webs
advertisement

Food Chains and Food Webs A Chaparral is a biome characterized by hot dry summers and cool moist winters and dominated by a dense growth of mostly small-leaved evergreen shrubs. In this exercise you will: 1. Show the energy flow through a food chain by constructing model food chains and food webs with the given drawings of organisms found on the Chaparral. 2. Predict what might happen if one organism is removed from the food web. You will need: Organism sheets (See page 2). Each picture also has information on what the organism eats. o Plants of the Chaparral o Insects of the Chaparral o Animals of the Chaparral scissors glue or tape Procedure: 1. Use scissors to cut the pictures apart (See page 2). 2. Sort the pictures into groups according to energy sources; producers, herbivores (primary consumers), 1st level carnivores (secondary consumers), 2nd level carnivore (tertiary consumers), scavengers and decomposers. 3. Construct 4 food chains as they would occur in the chaparral. 4. Paste or tape your pictures on a blank sheet paper. Use arrows to show that energy is passed from one organism to another. (Arrows go from the animal that is eaten to the animal doing the eating). 5. Use the same pictures to form a food web by first arranging them on your desk. Remember that a food web is several food chains linked together. 6. Construct a food web as it would occur in the chaparral. Glue or tape your food web to the back of the same sheet of paper. Again use arrows to show that energy is passed from one living organism to another. Questions: Answer these questions on new sheet of paper. 1. Would there be more predators or prey in a particular community? Explain. 2. Explain what may happen to the other organisms if disease were to kill off one of the 2nd level carnivores in your food web. Which organisms would increase in population? Why? Which organisms would decrease in population? Why? 3. Describe how humans might change (or are currently changing) the food web. Bonus question for extra credit 4. Why can't food chains go on forever? (8th order, 9th order and 10th order consumers?) 1 2